- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Abrocitinib bests dupilumab for treating moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Lancet
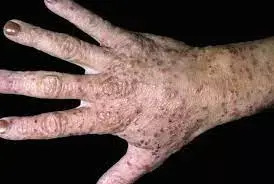
Abrocitinib 200 mg per day is more efficacious than dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis according to a recent study published in the Lancet.
Phase 3 trials have assessed the efficacy of abrocitinib versus placebo in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, a common immunoinflammatory skin disease. This study assessed the efficacy and safety of abrocitinib versus dupilumab.
This randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled, parallel-treatment, phase 3 trial enrolled adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis who required systemic therapy or had an inadequate response to topical medications. Participants were enrolled from 151 sites, located in Australia, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, Finland, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Latvia, Poland, Slovakia, South Korea, Spain, Taiwan, and the USA. These participants were then randomly assigned with block randomisation to receive oral abrocitinib (200 mg per day) or subcutaneous dupilumab (300 mg every 2 weeks) for 26 weeks. Participants were required to apply topical corticosteroids (medium or low potency), topical calcineurin inhibitors, or a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor to active lesion areas. Primary endpoints were responses based on achieving a 4-point or higher improvement in Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (PP-NRS4) at week 2 and a 90% or better improvement in Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-90) at week 4. Family-wise type 1 error was controlled via a sequential multiple-testing procedure ( Randomly assigned participants who received at least one dose of study intervention were included in the efficacy and safety analysis sets.
The results of the study are:
- Between June 11, 2020, and Dec 16, 2020, 940 patients were screened and 727 were enrolled (362 in the abrocitinib group and 365 in the dupilumab group).
- Compared with dupilumab, a larger proportion of patients treated with abrocitinib reached the primary outcomes, PP-NRS4 at week 2, and EASI-90 at week 4.
- Treatment-emergent adverse events were reported by 268 (74%) of 362 patients treated with abrocitinib and by 239 (65%) of 365 patients treated with dupilumab.
- Two non-treatment-related deaths occurred in the abrocitinib group.
Thus, Abrocitinib 200 mg per day was more efficacious than dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis on background topical therapy in inducing early reductions of itch and atopic dermatitis disease signs. Both treatments were well tolerated over 26 weeks.
Reference:
Kristian Reich, Jacob P Thyssen, Andrew Blauvelt, Kilian Eyerich, Weily Soong, Zakiya P Rice, H Chih-ho Hong, Norito Katoh, Fernando Valenzuela, Marco DiBonaventura, Tamara A Bratt, Fan Zhang, Claire Clibborn, Ricardo Rojo, Hernan Valdez, Urs Kerkmann. Efficacy and safety of abrocitinib versus dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomised, double-blind, multicentre phase 3 trial. July 23, 2022DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01199-0
Keywords:
Abrocitinib, efficacious, dupilumab, adults, moderate-to-severe, atopic, dermatitis, Kristian Reich, Jacob P Thyssen, Andrew Blauvelt, Kilian Eyerich, Weily Soong, Zakiya P Rice, H Chih-ho Hong, Norito Katoh, Fernando Valenzuela, Marco DiBonaventura, Tamara A Bratt, Fan Zhang, Claire Clibborn, Ricardo Rojo, Hernan Valdez, Urs Kerkmann, Efficacy and safety
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


