- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Dupilumab rapidly improves treatment outcomes in erythrodermic atopic dermatitis
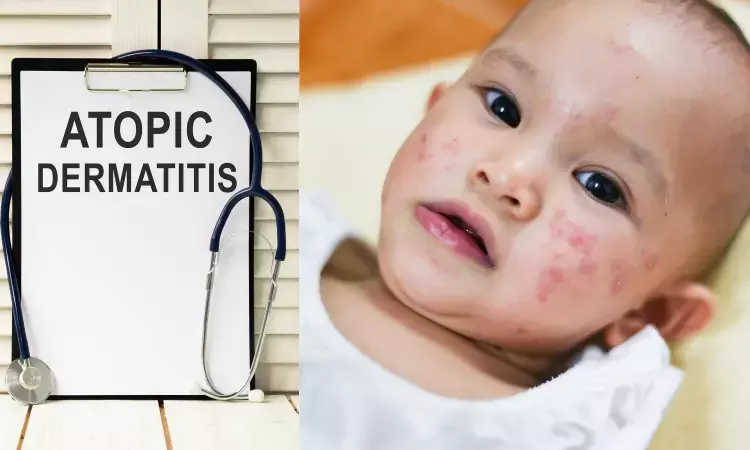
Illinois: An original investigation published in JAMA Dermatology has concluded that Dupilumab improves signs and symptoms of Atopic dermatitis (AD) with ensured safety.
Erythrodermic AD is a severe subtype of AD which is characterized by extensive skin involvement. The condition is complicated and requires hospitalization.
Researchers assessed the safety and efficacy of Dupilumab in such patients. The present study (post hoc analysis) included 209 patients with erythrodermic AD in 6 trials receiving dupilumab treatment vs placebo. These patients had AD affected 90 % of body surface area (BSA).
Dupilumab was given once weekly or every two weeks.
The primary outcomes and measures of the study included efficacy (BSA, EASI, PP-NRS score), serum biomarker changes and safety at week 16.
The results of the study could be summarised as follows:
- Out of 3075 patients, 209 met the criteria for erythrodermic AD.
- The median age in monotherapy and concomitant TCS trials was 31 and 39 years, respectively.
- In erythrodermic AD patients, dupilumab once weekly and every two weeks vs placebo significantly the improved percentage of BSA affected by AD with monotherapy −42.0% and −39.9% vs −17.2% and concomitant TCS −63.2% and −56.1% vs −14.5%.
- The values of EASI score with monotherapy −58.5% and −58.3% vs −22.3% , concomitant TCS −78.9% and −70.6% vs 19.3% , PP-NRS score in monotherapy −45.9% and −33.9% vs −0.6% and concomitant therapy −53.0% and −55.7% vs −26.0%.
- There was significant improvement seen as early as week 1.
- There were significantly reduced Biomarker levels vs placebo.
- Reaction at the injection site, conjunctivitis, and nasopharyngitis was seen in patients treated with dupilumab.
To conclude, dupilumab results in rapid and sustained improvements in AD patients and has a good safety profile.
Further reading:
JAMA Dermatol. Paller AS et al. Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab in Patients With Erythrodermic Atopic Dermatitis: A Post Hoc Analysis of 6 Randomized Clinical Trials. Published online February 01, 2023. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.6192
BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology
Dr. Aditi Yadav is a BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology. She has a clinical experience of 5 years as a laser dental surgeon. She also has a Diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance and is a Certified data scientist. She is currently working as a content developer in e-health services. Dr. Yadav has a keen interest in Medical Journalism and is actively involved in Medical Research writing.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


