- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Early emollient bathing closely associated with Atopic Dermatitis risk
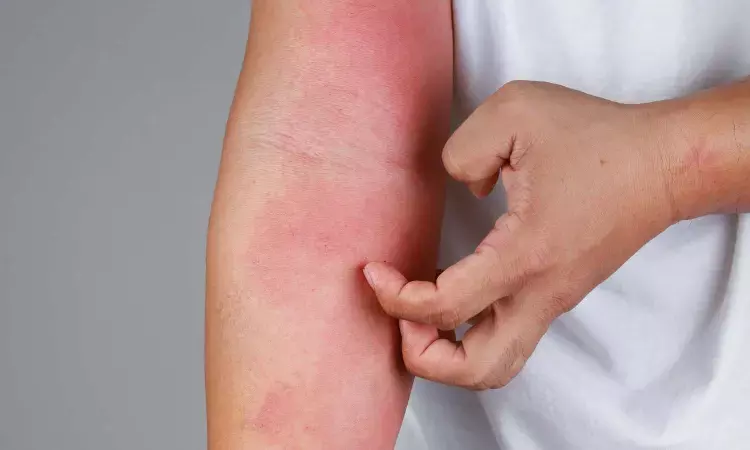
Recent research has focused on the role of the skin barrier in the pathogenesis of Atopic dermatitis (AD), a chronic inflammatory skin condition, and the use of emollients has been considered a potential preventive measure. However, a new study published in Pediatric Allergy and Immunology challenges this notion, revealing a surprising link between early emollient bathing and a higher risk of AD development in the first two years of life.
The "Babies After SCOPE: Evaluating the Longitudinal Impact Using Neurological and Nutritional Endpoints" Birth Cohort study, which enrolled 2183 infants, aimed to assess the relationship between emollient bathing at 2 months and the trajectory of AD during the first two years of life. The study collected data on early skincare practices, skin barrier function, parental history of atopy (genetic predisposition to allergic diseases), and AD outcomes to perform a comprehensive analysis while adjusting for potential confounding variables.
The results of the study were surprising and somewhat concerning for parents and healthcare professionals alike. Among the 1505 children with available AD status data at 6, 12, and 24 months, the prevalence of AD was found to be 18.6% at 6 months, 15.2% at 12 months, and 16.5% at 24 months.
The statistical analysis revealed a strong association between emollient bathing at 2 months and an increased risk of AD development. The odds of AD at any point in the first two years of life were significantly higher among infants who had received emollient baths at 2 months, even after adjusting for confounding variables (odds ratio (OR): 2.41, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.56 to 3.72, p < .001).
Further analysis delved deeper into the impact of different emollient practices. Infants who had both emollient baths and frequent emollient application at 2 months had even higher odds of AD at 6, 12, and 24 months compared to those who had neither (OR at 6 months: 1.74, 95% CI: 1.18–2.58, p = .038; OR at 12 months: 2.59, 95% CI: 1.69–3.94, p < .001; OR at 24 months: 1.87, 95% CI: 1.21–2.90, p = .009).
Reference:
O’Connor, C., Livingstone, V., O’B Hourihane, J., Irvine, A. D., Boylan, G., & Murray, D. (2023). Early emollient bathing is associated with subsequent atopic dermatitis in an unselected birth cohort study. In Pediatric Allergy and Immunology (Vol. 34, Issue 7). Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1111/pai.13998
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


