- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Efinaconazole 10% solution promising treatment of onychomycosis with longitudinal spikes: Study
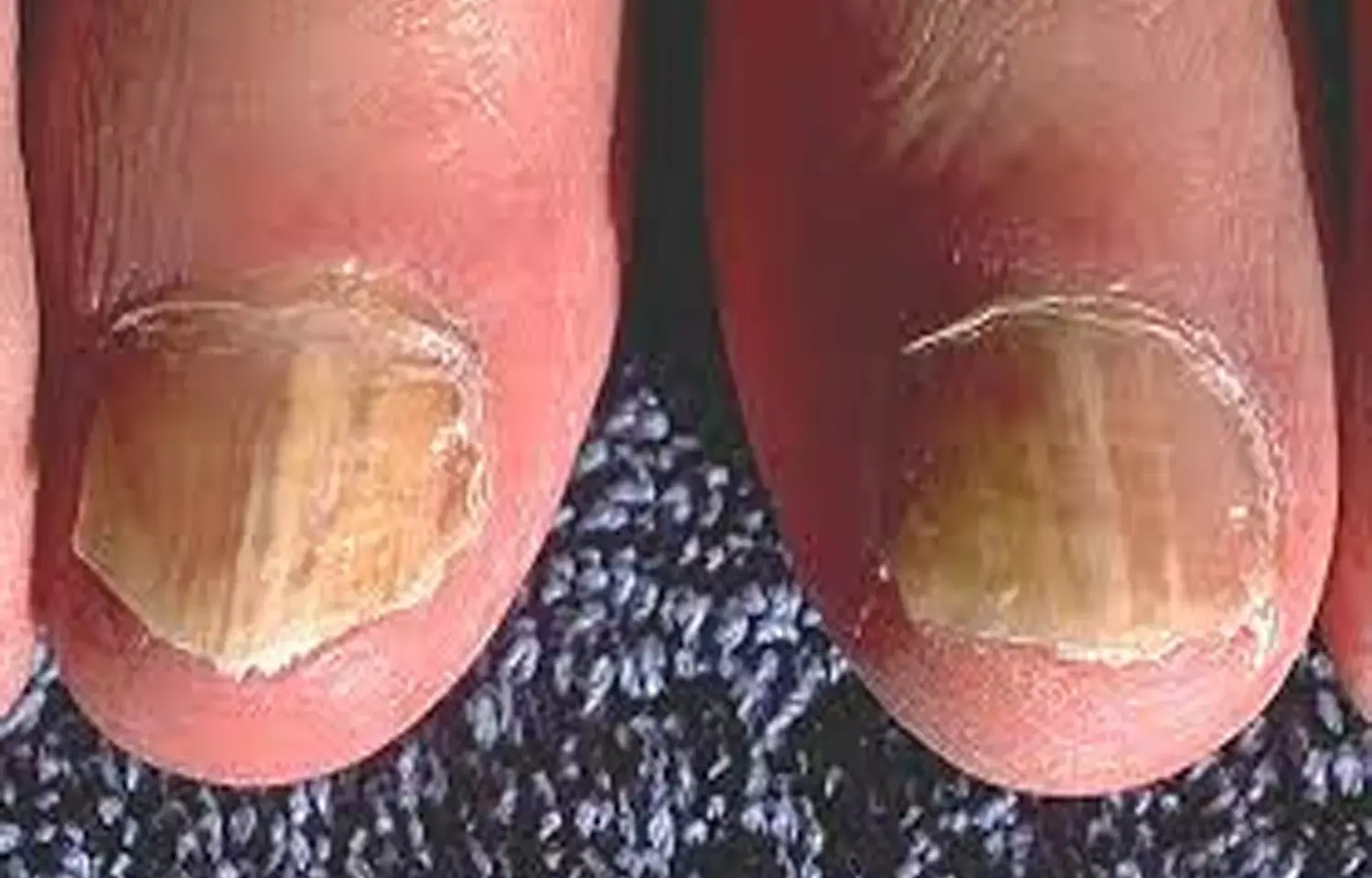
Japan: 10% efinaconazole solution (EFCZ) can be used as a first-line drug to treat onychomycosis with longitudinal spikes that are considered refractory to oral drugs, show findings from a multicenter study with a sample size of over 80 subjects.
The study, published in the Journal of Dermatology, clarified the clinical effectiveness of EFCZ for treating onychomycosis with longitudinal spikes and showed that EFCZ has a high therapeutic effect and can be the first-line therapy.
Onychomycosis is a fungal nail infection that causes thickening, discoloration, and separation from the nail bed. In daily clinical practice, oral antifungal drugs are used for its treatment. However, onychomycosis with longitudinal spikes in the nail plate has been shown to be refractory to oral drugs as with dermatophytoma.
Against the above background, Shinichi Watanabe, Department of Dermatology, Teikyo University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan, and colleagues aimed to evaluate the efficacy of 10% efinaconazole solution in the treatment of onychomycosis with longitudinal spikes.
For this purpose, the researchers performed a post-hoc analysis of 82 subjects (of the 223 subjects enrolled in a previous study) with longitudinal spikes.
Patients who were assessed to have onychomycosis with longitudinal spikes based on the images taken at the start date of the study by both the medical expert and the investigator of the study site were included.
The researchers found the following on analysis:
- The baseline opacity ratio (length of longitudinal spike/length of entire toenail x 10) was 8.1 and fell to 2.5 at week 24 and 0.9 at week 72.
- The disappearance rate was 41.3% at week 24 and 79.3% at week 48.
- At the final assessment, complete cure was achieved in 41.5% of patients and 64.6% of patients had a reduction in clinical involvement to ≤10% of the target nail.
Our findings showed that 10% efinaconazole solution can be a first-line drug for longitudinal spikes, which have been regarded as refractory to oral drugs, concluded the authors.
Reference:
The study titled, "Clinical effectiveness of efinaconazole 10% solution for treatment of onychomycosis with longitudinal spikes," is published in the Journal of Dermatology.
DOI: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1346-8138.16035
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


