- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Exposure to Epoxy Compounds can lead to Allergic-Contact Dermatitis, Eczema
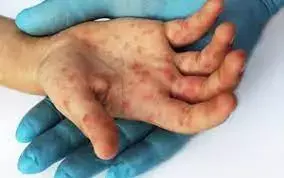
Exposure to epoxy compounds can lead to allergic contact dermatitis and eczema according to a recent study published in the Contact Dermatitis.
Occupational outbreaks of reactions to HMW allergens can occur episodically and can be severe and life altering for those affected. These allergies can affect large numbers of easily identified workers in specific industries which can reach epidemic proportions such as latex allergy and Baker's asthma.
The practical importance of two recently described epoxy hardener allergens — 1,3-benzenedimethanamine, N-(2-phenylethyl) derivatives (1,3-BDMA-D) and hydrogenated formaldehyde benzenamine polymer (FBAP) — as occupational allergens remains to be defined.
Researchers conducted a study to describe patients diagnosed at the Finnish Institute of Occupational Health (FIOH) with positive reactions to 1,3-BDMA-D or FBAP.
Researchers searched FIOH's patch test files from January 2017 to December 2020 for patients examined due to suspected occupational contact allergy to epoxy compounds. We analysed the patch test results and sources of exposure to various epoxy hardeners and focused on occupations, symptoms, and the sources of exposure to 1,3-BDMA-D and FBAP.
The Results of the study are:
During the study period, 102 patients were examined at FIOH for suspected occupational contact allergy to epoxy compounds. Of these, 19 (= 18 %) were diagnosed with contact allergy to 1,3-BDMA-D (n=10) or FBAP (n=12). The largest occupational group was sewage pipe reliners (n=8). Seven different hardener products contained FBAP, whereas 1,3-BDMA-D was only present in one hardener used by spray painters.
Thus, a substantial number of patients with suspected occupational epoxy resin system allergy tested positive to in-house test substances of 1,3-BDMA-D and/or FBAP.
Reference:
The study, "Characterization of patients with occupational allergy to two new epoxy hardener compounds," by Sari Suomela et al. was published in Contact Dermatitis.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/cod.14109
Keywords:
occupational allergy, Characterization of patients with occupational allergy, occupational allergy treatment, allergic-contact dermatitis, eczema, Exposure to epoxy compounds, cause of allergic-contact dermatitis, Contact Dermatitis, Sari Suomela, Maria Pesonen, Katriina Ylinen, Kristiina Aalto-Korte, Katri Suuronen
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


