- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Higher Calcium Levels Increase Rosacea Risk, While Potassium May Be Protective: Study
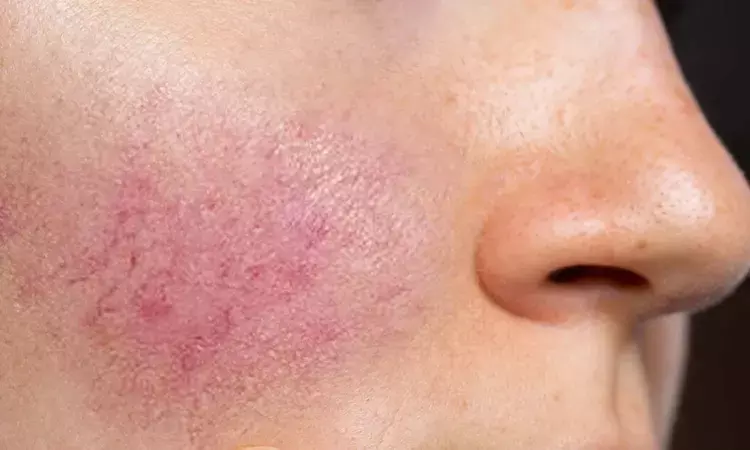
Researchers have found in a new study that a high level of calcium may make one prone to rosacea, while the level of potassium may have a protective effect. A recent analysis with the use of Mendelian Randomization (MR) has provided fresh insight into the potential causal roles of these micronutrients in rosacea, an inflammatory facial dermatosis. These associations might eventually form the foundation for new prevention and therapy in individuals at risk of rosacea development. The study was published in the Clinical Cosmetic & Investigational Dermatology by Yankun Z. and fellow researchers.
The principal aim of this study was to determine whether serum levels of calcium, copper, selenium, zinc, iron, potassium, and magnesium are causally linked to rosacea risk. Researchers performed a two-sample Mendelian Randomization (MR) analysis of genetic data collected from genome-wide association studies (GWAS).
The analysis in MR was primarily done using the Inverse Variance Weighted (IVW) method, and additional statistical techniques such as weighted median, weighted mode, and MR-Egger regression were employed. Sensitivity analysis such as MR-Egger, MR-PRESSO, Cochran's Q, and leave-one-out methods were utilized to establish consistency in the results. 301 instrumental variables were utilized in the final analysis.
Key Findings
• The study established a significant association of genetically predicted serum calcium with an increased risk of rosacea:
• An elevated level of serum calcium was found to have an increased risk of rosacea (OR = 2.27, 95% CI: 2.02–2.55, P < 0.001).The association was corroborated by all the other MR approaches, attesting to its credibility.
• Serum potassium concentration was inversely associated with risk of rosacea (OR = 0.36, 95% CI: 0.14–0.93, P = 0.0354). The protective association was also established when employing the weighted median approach.
• Sensitivity analyses confirmed that the findings were stable, with no indication of horizontal pleiotropy or high bias.-
˜These results indicate that calcium could play a role in rosacea pathogenesis, whereas potassium could be protective.
This study establishes causal association between genetically predicted serum calcium and potassium levels and rosacea risk. High calcium was associated with an increased risk for rosacea, while potassium provided protection. Such findings highlight the importance of determining the micronutrient contribution to rosacea pathogenesis, with particular attention to their possible role in the neurovascular and oxidative stress pathways.
Reference:
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


