- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Intralesional Triamcinolone More Effective for Keloids, but Vitamin D3 Offers Safer Alternative: Study
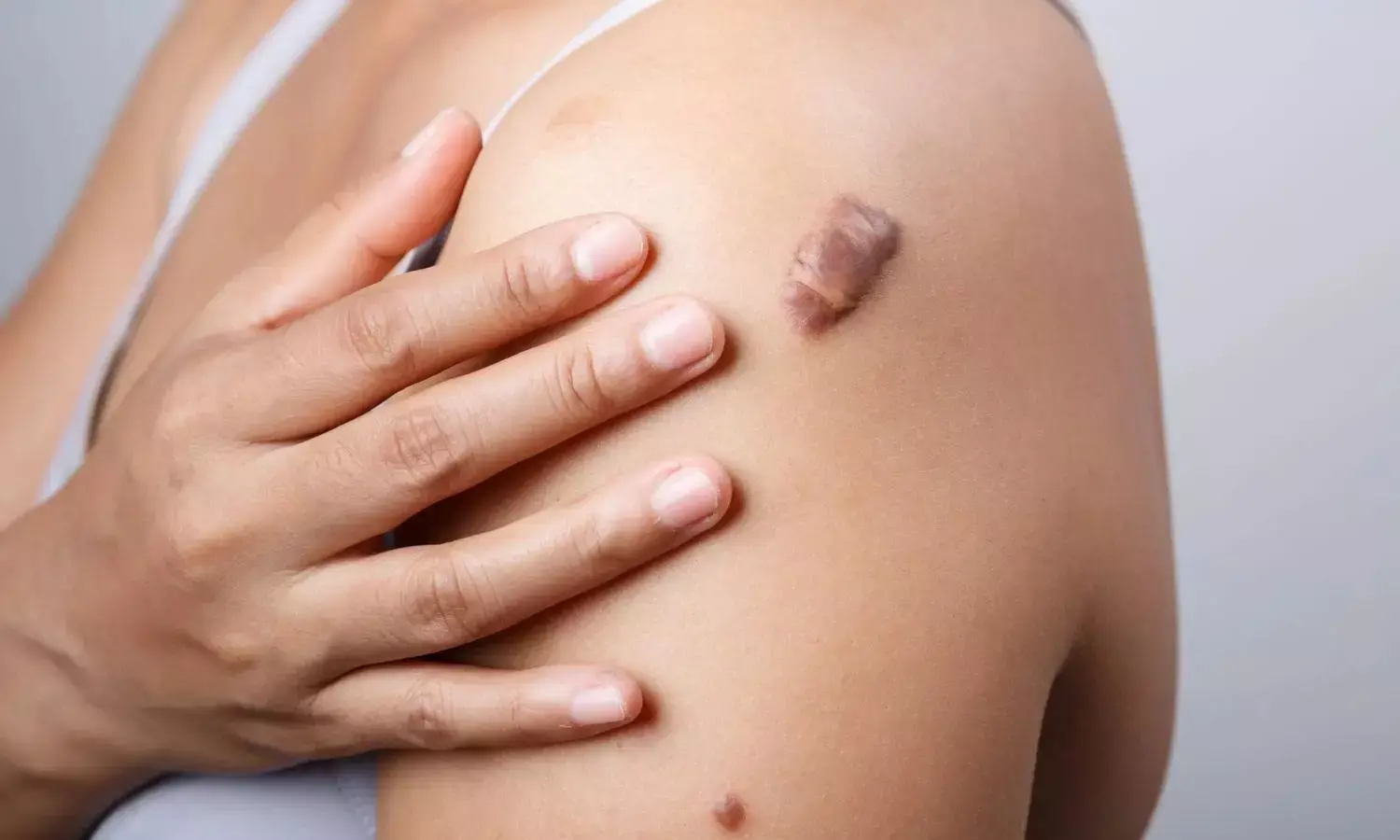
India: In a double-blinded randomized controlled trial, researchers have investigated the safety and effectiveness of intralesional vitamin D3 versus intralesional triamcinolone for treating keloids, a common dermatological condition characterized by raised scars. The study, published in Wound Repair and Regeneration, also explored the correlation between tissue expression of vitamin D receptors and treatment outcomes.
The researchers discovered that triamcinolone acetonide and vitamin D effectively treat keloids. While triamcinolone demonstrated greater efficacy, vitamin D proved a safer option, positioning it as a promising alternative for keloid management.
Keloids often result from excessive collagen formation during wound healing, leading to disfiguring scars that can cause both physical and emotional distress. Current standard treatment typically involves intralesional injections of corticosteroids, with triamcinolone acetonide being the most widely used option. While effective, concerns about potential side effects, such as skin atrophy and pigmentation changes, have spurred interest in alternative therapies. Considering this, a need arises for safer and more effective treatments.
Against the above background, Tarun Narang, Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India, and colleagues aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of intralesional vitamin D with triamcinolone for treating keloids, while also examining the correlation between tissue expression of vitamin D receptors (VDRs) and treatment outcomes.
For this purpose, the researchers randomly assigned sixty patients into two groups: Group A received intralesional vitamin D, while Group B was treated with intralesional triamcinolone. Each participant received four injections at four-week intervals, followed by an eight-week follow-up. Biopsies were collected before and after treatment to assess VDR expression levels and their correlation with treatment outcomes.
The primary outcome measured was the percentage of patients achieving at least a 50% reduction in the Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS). Secondary outcomes included the incidence of adverse effects and changes in VDR expression before and after treatment.
The study led to the following findings:
- Baseline VSS scores were recorded as 9.73 ± 1.01 for the vitamin D group and 10.13 ± 1.07 for the triamcinolone group.
- Post-treatment, the mean VSS decreased to 5.17 ± 0.59 for the vitamin D group and 4.77 ± 0.77 for the triamcinolone group, with the triamcinolone group showing a significantly better response.
- A greater proportion of patients in the triamcinolone group achieved more than a 50% reduction in VSS scores (76.7% versus 50%).
- There were no recurrences during the eight-week follow-up. However, adverse effects were more prevalent in the triamcinolone group, with hypopigmentation occurring in 80% compared to 36.7% in the vitamin D group and atrophy in 73.3% versus 40%.
- In either group, there were no significant differences in VDR receptor expression before and after treatment.
"The findings showed that intralesional triamcinolone was more effective in treating keloids but was associated with a higher incidence of side effects. In contrast, vitamin D3 emerged as a safer alternative for keloid management, offering a promising option for patients concerned about the adverse effects of corticosteroids," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Goyal, A., Mehta, H., Narang, T., Vinay, K., Chhabra, S., Kaushik, H., Kaur, M., Sachdeva, N., & Dogra, S. (2024). A double-blinded randomised control study to compare the effectiveness and safety of intralesional vitamin D3 with intralesional triamcinolone and its correlation with tissue expression of vitamin D receptors in patients with keloid. Wound Repair and Regeneration, 32(5), 696-703. https://doi.org/10.1111/wrr.13209
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


