- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Investigational drug Litifilimab effective against cutaneous lupus erythematosus: LILAC trial
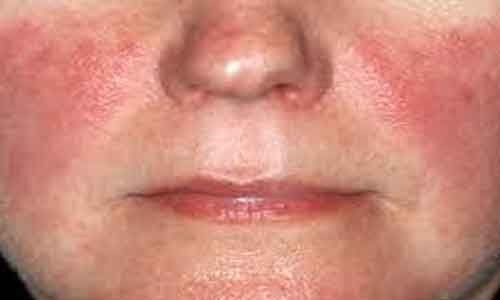
USA: Treatment with litifilimab reduced skin disease activity over a period of 16 weeks in patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus, according to the phase II LILAC study published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Litifilimab is an investigational drug targeting the blood dendritic cell antigen 2 (BDCA2) receptor.
"Longer and larger trial are, however, needed to determine the safety and effects of litifilimab for cutaneous lupus erythematosus treatment, "Victoria P. Werth, and colleagues wrote in their study.
Blood dendritic cell antigen 2 (BDCA2) is a receptor that is expressed exclusively on plasmacytoid dendritic cells that are implicated in lupus erythematosus pathogenesis. However, there is no extensive study of whether treatment with litifilimab, a humanized monoclonal antibody against BDCA2, would be effective in reducing disease activity in cutaneous lupus erythematosus patients.
Against the above background, the researchers performed a phase 2 trial that enrolled 132 adults with histologically confirmed cutaneous lupus erythematosus with or without systemic manifestations. They were randomly assigned in the ratio of 1:1:1:1 to receive subcutaneous litifilimab (at a dose of 50, 150, or 450 mg) or placebo at weeks 0, 2, 4, 8, and 12. 26 were assigned to the 50-mg litifilimab group, 25 to the 150-mg litifilimab group, 48 to the 450-mg litifilimab group, and 33 to the placebo group.
A dose–response model was used to assess whether there was a response across the four groups on the basis of the primary end point. Percent change from baseline to 16 weeks in the Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index–Activity score (CLASI-A; scores range from 0 to 70, with higher scores indicating more widespread or severe skin involvement) was the primary endpoint. Safety assessment was also done.
Based on the study, the researchers reported the following findings:
- Mean CLASI-A scores for the groups at baseline were 15.2, 18.4, 16.5, and 16.5, respectively.
- The difference from placebo in the change from baseline in CLASI-A score at week 16 was −24.3 percentage points in the 50-mg litifilimab group, −33.4 percentage points in the 150-mg group, and −28.0 percentage points in the 450-mg group.
- The least squares mean changes were used in the primary analysis of a best-fitting dose–response model across the three drug-dose levels and placebo, which showed a significant effect.
- Most of the secondary end points did not support the results of the primary analysis.
- Litifilimab was associated with three cases each of hypersensitivity and oral herpes infection and one case of herpes zoster infection.
- One case of herpes zoster meningitis occurred 4 months after the participant received the last dose of litifilimab.
"Treatment with litifilimab was superior to placebo with regard to a measure of skin disease activity over a period of 16 weeks in a phase 2 trial involving participants with cutaneous lupus erythematosus," the researchers wrote in their study.
Reference:
Werth VP, et al "Trial of anti-BDCA2 antibody litifilimab for cutaneous lupus erythematosus" N Engl J Med 2022; DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2118024.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


