- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
lntradermal heparin sodium cost-effective and less-invasive treatment than CO2 laser for early mild xanthelasma
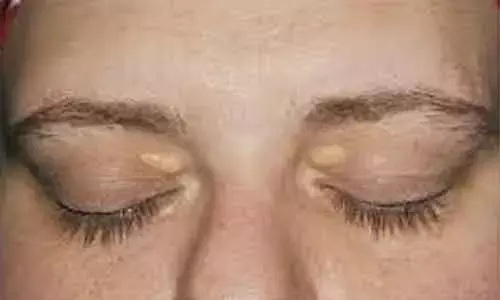
Xanthelasma, characterized by yellowish cholesterol deposits around the eyelids, often necessitates therapeutic interventions. Ablative CO2 laser treatment is a common approach, yet associated complications warrant exploration of alternative therapies. Recently, intradermal heparin sodium injections emerged as a potential treatment. A study compares the efficacy of CO2 laser versus heparin sodium injections in managing xanthelasma lesions. This study was published in the journal Photodermatology, Photoimmunology and Photomedicine by Yomna M. and colleagues.
- CO2 Laser vs. Heparin Sodium:
A pilot study involving 30 xanthelasma patients divided into two groups:
Group A underwent CO2 laser ablation (2 sessions every 4 weeks).
Group B received intradermal heparin sodium injections (10 sessions every week).
- Therapeutic Efficacy:
Both interventions exhibited significant reduction in xanthelasma lesions.
CO2 laser treatment was notably more effective than intradermal heparin sodium overall.
- Treatment Specifics:
Intradermal heparin sodium demonstrated comparable effectiveness to CO2 laser in early-stage (grade I and II) xanthelasma, particularly within <2 years duration.
Notably, heparin sodium showed a lower incidence of post-therapy side effects compared to CO2 laser.
- Clinical Implications:
Heparin sodium injections present as a safe and cost-effective therapeutic technique for early-stage mild xanthelasma (grade I and II).
Additionally, it might serve as a pre-operative management for advanced xanthelasma (grade III and IV), aiding in lesion reduction before CO2 laser ablation.
The study highlights the comparative efficacy of CO2 laser and intradermal heparin sodium injections in managing xanthelasma. While CO2 laser remains more effective overall, heparin sodium emerges as a promising alternative, particularly in treating early-stage xanthelasma with fewer side effects. This research offers valuable insights into diversifying therapeutic options for xanthelasma management.
Reference:
Neinaa, Y. M. E.-H., Awara, B. S. E.-S., Shalaby, O. E.-S., & Abd El-Naby, N. M. Clinical and dermoscopic assessment of ablative carbon dioxide laser versus intradermal heparin sodium in xanthelasma. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine,2023;39(6):648–656. https://doi.org/10.1111/phpp.12915
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


