- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ruxolitinib cream highly effective in treatment of cutaneous lichen planus: Study
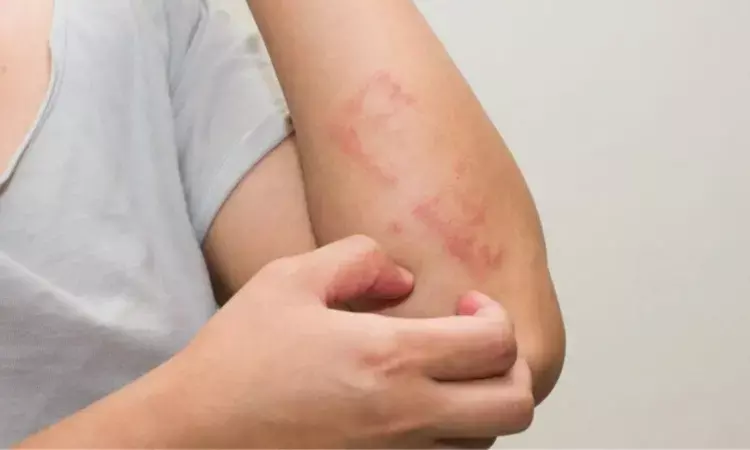
Arizona: Topical ruxolitinib is highly effective for treating cutaneous lichen planus (LP), according to findings from a small pilot study in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology. The transcriptomic analysis provided confirmation of LP being an interferon-driven disease and the downregulation of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) corresponds to disease response.
Lichen planus is an inflammatory skin condition that affects the skin and mucosal surfaces. Cutaneous lichen planus is a clinical type of lichen planus that shares similar features on histopathology. Its symptoms can range from none (uncommon) to intense itch.
Ruxolitinib is an inhibitor of Janus kinase 1/2 that blocks signal transduction of a critical cytokine involved in the pathogenesis of cutaneous LP called interferon-gamma. In the prospective phase II study, Aaron R. Mangold, Department of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic Arizona, and colleagues investigated the efficacy of topical ruxolitinib in cutaneous LP and performed transcriptomic analysis pre-and post-therapy.
The study included 12 patients with cutaneous LP who were applied topical ruxolitinib twice daily for 8 weeks. Primary endpoints were changes in total lesion count and modified Composite Assessment of Index Lesion Severity (mCAILS) score in index treated and untreated index control lesions at week 4.
Key findings of the study include:
- Total lesion count decreased by a median of 50 lesions (interquartile range 25, 723).
- mCAILS scores decreased by a mean difference of 7.6 (standard deviation 8.8) between index treated and control lesions.
- Type I and II interferon pathways were enriched in LP and responsive disease displayed downregulation of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs).
"Findings revealed that topical ruxolitinib is highly effective in the treatment of cutaneous LP," wrote the authors. "Transcriptomic analysis confirmed LP as an interferon-driven disease and downregulation of ISGs correlated with disease response."
Reference:
The study titled, "Ruxolitinib cream in the treatment of cutaneous lichen planus: A prospective, open-label study," was published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2022.01.015
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


