- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Study Explores Unreported Allergic Contact Dermatitis due to Salicylic Acid
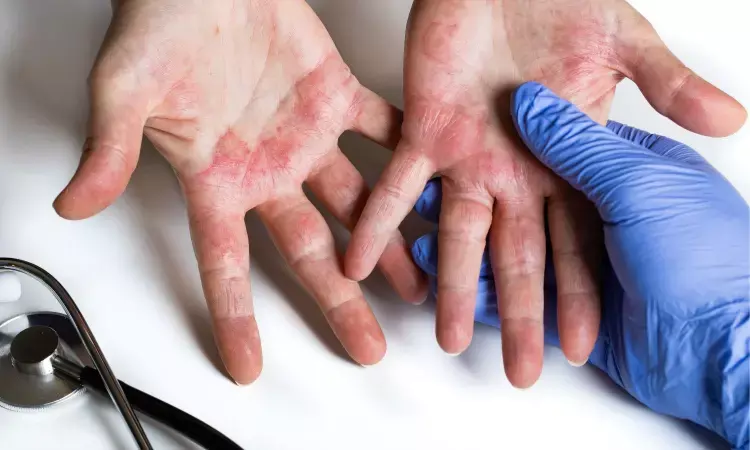
A recent study from a dermatology clinic, published in the recent issue of Contact Dermatitis journal highlighted the underreported issue of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) which is caused by salicylic acid (SA). Despite the well-documented cross-reactivity among salicylates, the reports of such reactivity that specifically involved SA have been scarce.
The objective of the study was to describe the clinic's experience with patch testing for SA by highlighting seven notable cases of allergic reactions. The study analyzed results from patch tests conducted between January 1, 2020 and February 9, 2024 using a 5% SA in petrolatum solution.
Out of 489 patients who underwent patch testing for SA, 27.5% (approximately 135 patients) were tested. Among these, 21 participants showed positive reactions. The breakdown of reactions included seven doubtful (+/−) cases and 14 weak positive (+) cases. Also, there were no strong or extreme positive reactions observed. Four more irritant reactions were documented which indicated some level of irritation but not necessarily an allergic response.
Of the 14 weak positive reactions, 7 cases were deemed to have definite or probable clinical relevance which means the allergic reaction was likely connected to their clinical symptoms. Also, five of these seven relevant cases also expressed reactivity to other salicylates that suggests a probable cross-reactivity.
The study concludes that ACD to SA is likely underreported due to insufficient testing. The findings indicate that patch testing with 5% SA in petrolatum is generally tolerable for patients which showed minimal significant irritation. The probable cross-reactivity between SA and other salicylates underlines the need for more comprehensive testing and awareness among clinicians.
The outcomes of this research emphasize that while SA appears to be a primary sensitizer in some cases, further studies are imperative to determine its role as a potential marker for the salicylate allergy. This discovery could lead to better diagnostic practices and management strategies for the patients with suspected salicylate allergies.
The results of this study highlight the necessity for increased vigilance and reporting of ACD cases related to SA. Given the widespread use of SA in various skincare and medicinal products, understanding its allergenic potential is highly crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Improved awareness and more rigorous testing protocols could lead to more accurate diagnoses and enhanced patient outcomes in the participants with salicylate sensitivities.
Source:
Brumley, C., Arora, P., Neeley, A., & Hylwa, S. (2024). Allergic contact dermatitis to salicylic acid: A case series of relevant sensitization. In Contact Dermatitis. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1111/cod.14573
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


