- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Topical Triple-Agent FDC Gel Found Most Effective and Safe for Moderate-to-Severe Acne in New Meta-Analysis
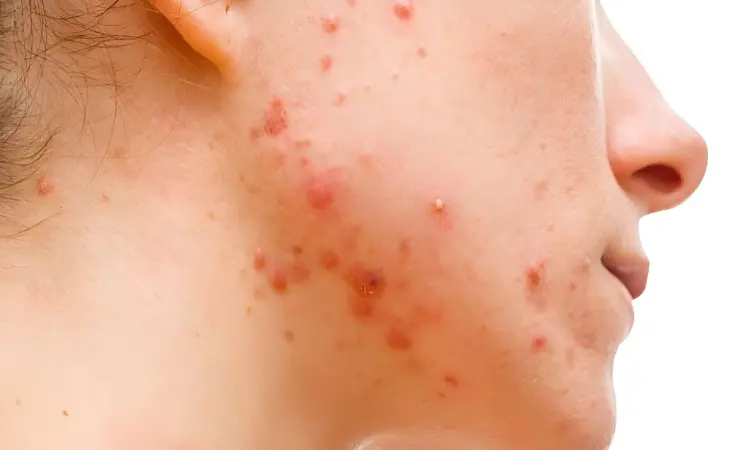
USA: Among nearly 20 different agents and treatment combinations, the topical triple-agent fixed-dose combination (FDC) gel proved to be the most effective for treating moderate-to-severe acne, according to a network meta-analysis (NMA). The findings were published online in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
There are several treatment options available for managing moderate-to-severe acne. Topical treatments, such as the triple-agent FDC gel, are often preferred due to their targeted application and reduced risk of systemic side effects compared to oral medications. This gel combines proven acne-fighting agents that work synergistically to address multiple aspects of acne pathology, including inflammation, bacterial growth, and excess oil production.
Julie C Harper, The Dermatology and Skin Care Center of Birmingham, AL, and colleagues aimed to systematically examine the comparative effectiveness (efficacy/safety) of moderate-to-severe acne treatments.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted a systematic literature review (SLR) to identify randomized controlled trials involving at least four weeks of treatment—whether topical, oral, physical, or a combination—for moderate-to-severe facial acne in patients aged nine years and older. The study aimed to evaluate efficacy outcomes, including the percentage of patients achieving a two-grade reduction from baseline and those classified as “clear” or “almost clear” for global severity score (treatment success), as well as the absolute changes in inflammatory (ILs) and noninflammatory lesion counts (NILs).
A random-effects network meta-analysis was then performed to assess these efficacy outcomes, with treatments ranked based on posterior rank plots and surface under the cumulative ranking values. The SLR/NMA included a total of 85 studies.
The researchers reported the following findings:
- Topical triple-agent fixed-dose combination gel (clindamycin phosphate 1.2%/adapalene 0.15%/benzoyl peroxide 3.1%) and combinations of double-agent fixed-dose topical treatments with oral antibiotics (TOA3) consistently ranked in the top 3 treatments.
- Topical triple-agent FDC gel was numerically superior to TOA3 for treatment success (log-odds ratios: 1.84) and 1.69 vs placebo/vehicle).
- TOA3 was numerically superior to topical triple-agent FDC gel for reduction of ILs (mean difference: -8.21) and -10.40 versus placebo/vehicle) and NILs (mean difference: -13.41 and -17.74 versus placebo/vehicle).
The research team concluded that the topical triple-agent fixed-dose combination (FDC) gel was more effective than all other treatments for moderate-to-severe acne. Its use helps reduce the reliance on oral antibiotics, which in turn lowers the risk of developing antibiotic resistance.
Additionally, the findings indicate that combining an oral antibiotic with a double-agent FDC gel does not provide significant advantages over using the triple-agent FDC gel alone.
Reference:
Harper JC, Baldwin H, Choudhury SP, Rai D, Ghosh B, Aman MS, Choudhury AR, Dutta SK, Dey D, Bhattacharyya S, Lin T, Joseph G, Dashputre AA, Tan JKL. Treatments for Moderate-to-Severe Acne Vulgaris: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2024 Apr 1;23(4):216-226. doi: 10.36849/JDD.8148. PMID: 38564399.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


