- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Diabetes associated with high prevalence of sarcopenia, study finds
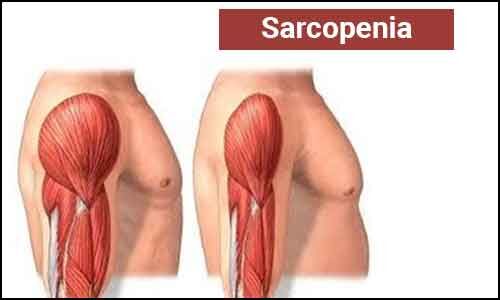
China: A recent study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism has suggested that sarcopenia is more common in diabetes patients. The probable risk factors include age, HbA1c, diabetic nephropathy, visceral fat area (VFA), duration of diabetes, and HS-CRP.
Sarcopenia is the loss of muscle mass related specifically to aging. It affects your balance, gait, and overall ability to perform daily tasks. Previous studies have shown sarcopenia prevalence in diabetes patients to be three times higher than in non-diabetic patients and are related to poor prognosis. Bin Ma, Key Laboratory of Evidence-Based Medicine and Knowledge Translation of Gansu Province, Lanzhou, P.R.China, and colleagues aimed to investigate the global pooled prevalence and risk factors of sarcopenia in diabetes patients.
For this purpose, the researchers identified relevant studies published until November 30, 2020, from online databases. The study included participants with age ≥18 years with clinically diagnosed diabetes. Sex and diabetes type were not restricted. Two reviewers independently extracted the data using a standard collection form.
Key findings include:
- The pooled prevalence of sarcopenia in patients with diabetes was 18%; subgroup analysis showed that sarcopenia was more prevalent in males than in females, as well as being more prevalent in Asia than in South America and Oceania.
- Age (OR, 1.10), HbA1c (OR, 1.16), visceral fat area (VFA) (OR, 1.03), diabetic nephropathy (OR, 2.54), duration of diabetes (OR, 1.06), and HS-CRP (OR, 1.33) were risk factors for sarcopenia in patients with diabetes.
Based on the findings the researchers concluded that in the future, medical staff should not only pay attention to the early screening of sarcopenia in high-risk groups but also provide information on its prevention.
Reference:
Liyuan Feng, Qianqian Gao, Kaiyan Hu, Mei Wu, Zhe Wang, Fei Chen, Fan Mei, Li Zhao, Bin Ma, Prevalence and risk factors of sarcopenia in patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2021;, dgab884, https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgab884
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


