- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
High levels of serum progesterone associated with Diabetic retinopathy; finds study
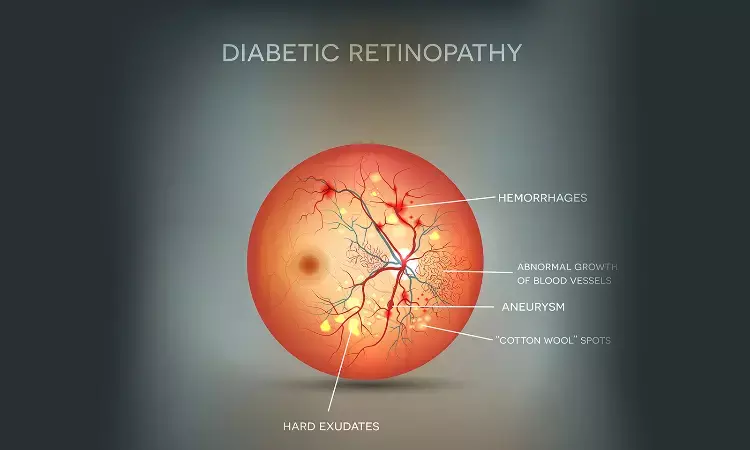
Researchers at Qingdao University, Qingdao, China conducted a study to investigate the relationship between serum progesterone (P) and retinopathy in male patients with type 2 diabete (T2DM)and to investigate whether serum progesterone (P) is associated with its progression.
They found that High levels of serum progesterone are significantly associated with Diabetic retinopathy in male hospitalized patients.The findings from a recent trial have been published in Journal of Diabetes Investigation. Researchers further highlighted that higher Progesterone level in men can be a potential clinical factor to identify DR.
The most common complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is DR, which is a microvascular and neural complication of the retina and remains one of the leading causes of visual loss in adults aged 20–74 years . Interestingly, the male sex has been reported to be an independent risk factor for advanced diabetic retinopathy in T2DM , which suggests the effect of sex hormones. Estrogen can play different roles according to the stage of retinopathy: in the initial stage, the proliferation of endothelial cells induced by estradiol has a beneficial effect and protects the retina through the induced repair process, while in the proliferative phase, this effect aggravates the retinopathy .
Historically, the relationship between gonadal hormones and DR risk has received scarce attention, and no previous study has investigated the interaction between serum P and DR.
So,researchers undertook the present study to investigate the relationship between serum progesterone (P) and retinopathy in male patients with type 2 diabetes(T2DM)and to investigate whether P is associated with its progression.
For the study design, a total of 1376 male participants with T2DM were recruited from Affiliated Hospital of Medical College Qingdao University. Through Logistic regression analysis after adjusting the potential confounding variation, the odds ratio (OR) and the corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) related to the quartiles of progesterone were obtained.
On data analysis, the following facts emerged.
- According to the quartiles of P levels, the prevalence rate of diabetic retinopathy (DR) in the last quartile is obviously greater to other quartiles (52.5% to 34.9%, 31.9%, 37.5%, ) .
- Compared with those in the first quartile, the prevalence of DR for the last quartile had an OR of 1.85 in NPDR while OR was 8.35 in PDR .
- When adjusted for age, BMI, duration of T2DM, HbA1c, BP and other variables, the ORs for DR (95%CI) in Q4 were 2.13 (1.49,3.06) in NPDR and 8.44(2.69,26.43) in PDR .
- The positive association between P and DR risk is independently in adjusted logistic regression.
"The relationship between P and DR will open up a new research field, and large-scale clinical studies in the future may help to identify whether progesterone therapy is sex-specific. Therefore, progesterone therapy still requires careful and comprehensive consideration. Prospective cohort studies are needed to identify the causality."wrote the team.
For full article follow the link: https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.13463
Primary source; Journal of Diabetes Investigation
Dr Satabdi Saha (BDS, MDS) is a practicing pediatric dentist with a keen interest in new medical researches and updates. She has completed her BDS from North Bengal Dental College ,Darjeeling. Then she went on to secure an ALL INDIA NEET PG rank and completed her MDS from the first dental college in the country – Dr R. Ahmed Dental College and Hospital. She is currently attached to The Marwari Relief Society Hospital as a consultant along with private practice of 2 years. She has published scientific papers in national and international journals. Her strong passion of sharing knowledge with the medical fraternity has motivated her to be a part of Medical Dialogues.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


