- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Hearing loss in elderly preventable by integrated care, finds study
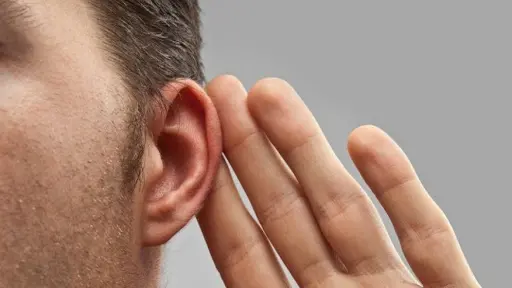
Researchers at University of Manchester researchers have proposed a way to prevent hearing loss in older people by addressing socioeconomic inequalities encountered while young.
Recent research has revealed that the management of hearing loss must involve integrated care, which entails considering an individual's entire health profile and providing ongoing support for each person's adaptation and self-management.
In that way, a more substantial proportion of the population will receive high-quality health care and this indeed will maximize the opportunity for healthy aging.
The study is published in the SAGE Journals.
Hearing loss is a major health challenge that can have severe physical, social, cognitive, economic, and emotional consequences on people's quality of life. Currently, the modifiable factors linked to socioeconomic inequalities in hearing health are poorly understood.
Therefore, the team from the Centre for Primary Care and Health Services Research, Institute for Health Policy and Organisation (IHPO), School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Biology, Medicine and Health, The University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom led by Dialechti Tsimpida and colleagues carried out an online database search to identify literature that relates hearing loss to health inequalities as a determinant or health outcome.
The authors selected a total of 53 studies to thematically summarize the existing literature, using a critical interpretive synthesis method, where the subjectivity of the researcher is intimately involved in providing new insights with explanatory power.
The evidence provided by the literature was summarized under four key themes:
(a) There might be a vicious cycle between hearing loss and socioeconomic inequalities and lifestyle factors,
(b) socioeconomic position may interact with less healthy lifestyles, which are harmful to hearing ability,
(c) increasing health literacy could improve the diagnosis and prognosis of hearing loss and prevent the adverse consequences of hearing loss on people's health, and
(d) people with hearing loss might be vulnerable to receiving low-quality and less safe health care.
This study used elements from theoretical models of health inequalities to formulate a highly interpretive conceptual model for examining hearing health inequalities. This model depicted the specific mechanisms of hearing health and their evolution over time.
There are many modifiable determinants of hearing loss, in several stages across an individual's life span; tackling socioeconomic inequalities throughout the life-course could improve the population's health, maximizing the opportunity for healthy aging.
Hence, it was concluded that "the increase in the aging population and the burden of hearing loss and the concentration of ill-health among older adults have highlighted the urgent need to investigate factors that contribute to socioeconomic inequalities in hearing health."
Although previous studies have found correlations between (a) socioeconomic inequalities and hearing loss, (b) hearing loss and comorbidity, and (c) hearing impairment and related socioeconomic disparities, this review is the first to examine the mechanisms and explain the relationship between socioeconomic inequalities and hearing health in a life-course perspective, synthesizing the existing evidence, they further inferred.
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


