- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Preoperative CT shows promise in increasing success rates of rhinoplasty;claims study
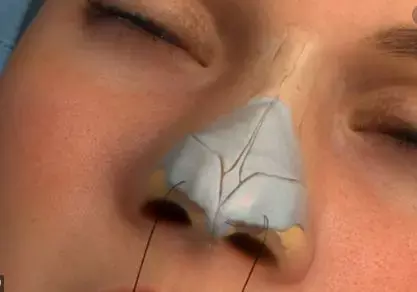
According to a recently published study in International Journal of Otolaryngology, perioperative CT is associated with greater patients' satisfaction and quality of life after rhinoplasty compared to either nasal endoscopy or anterior rhinoscopy.
Previous studies have pointed out that the primary reason for revision rhinoplasty is nasal tip asymmetry followed by breathing difficulties or nasal obstruction . Therefore, the endonasal mucosal or anatomic pathologies which could lead to poor functional results and dissatisfaction should not be neglected when planning for surgery . A thorough perioperative assessment of patients can lead to proper patient selection, planning, and better functional and aesthetic outcomes . Although computed tomography (CT) scan has become an integral part of the diagnostic paradigm for patients with pathologies of the paranasal sinuses, the use of CT scan for preoperative evaluation of patients seeking rhinoplasty is up for debate.
Researchers soughtto carry out the present study with the aim to compare the efficacy of CT scan in diagnosing nasal pathologies with other evaluating tools in patients undergoing rhinoplasty.
As for the study design,In this randomized controlled trial study, 74 consecutive patients seeking cosmetic rhinoplasty referred to otorhinolaryngology clinic were randomly assigned into three groups based on the perioperative evaluation method: the CT group, the nasal endoscopy group, and the control group (anterior rhinoscopy only). Surgical planning was made according to perioperative findings, and the identified endonasal pathologies were corrected during the surgery.
The functional and aesthetic outcomes of the rhinoplasty were assessed by Nasal Obstruction Symptom Evaluation (NOSE), Rhinoplasty Outcome Evaluation (ROE), and the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) tools before surgery and at 12-month follow-up.
Data analysis revealed some interesting facts.
- All outcome measures improved significantly in either group toward one year after rhinoplasty (all with value <0.05).
- Subjects in the CT group demonstrated greater improvement in the NOSE, VAS, and ROE compared to other two groups (NOSE: value = 0.17; VAS: value = 0.024; ROE: value = 0.042).
"In summary, tough the identification of endonasal deformities could be feasible with different evaluation tools, CT scan seems to be a superior method with better subjective outcomes after rhinoplasty compared to anterior rhinoscopy and nasal endoscopy."the team concluded.
For the full article follow the link: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5929754
Primary source: International Journal of Otolaryngology
Dr Satabdi Saha (BDS, MDS) is a practicing pediatric dentist with a keen interest in new medical researches and updates. She has completed her BDS from North Bengal Dental College ,Darjeeling. Then she went on to secure an ALL INDIA NEET PG rank and completed her MDS from the first dental college in the country – Dr R. Ahmed Dental College and Hospital. She is currently attached to The Marwari Relief Society Hospital as a consultant along with private practice of 2 years. She has published scientific papers in national and international journals. Her strong passion of sharing knowledge with the medical fraternity has motivated her to be a part of Medical Dialogues.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


