- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Saliva may be helpful in detection of dysplastic cells in oral cancer: study
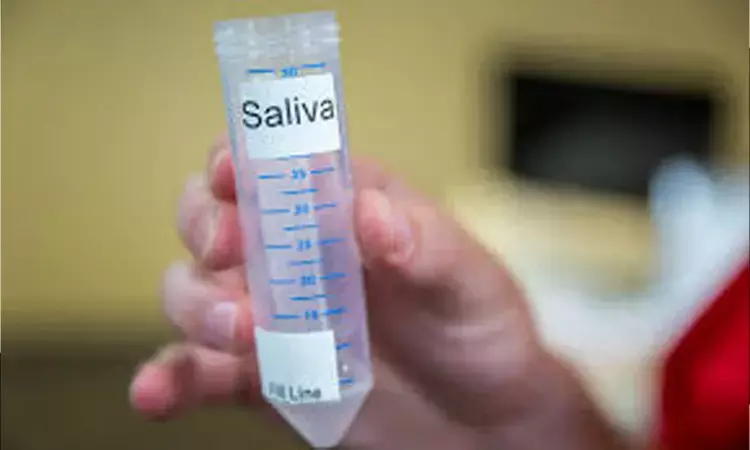
Researchers from a recent study have shown that since saliva is readily available it can be collected non- invasively for detecting dysplastic cells.
The study is published in the Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.
Saliva is an ideal tool for liquid biopsy as it is noninvasive, easily collected, and easily transported. Saliva is used to detect various biomarkers in oral cancer patients, but none used for detecting salivary dysplastic cells in potentially malignant and malignant disorders.
Therefore, Lakshmi Narayana Mada and colleagues from the Department of ENT, PESIMSR, Kuppam, Andhra Pradesh, India carried out the present study to detect the presence of dysplastic cells from saliva in oral cancer and potentially malignant patients and compare it with wedge biopsy.
All potentially malignant and malignant cases of oral cavity were included in this study. In these patients, unstimulated saliva was collected and centrifuged. The concentrated salivary substrate was stained by Haematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stain, PAP (Papanicolaou) method and May Grunwald Giemsa stain (MGG) and analyzed.
Wedge biopsy was performed from the representative area in the oral cavity and compared with salivary cells.
The results highlighted that -
a. Out of 24 patients, 16 cases were malignant, and 8 were potentially malignant.
b. 12 patients were found to be positive for atypical cells, 10 patients were found to be positive for dysplastic cells and atypical cells, and two patients were negative for atypical cells/dysplastic cells.
c. In 10 patients who were positive for dysplastic cells, all were diagnosed histologically as malignancies (P = 0.001).
d. The two patients who were negative for atypical cells/dysplastic cells showed precursor epithelial lesion with hyperplasia in the biopsy.
e. Few neutrophils were found in 15 patients and increased in 9 patients (P = 0.039).
Therefore, it was concluded that "Saliva is readily available, and can be collected noninvasively for detecting dysplastic cells."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


