- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Antibiotics Found Effective in Reducing Surgical Interventions for Uncomplicated Diverticulitis
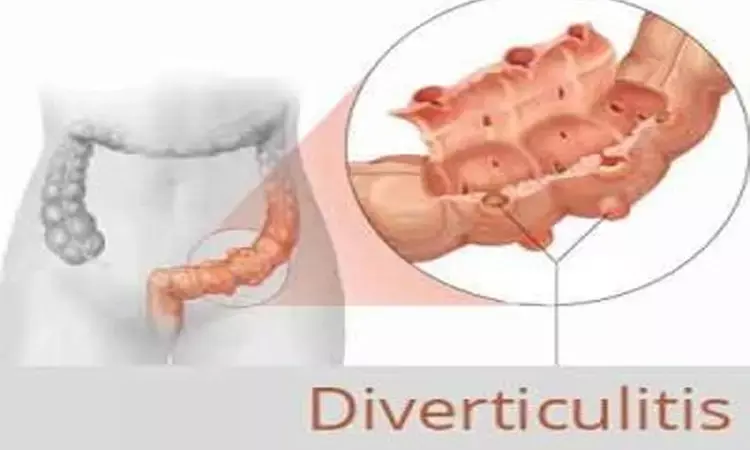
A recent study has shed light on the controversial debate surrounding the use of antibiotics for uncomplicated diverticulitis. The research aimed to investigate the efficacy of antibiotics in managing this condition, and the findings provide valuable insights into reducing the need for surgical interventions.This study was published in Digestion by Rintaro Moroi and colleagues.
The study, which collected admission data from a nationwide database, examined patients with acute uncomplicated diverticulitis. The patients were categorised into two groups: those who initiated antibiotics within two days after admission (antibiotic group) and those who did not receive antibiotics (non antibiotic group). After conducting propensity score matching, the study compared the rates of surgery, in-hospital mortality, and medical costs between the two groups.
- The results were enlightening. In the antibiotic group, the rates of both intestinal resection and stoma creation were significantly lower than in the non antibiotic group.
- Specifically, the rates were 0.61% vs. 3.09% for intestinal resection and 0.08% vs. 0.26% for stoma creation.
- Additionally, the study found that while the median medical costs in the antibiotic group were higher than in the non antibiotic group, the benefits of reduced surgical interventions likely outweighed the increased expenses.
The study's findings suggest that the use of antibiotics for acute uncomplicated diverticulitis, especially when moderate to severe disease activity is expected, can significantly reduce the risk of requiring surgical interventions such as intestinal resection and stoma creation. This conclusion offers a potential breakthrough in the treatment of this condition and may lead to more conservative and effective management strategies.
The study adds crucial evidence to the ongoing discussion about the use of antibiotics for uncomplicated diverticulitis. While the results are promising, further investigations are needed to refine guidelines and provide more specific recommendations for healthcare providers. The study's findings may encourage a more conservative approach to treatment, thereby reducing the healthcare burden and improving the patient's quality of life.
Reference:
Moroi, R., Tarasawa, K., Nagai, H., Shimoyama, Y., Naito, T., Shiga, H., Hamada, S., Kakuta, Y., Fushimi, K., Fujimori, K., Kinouchi, Y., & Masamune, A. Effectiveness of antibiotics for uncomplicated diverticulitis: A retrospective investigation using a nationwide database in japan. Digestion,2023;1–9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000534167
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


