- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Cold EMR safer than hot EMR for large duodenal adenomas: BMJ
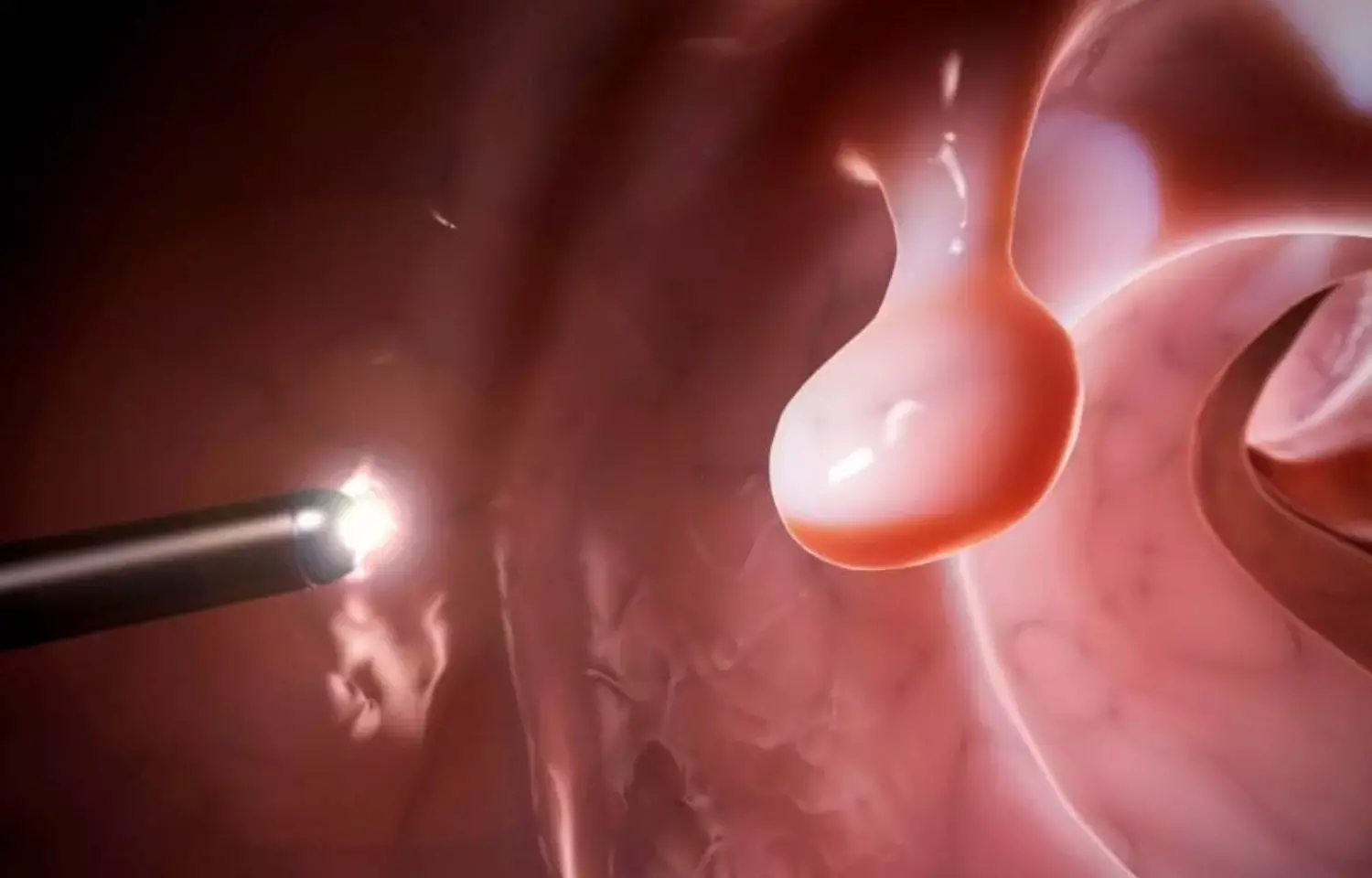
Italy: Cold snare endoscopic resection is safe as compared to a historical cohort of hot technique in a retrospective cohort of large duodenal adenomas, says a recent article published in the BMJ journal Gut. The study found no serious adverse events with cold snaring versus the hot snare group. Also, procedural time was substantially reduced.
Previous studies have shown that for large (>20 mm), sporadic non-ampullary duodenal adenomas, conventional endoscopic mucosal resection using electrocoagulation (hot EMR) is associated with a high complication rate. Antonio Capogreco, IRCCS Humanitas Research Hospital, Rozzano, Italy, and colleagues, therefore, aimed to compare the outcomes of cold and hot endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) for nonampullary duodenal adenomas >20 mm in a retrospective study.
For this purpose, the researchers performed a retrospective analysis comparing 33 patients treated this way to 101 patients who had hot EMR for their duodenal adenomas based on favorable colonic experience with cold EMR/without electrocautery. Data collection was done from four tertiary centers in two time periods.
Key findings of the study include:
- No serious adverse events (SAEs) occurred in the cold group, there were 17 intraprocedural SAEs (16.8%) and 26 postprocedural SAEs (25.7%) in the hot EMR group.
- Procedure time was significantly lower for cold EMR (49±25.1 min vs 96.9±56 min).
- Recurrence seen at first follow-up endoscopy was comparable in both groups (cold EMR: 12.1% versus hot EMR: 20.8%).
The researchers conclude, "our findings suggest that cold EMR is a safe and feasible option for the removal of large non-ampullary duodenal adenomas.
"This indicates that the implementation of cold snaring may substantially affect the safety of endoscopic resection of non-ampullary duodenal lesions without indirect signs of invasive cancer," the researchers wrote. "The very low incidence of adverse events may also reduce the intensity of care that is routinely required to remove duodenal lesions."
Reference:
Repici A, Capogreco A, Marco S, et alCold versus hot EMR for large duodenal adenomasGut Published Online First: 04 July 2022. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327171
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


