- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Flavonoids Show Therapeutic Potential in NAFLD Management: Study
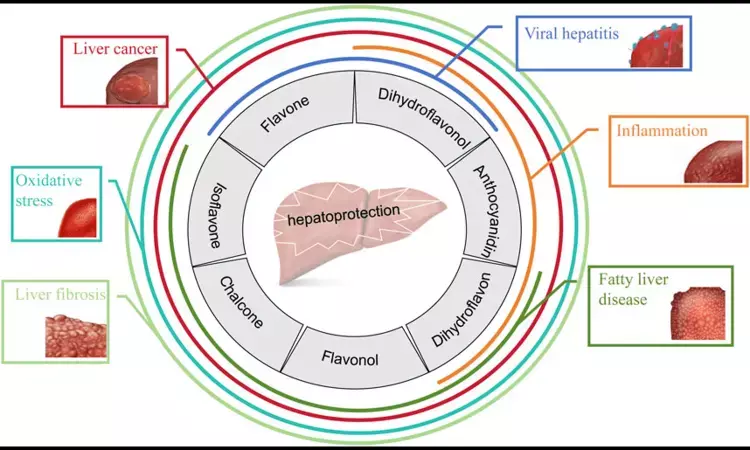
A new meta-analysis suggests that flavonoid supplementation offers promising benefits for people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Researchers reviewed 25 randomized controlled trials involving more than 1,600 participants to evaluate how different types of flavonoids—such as quercetin, anthocyanins, genistein, silymarin, and naringenin—affect liver health, blood lipids, and insulin sensitivity. The findings showed significant reductions in liver enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP), total cholesterol, triglycerides, fasting blood sugar, insulin levels, and body mass index. Participants also showed improved insulin sensitivity, suggesting that flavonoids may help manage early metabolic dysfunction linked to fatty liver.
Despite these improvements, the study found limited effects on inflammation and liver fibrosis, which are key indicators of disease progression. While flavonoids lowered markers of liver stress, they did not significantly improve γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT), LDL or HDL cholesterol, or fibrosis scores. Researchers explained that this might be due to differences in study design, dosage, and the specific types of flavonoids used. They also noted that liver fibrosis develops slowly, and many trials were too short to capture meaningful structural changes. For that reason, longer studies using advanced imaging or biopsy assessments are needed to determine whether flavonoids can slow or reverse fibrosis.
In essence, flavonoids appear to be a helpful add-on rather than a replacement for standard NAFLD management. Their strongest benefits seem to be in improving liver enzyme levels, metabolic function, and lipid balance. Researchers emphasize the need for large-scale, long-term clinical trials to confirm the safety, ideal dosage, and potential synergistic effects when used alongside other therapies. For now, incorporating flavonoid-rich foods such as berries, citrus fruits, soy, and green tea could support liver and metabolic health while further research continues.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


