- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
MDS Prosthodontics, Crown and Bridge: Admissions, Dental Colleges, Fees, Syllabus, Eligibility criteria details
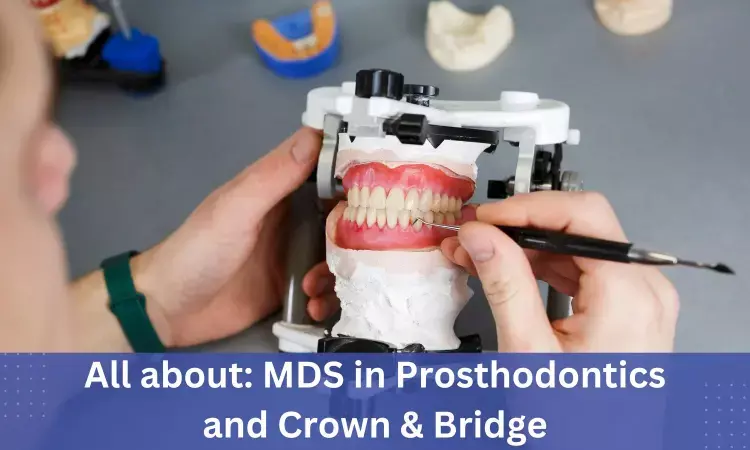
Masters of Dental Surgery (MDS) in Prosthodontics and Crown & Bridge is a post-graduation specialty course for doctors who have graduated in Dental Science and want to work as dentists in India or abroad. They do it after the completion of their BDS (Bachelor of Dental Surgery) or an equivalent qualification recognized by the Dental Council of India and should have obtained permanent registration with the State Dental Council.
The duration of this Postgraduate course is three years, and it focuses on the study of specialization of dental art and science about the restoration and maintenance of oral function, health, comfort, and appearance by the replacement of missing or lost natural teeth and associated tissues either by fixed or removable artificial substitutes.
The course is a full-time course pursued at various accredited institutes/hospitals nationwide. Some top accredited institutes/hospitals offering this course include Lady Hardinge Medical College & Smt. Sucheta Kriplani Hospital, New Delhi; Maulana Azad Dental College & Hospital, New Delhi; Manipal College of Dental Sciences, Manipal, Karnataka, and many more.
Admission to this course is made through the NEET-MDS Entrance exam conducted by the National Board of Examinations in Medical Science (NBEMS), followed by counseling based on the scores of the exam that DGHS/DCI/State Authorities conduct. However, several institutes, such as AIIMS, conduct a university-level entrance examination to offer MDS admission. MDS Admission in the AIIMS, New Delhi, is done based on the AIIMS INI CET. The Dental Council of India (DCI) regulates dental education in the country.
The fee for pursuing MDS varies from accredited institutes/hospital to hospital and may range from Rs. 20,000 to Rs.27 lakhs per year.
After completing their respective course, doctors can join the job market or pursue Fellowship programs recognized by DCI. Candidates can work as a dentist in Government or private hospitals or nursing homes or start their own dental clinics. The average starting salary range is from Rs. 6.5 lakhs to Rs. 18 lakhs per year (approx.).
Through MDS, aspirants can improve the skills of critical analysis, research, and advanced clinical skills. After pursuing this degree, one can become an expert in this field.
What is MDS?
Master of dental surgery (MDS) is a three-year post-graduate program that doctors can pursue after completing Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS).
MDS degree is recognized by the Dental Council of India (DCI) and is offered in various specializations, including:
• Prosthodontics and Crown & Bridge
• Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics
• Periodontology
• Orthodontics & Dentofacial Orthopedics
• Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery
• Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology and Oral Microbiology
• Oral Medicine & Radiology
• Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry
• Public Health Dentistry
MDS focuses on diseases related to the tooth, jaw, and other facial tissues, and dental science deals with maintaining oral health. Moreover, for surgeries such as dental implants, artificial replacements, treating jaw and gum-related diseases and surgeries, correcting misaligned/dispositioned teeth and jaw, treating dental tissues, facial diseases diagnosis and surgeries, and cosmetic treatments.
The required training during under-graduation would help the doctor recognize the community's health needs.
The candidate should regularly attend conferences and workshops to upgrade their knowledge.
Course Highlights
Here are some of the course highlights of the Masters of Dental Surgery:
| Name of Course | MDS Masters of Dental Surgery in Prosthodontics and Crown & Bridge |
| Level | Post-graduate |
| Duration of Course | Three years |
| Course Mode | Full Time |
| Minimum Academic Requirement | Candidates must have a BDS degree from a dental college/institute recognized by the Dental Council India and must have completed their Internship for BDS before taking admission to the MDS course. Some dental colleges mention minimum marks in the qualifying degree examination for admissions to MDS courses, such as 55% aggregate of all subjects in BDS course. |
| Admission Process / Entrance Process / Entrance Modalities | Entrance Exam NEET-MDS AIIMS INI-CET Merit-based Counseling conducted by DCI |
| Course Fees | Rs.20,000 to Rs. 27 lakhs |
| Average Salary | Rs. 6.5 lakhs to Rs. 18 lakhs |
Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility criteria for MDS are defined as the set of rules or minimum prerequisites that aspirants must meet to be eligible for admission, which include:
A candidate for admission to MDS must have a recognized degree of BDS awarded by an Indian University in respect of a recognized Dental College under Section 10(2) of the Dentists Act, 1948 or an equivalent qualification recognized by the Dental Council of India and should have obtained permanent registration with the State Dental Council.
Candidates who possess a PG diploma recognized by the DCI with a duration of 2 years (proposed) in a particular specialty are eligible for admission to MDS in the same specialty and the time will be two years. The syllabus for the two years will be as per the concerned university guidelines.
SELECTION OF POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS:
(1) Students for postgraduate dental courses (MDS) shall be selected strictly based on their academic merit.
(2) For determining the academic merit, the university/institution may adopt any one of the following procedures both for P.G. Diploma and MDS degree courses:
(i) based on merit as determined by a competitive test conducted by the State Government or by the competent authority appointed by the State Government or by the University/group of universities in the same state;
or
(ii) based on merit as determined by a centralized competitive test held at the national level;
or
(iii) based on the individual cumulative performance at the first, second, third & Final B.D.S. examinations, if such studies have been passed from the same university;
or (iv) a combination of (i) and (iii); (iii)
Provided that wherever the entrance test for Postgraduate admissions is held by a State Government or a university or any other authorized examining body, the minimum percentage of marks for eligibility for access to postgraduate Dental courses shall be 50% for general category candidates and 40% for the candidates belonging to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
Provided further that in non-Governmental institutions, fifty percent of the total seats shall be filled by the competent authority and the remaining percent by the institution's management on the basis of merit.
Admission Process:
The admission process contains a few steps to be followed by the candidates for admission to Masters of Dental Surgery. Candidates can view the complete admission process for MDS mentioned below:
The NEET-MDS or National Eligibility Entrance Test for MDS is a national-level postgrad level examination conducted by the NBE for admission to MDS courses in approved/recognized Dental Colleges/ Deemed Universities /Institutes.
These eligibility criteria are decided by the Dental Council of India (DCI) with the approval of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW). The basic requirements to appear for NEET MDS can be checked below: -
Candidates must hold a BDS degree from a recognized institute to fulfill NEET MDS eligibility criteria for 2023.
Provisional/permanent registration with State Dental Council (SDC) or DCI by July 31, 2023.
Completing a one-year compulsory rotatory internship by July 31 of the academic year that a candidate is seeking admission is mandatory.
Common Counselling:
MCC conducts the counseling of NEET MDS 2023 for the admission process to 50% All India Quota seats, deemed/central university seats, ESIC, and AFMC seats.
Jammu and Kashmir do not participate in the central pool quota. Therefore, the counseling for seats in government dental colleges is allotted by the state body responsible.
The authority conducts three rounds of seat allotment for All India quota seats, while a mop-up round will be organized for deemed, central and ESIC colleges. In order to participate in NEET MDS 2023 counseling process, aspirants must secure equal to more than the minimum cut-off percentile.
The qualifiers can participate in the counseling process by registering themselves and providing their preferences for colleges as well as courses.
Based on the choice filled, NEET MDS rank, seat availability in the particular college, reservation criteria, and other factors, the admission to MDS course will be granted.
While the seat allotment process for 50% state quota and seats in private dental colleges will be conducted by the state counseling body as selected by the state government. The respective regulatory bodies will either organize the counseling process in online or offline mode.
NEET MDS admissions in the states include application forms, merit lists, and seat allotment procedures. However, to apply for state MDS admissions, the qualified candidates must fulfill certain eligibility criteria of domicile, age, nationality, and other aspects as laid down by the state counseling authorities.
Fees Structure
The fee structure for MDS varies from accredited institute/hospital to hospital. The fee is generally less for Government Institutes and more for private institutes. The average fee structure for BDS is around Rs. 20,000 to Rs.27 lakhs per year.
Colleges offering Masters of Dental Surgery
There are various accredited institutes/hospitals across India that offer courses for pursuing MDS.
As per the Dental Council of India website, the following accredited institutes/hospitals are offering courses for the academic year 2022-23.
| S.No. | College Name | State | Type | Permitted Seats for Academic Year 2022-23 | ||||||
| 1 | Anil Neerukonda Institute of Dental Sciences, Visakhapatnam | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 2 | C.K.S. Teja Institute of Dental Sciences & Research, Tirupati | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 3 | Drs. Sudha & Nageswara Rao Siddhartha Institute of Dental Sciences, Gannavaram Mandalam | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 4 | G. Pulla Reddy Dental College & Hospital, Kurnool | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 5 | Gitam Dental College & Hospital, Vishakhapatnam | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 7 | Govt. Dental College, RIMS, Kadapa | Andhra Pradesh | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 8 | GSL Dental College & Hospital, Rajahmundry | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 9 | KIMS Dental College, Amalapuram | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 10 | Lenora Institute of Dental Sciences, Rajahmundry | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 11 | Narayana Dental College & Hospital, Nellore | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 12 | Sibar Institute of Dental Sciences, Guntur | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 13 | Sree Sai Dental College & Research Institute, Srikakulam | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 14 | St. Joseph Dental College, Duggirala | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 15 | Vishnu Dental College, Bhimavaram | Andhra Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 16 | Regional Dental College, Guwahati | Assam | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 17 | Buddha Institute of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Kankarbagh, Patna | Bihar | Private |
| ||||||
| 18 | Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Institute of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Patna | Bihar | Private |
| ||||||
| 19 | Mithila Minority Dental College & Hospital, Darbhanga | Bihar | Private |
| ||||||
| 20 | Patna Dental College & Hospital, Patna | Bihar | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 21 | Dr Harvansh Singh Judge Institute of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Chandigarh | Chandigarh | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 22 | Chhattisgarh Dental College & Research Institute, Rajnandgaon | Chhattisgarh | Private |
| ||||||
| 23 | Govt. Dental College, Raipur, Chhattisgarh | Chhattisgarh | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 24 | Maitri College of Dentistry and Research Centre, Durg | Chhattisgarh | Private |
| ||||||
| 25 | New Horizon Dental College & Research Institute, Bilaspur | Chhattisgarh | Private |
| ||||||
| 26 | Rungta College of Dental Sciences & Research, Bhilai | Chhattisgarh | Private |
| ||||||
| 27 | Triveni Institute of Dental Sciences, Hosptial & Research Centre, Bilaspur | Chhattisgarh | Private |
| ||||||
| 28 | Army Hospital (Research and Referral) Delhi Cantt, Delhi | Delhi | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 30 | Maulana Azad Dental College & Hospital, New Delhi | Delhi | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 31 | University College of Medical Sciences, Dilshad Garden | Delhi | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 32 | Goa Dental College & Hospital, Goa | Goa | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 33 | Ahmedabad Dental College & Hospital, Gandhinagar | Gujarat | Private |
| ||||||
| 34 | AMC Dental College, Ahmedabad | Gujarat | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 35 | College of Dental Sciences and Research Centre, Ahmedabad | Gujarat | Private |
| ||||||
| 36 | College of Dental Sciences, Amargadh | Gujarat | Private |
| ||||||
| 37 | Faculty of Dental Science, Dharmsinh Desai University, Nadiad | Gujarat | Private |
| ||||||
| 38 | Goenka Research Institute of Dental Sciences, Gandhinagar | Gujarat | Private |
| ||||||
| 39 | Govt. Dental College & Hospital, Ahmedabad | Gujarat | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 41 | K.M. Shah Dental College & Hospital, Vadodara | Gujarat | Private |
| ||||||
| 42 | Karnavati School of Dentistry, Gandhinagar | Gujarat | Private |
| ||||||
| 43 | Manubhai Patel Dental College & Dental Hospital & SSR General Hospital, Vadodara | Gujarat | Private |
| ||||||
| 44 | Narsinhbhai Patel Dental College & Hospital, Visnagar | Gujarat | Private |
| ||||||
| 45 | D.A.V. Centenary Dental College, Yamuna nagar | Haryana | Private |
| ||||||
| 46 | Jan Nayak Ch. Devi Lal Dental College, Sirsa | Haryana | Private |
| ||||||
| 47 | Maharishi Markandeshwar College of Dental Sciences & Research, Mullana | Haryana | Private |
| ||||||
| 48 | Manav Rachana Dental College, Faridabad | Haryana | Private |
| ||||||
| 49 | PDM Dental College & Research Institute, Jhajjar | Haryana | Private |
| ||||||
| 50 | Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences, Rohtak | Haryana | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 51 | Sri Govind Tricentenary Dental College, Hospital & Research Institute | Haryana | Private |
| ||||||
| 52 | Sudha Rustagi College of Dental Sciences & Research, Faridabad | Haryana | Private |
| ||||||
| 53 | Swami Devi Dyal Hospital & Dental College, Panchkula | Haryana | Private |
| ||||||
| 54 | Bhojia Dental College & Hospital, Nalagarh | Himachal Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 55 | H.P. Govt. Dental College & Hospital, Shimla | Himachal Pradesh | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 56 | Himachal Dental College, Sunder Nagar | Himachal Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 57 | Himachal Institute of Dental Sciences, Poanta Sahib | Himachal Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 59 | Indira Gandhi Government Dental College, Jammu | Jammu & Kashmir | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 60 | Awadh Dental College & Hospital, Jamshedpur | Jharkhand | Private |
| ||||||
| 61 | Hazaribag College of Dental Sciences and Hospital, Hazaribag | Jharkhand | Private |
| ||||||
| 62 | Vananchal Dental College & Hospital, Garhwa | Jharkhand | Private |
| ||||||
| 63 | A.B. Shetty Memorial Institute of Dental Sciences, Mangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 64 | A.J. Institute of Dental Sciences, Mangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 66 | Al-Badar Rural Dental College & Hospital, Gulbarga | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 67 | AME’s Dental College & Hospital, Raichur | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 68 | Bangalore Institute of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 69 | Bapuji Dental College & Hospital, Davangere | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 70 | College of Dental Sciences, Davangere | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 71 | Coorg Institute of Dental Sciences, Virajpat | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 72 | D.A. Pandu Memorial R.V. Dental College, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 73 | Dayanand Sagar College of Dental Sciences, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 74 | Dr Syamala Reddy Dental College, Hospital & Research Centre, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 75 | Farooqia Dental College & Hospital, Mysore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 76 | Govt. Dental College, Bangalore | Karnataka | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 77 | H.K.E. Society's, S. Nijalingappa Institute of Dental Sciences & Research | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 78 | JSS Dental College & Hospital, Mysore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 79 | K.V.G. Dental College & Hospital, Sullia | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 80 | KLE Society’s Institute of Dental Sciences, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 81 | KLE Vishwanath Katti Institute of Dental Sciences, Belgaum | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 82 | Krishnadevaraya College of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 83 | M.R. Ambedkar Dental College & Hospital, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 84 | M.S. Ramaiah Dental College, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 85 | Maaruti College of Dental Sciences & Research Centre, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 86 | Manipal College of Dental Sciences, Mangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 87 | Manipal College of Dental Sciences, Manipal | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 88 | Maratha Mandal’s Dental College & Research Centre, Belgaum | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 89 | Navodaya Dental College, Raichur | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 90 | P.M.N.M. Dental College & Hospital, Bagalkot | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 91 | Rajarajeswari Dental College & Hospital, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 92 | S.B. Patil Dental College & Hospital, Bidar | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 94 | SDM College of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Dharwad | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 95 | Sharavathi Dental College & Hospital, Shimoga | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 96 | Sri Hasanamba Dental College & Hospital, Hassan | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 97 | Sri Rajiv Gandhi College of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 98 | Sri Siddhartha Dental College, Tumkur | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 99 | Srinivas Institute of Dental Sciences, Mangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 100 | Subbaiah Institute of Dental Sciences, Purale, Shimoga | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 101 | The Oxford Dental College, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 102 | V.S. Dental College, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 103 | Vydehi Institute of Dental Sciences & Research, Bangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 104 | Yenepoya Dental College & Hospital, Mangalore | Karnataka | Private |
| ||||||
| 105 | Amrita School of Dentistry, Kochi | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 106 | Annoor Dental College & Hospital, Ernakulam | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 107 | Azeezia College of Dental Sciences & Research, Kollam | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 108 | Educare Institute of Dental Sciences, Malappuram | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 109 | Govt. Dental College, Kottayam | Kerala | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 110 | Govt. Dental College, Kozhikode | Kerala | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 111 | Govt. Dental College, Trivandrum | Kerala | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 112 | Kannur Dental College, kannur | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 113 | KMCT Dental College, Calicut | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 114 | Malabar Dental College & Research Centre, Malappuram | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 115 | Mar Baselios Dental College, Kothamangalam | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 116 | MES Dental College, Malappuram | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 118 | PMS College of Dental Science & Research, Thiruvananthpuram | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 119 | PSM College of Dental Sciences & Research, Trichur | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 120 | Pushpagiri College of Dental Sciences, Tiruvalla | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 121 | Royal Dental College, kerala | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 122 | Sree Anjaneya Medical Trust, Calicut | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 123 | Sri Sankara Dental College, Thiruvananthapuram | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 124 | St. Gregorios Dental College, Ernakulam | Kerala | Private |
| ||||||
| 125 | Bhabha College of Dental Sciences, Bhopal | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 126 | College of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Indore | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 127 | College of Dentistry- Indore | Madhya Pradesh | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 128 | Hitkarini Dental College & Hospital, Jabalpur | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 129 | Index Institute of Dental Sciences, Indore | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 130 | Maharana Pratap College of Dentistry & Research Centre, Gwalior | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 131 | Mansarover Dental College, Bhopal | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 132 | Modern Dental College & Research Centre, Indore | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 133 | People’s Dental Academy, Bhopal | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 134 | Peoples College of Dental Sciences & Research Centre, Bhopal | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 135 | Rishiraj College of Dental Sciences & Research Centre, Bhopal | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 136 | RKDF Dental College & Research Centre, Bhopal | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 137 | Sri Aurobindo College of Dentistry, Indore | Madhya Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 138 | Aditya Dental College, Beed | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 139 | Annasaheb Chudaman Patil Memorial Dental College, Dhule | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 140 | Armed Forces Medical College, Pune-1 | Maharashtra | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 141 | Bharati Vidyapeeth Dental College & Hospital, Navi Mumbai | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 142 | Bharati Vidyapeeth Dental College & Hospital, Pune | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 143 | Bharati Vidyapeeth Dental College & Hospital, Sangli | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 144 | Chatrapati Shahu Maharaj Shikshan Sanstha’s Dental College & Hospital, Aurangabad | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 146 | Dr. D.Y. Patil Dental College & Hospital, Pune | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 147 | Dr. Hedgewar Smruti Rugna Seva Mandals Dental College & Hospital, Hingoli | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 148 | Dr. Rajesh Ramdasji Kambe Dental College & Hospital, Akola | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 149 | Govt. Dental College & Hospital, Aurangabad | Maharashtra | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 150 | Govt. Dental College & Hospital, Mumbai | Maharashtra | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 151 | Govt. Dental College & Hospital, Nagpur | Maharashtra | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 152 | Late Shri Yashwantrao Chavan Memorial Medical & Rural Development Foundation's Dental College & Hospital, Ahmednagar | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 153 | M.A. Rangoonwala College of Dental Sciences & Research Centre, Pune | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 154 | Maharashtra Institute of Dental Sciences & Research (Dental College) | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 155 | Mahatma Gandhi Missions Dental College & Hospital, Kamothe, Navi Mumbai | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 156 | Mahatma Gandhi Vidya Mandir’s Dental College & Hospital, Nashik | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 157 | Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai | Maharashtra | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 158 | Padmashree Dr. D.Y. Patil Dental College & Hospital, Navi Mumbai | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 159 | Pandit Dindayal Upadhyay Dental College, Solapur | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 160 | Rural Dental College, Loni | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 161 | S.M.B.T. Dental College & Hospital, Amrutnagar | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 162 | Saraswati Danwantri Dental College & Hospital, Parbhani | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 163 | School of Dental Sciences, Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Karad | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 164 | Sharad Pawar Dental College & Hospital, Wardha | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 165 | Sinhgad Dental College & Hospital, Pune | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 166 | SMBT Institute of Dental Sciences and Research, Nandihills, Nashik | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 167 | Swargiya Dadasaheb Kalmegh Smruti Dental College & Hospital, Nagpur | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 168 | Tatyasaheb Kore Dental College & Research Centre, New Pargaon | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 169 | Terna Dental College & Hospital, Navi Mumbai | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 170 | Vasantdada Patil Dental College and Hospital, Sangli | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 171 | Vidarbha Youth Welfare Society’s Dental College & Hospital, Amravati | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 172 | VSPM’s Dental College & Research Centre, Nagpur | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 173 | Yerala Medical Trust & Research Centre’s Dental College & Hospital, Navi Mumbai | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 174 | Yogita Dental College & Hospital, Ratnagiri | Maharashtra | Private |
| ||||||
| 175 | Hi-Tech Dental College & hospital, Bhubaneswar | Orissa | Private |
| ||||||
| 178 | S.C.B. Dental College & Hospital, Cuttack | Orissa | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 179 | Indira Gandhi Institute of Dental Sciences, Pondicherry | Pondicherry | Private |
| ||||||
| 180 | Mahatma Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences, Puducherry | Pondicherry | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 181 | Mahe Institute of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Mahe | Pondicherry | Private |
| ||||||
| 182 | Sri Venkateshwara Dental College, Puducherry | Pondicherry | Private |
| ||||||
| 184 | Baba Jaswant Singh Dental College Hospital & Research Institute, Ludhiana | Punjab | Private |
| ||||||
| 185 | Christian Dental College, Ludhiana | Punjab | Private |
| ||||||
| 186 | Dasmesh Institute of Research & Dental Sciences, Faridkot | Punjab | Private |
| ||||||
| 187 | Desh Bhagat Dental College & Hospital, Mandi Gobindgarh | Punjab | Private |
| ||||||
| 188 | Genesis Institute of Dental Sciences & Research, Ferozepur | Punjab | Private |
| ||||||
| 189 | Govt. Dental College & Hospital, Patiala | Punjab | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 190 | Guru Nanak Dev Dental College & Research Institute, Sunam | Punjab | Private |
| ||||||
| 191 | Luxmi Bai Institute of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Patiala | Punjab | Private |
| ||||||
| 192 | National Dental College & Hospital, Gulabgarh | Punjab | Private |
| ||||||
| 193 | Pb. Govt. Dental College & Hospital, Amritsar | Punjab | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 194 | Sri Guru Ram Das Institute of Dental Sciences & Research, Amritsar | Punjab | Private |
| ||||||
| 195 | Darshan Dental College & Hospital, Udaipur | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 196 | Daswani Dental College & Research Centre, Kota | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 197 | Geetanjali Dental & Research Institute, Udaipur | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 198 | Govt. Dental College & Hospital, Jaipur | Rajasthan | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 199 | Jaipur Dental College, Jaipur | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 200 | Jodhpur Dental College General Hospital, Jodhpur | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 201 | Maharaja Ganga Singh Dental College & Research Centre, Sri Ganganagar | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 202 | Mahatma Gandhi Dental College & Hospital, Sitapura, Jaipur | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 203 | NIMS Dental College, Jaipur | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 204 | Pacific Dental College & Research Centre | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 205 | Pacific Dental College, udaipur | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 206 | Rajasthan Dental College & Hospital, Jaipur | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 207 | Surendera Dental College & Research Institute, Sri Ganganagar | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 208 | Vyas Dental College & Hospital, Jodhpur | Rajasthan | Private |
| ||||||
| 209 | Adhiparasakthi Dental College & Hospital, Melmaruvathur | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 211 | Chettinad Dental College & Research Institute, Kancheepuram | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 212 | CSI College of Dental Sciences & Research, Madurai | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 213 | Faculty of Dentistry, Rajah Muthiah Dental College & Hospital, Annamalai Nagar | Tamil Nadu | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 214 | JKK Natrajah Dental College & Hospital, Komarapalayam | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 215 | K.S.R. Institute of Dental Science & Research, Tiruchengode | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 216 | Karpaga Vinayaga Institute of Dental Sciences, Kanchipuram | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 217 | Madha Dental College & Hospital, Kundrathur | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 218 | Meenakshi Ammal Dental College & Hospital, Chennai | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 219 | R.V.S. Dental College & Hospital, Sulur | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 220 | Ragas Dental College & Hospital, Chennai | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 221 | Rajas Dental College & Hospital, Kavalkinaru Jn | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 222 | S.R.M. Dental College, Ramapuram, Chennai | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 224 | Saveetha Dental College & Hospital, Chennai | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 225 | Sree Balaji Dental College & Hospital, Narayanpuram | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 226 | Sree Mookambika Institute of Dental Sciences, Kulasekharam | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 227 | Sri Ramachandra Dental College & Hospital, Porur | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 228 | Sri Ramakrishna Dental College & Hospital, Coimbatore | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 229 | Sri Venkateswara Dental College & Hospital, Kancheepuram | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 230 | SRM Kattankulathur Dental College & Hospital, Kanchipuram | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 231 | Tagore Dental College & Hospital, Chennai | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 232 | Tamil Nadu Government Dental College & Hospital, Chennai | Tamil Nadu | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 233 | Thai Moogambigai Dental College & Hospital, Chennai | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 234 | Vinayaka Mission’s Sankarachariyar Dental College, Salem | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 235 | Vivekanandha Dental College for Women, Elayampalayam | Tamil Nadu | Private |
| ||||||
| 236 | Army College of Dental Sciences, Secunderabad | Telangana | Private |
| ||||||
| 237 | Government Dental College and Hospital, Hyderabad | Telangana | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 238 | Kamineni Institute of Dental Sciences, Nalgonda | Telangana | Private |
| ||||||
| 240 | Malla Reddy Institute of Dental Sciences,Hyderabad | Telangana | Private |
| ||||||
| 241 | Mamata Dental College, Khamam | Telangana | Private |
| ||||||
| 242 | Meghna Institute of Dental Sciences, Nizamabad | Telangana | Private |
| ||||||
| 245 | Sri Balaji Dental College, Hyderabad | Telangana | Private |
| ||||||
| 246 | Sri Sai College of Dental Surgery, Vikarabad | Telangana | Private |
| ||||||
| 247 | Sri Venkata Sai Institute of Dental Sciences, Hyderabad | Telangana | Private |
| ||||||
| 248 | Babu Banarasi Das College of Dental Sciences, Lucknow | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 249 | Career Institute of Dental Sciences & Hospital, Lucknow | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 250 | Chandra Dental College & Hospital, safedabad | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 251 | D.J. College of Dental Sciences & Research, Modi Nagar | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 252 | Dental College Azamgarh | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 253 | Dr. Ziauddin Ahmad Dental College, Aligarh | Uttar Pradesh | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 254 | Faculty of Dental Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi | Uttar Pradesh | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 255 | Faculty of Dental Sciences, Lucknow | Uttar Pradesh | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 256 | I.T.S. Centre for Dental Studies & Research, Ghaziabad | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 257 | I.T.S. Dental College, Hospital & Research Centre, Gr. Noida | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 258 | Inderprastha Dental College & Hospital, Ghaziabad | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 259 | Institute of Dental Sciences, Bareilly | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 260 | Institute of Dental Studies & Technology, Modinagar | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 261 | K.D. Dental College, Mathura | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 262 | Kalka Dental College & Hospital, Meerut | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 263 | Kothiwal Dental College & Research Centre, Moradabad | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 264 | Rama Dental College, Hospital & Research Centre, Kanpur | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 265 | Santosh Dental College & Hospital, Ghaziabad | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 266 | Saraswati Dental College, Lucknow | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 267 | Sardar Patel Post Graduate Institute of Dental & Medical Sciences, Lucknow | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 268 | School of Dental Sciences, Greater Noida | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 269 | Shree Bankey Bihari Dental College & Research Centre, Masuri | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 270 | Subharati Dental College, Meerut | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 271 | Teerthanker Mahaveer Dental College & Research Centre, Moradabad | Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| ||||||
| 273 | Seema Dental College & Hospital, Rishikesh | Uttrakhand | Private |
| ||||||
| 274 | Uttaranchal Dental College & Medical Research Institute, Dehradun | Uttrakhand | Private |
| ||||||
| 275 | Dr. R. Ahmed Dental College & Hospital, Calcutta | West Bengal | Govt. |
| ||||||
| 276 | Gurunanak Institute of Dental Science & Research, Kolkatta | West Bengal | Private |
| ||||||
| 277 | Haldia Institute of Dental Sciences and Research, Banbishnupur | West Bengal | Private |
|
Syllabus
MDS in Prosthodontics and Crown and Bridge is a three-year post-graduation course that provides training in dental surgery.
According to the Dental Council of India's MDS Course Regulations 2017, the Syllabus for MDS in Prosthodontics and Crown and Bridge is as follows:
Syllabus
Part-I
To train the dental graduates so as to ensure a higher level of competence in both general and specialty areas of Prosthodontics and prepare candidates with teaching, research and clinical abilities including prevention and aftercare in Prosthodontics – removable dental prosthodontics, fixed dental prosthodontics (Crown &Bridge), implantology, maxillofacial prosthodontics, and esthetic dentistry.
GENERAL OBJECTIVES OF THE COURSE:
Training program for dental graduates in Prosthetic dentistry– removable dental prosthodontics, fixed dental prosthodontics (Crown & Bridge), implantology, maxillofacial
prosthodontics and esthetic dentistry and Crown & Bridge including Implantology is structured to achieve knowledge and skill in theoretical and clinical laboratory, attitude,
communicative skills and ability to perform research with a good understanding of social, cultural, educational and environmental background of the society.
• To have adequate acquired knowledge and understanding of applied basic and systemic medical sciences, both in general and in particularly of head and neck region.
• The postgraduates should be able to provide Prosthodontic therapy for patients with competence and working knowledge with understanding of applied medical, behavioral and clinical science, that are beyond the treatment skills of the general BDS graduates and MDS graduates of other specialties,
• To demonstrate evaluative and judgment skills in making appropriate decisions regarding prevention, treatment, aftercare and referrals to deliver comprehensive care to patients.
KNOWLEDGE:
The candidate should possess knowledge of applied basic and systemic medical sciences.
• On human anatomy, embryology, and histology, applied in general and particularly to head and neck, Physiology & Biochemistry, Pathology Microbiology & virology; health and
diseases of various systems of the body (systemic) principles in surgery and medicine, pharmacology, nutrition, behavioral science, age changes, genetics, Immunology, Congenital defects & syndromes and Anthropology, Bioengineering, Bio-medical & Biological Principles
• The student shall acquire knowledge of various Dental Materials used in the specialty and be able to provide an appropriate indication, understand the manipulation characteristics,
compare with other materials available, be adept with recent advancements of the same.
• Students shall acquire knowledge and practice of history taking, Diagnosis, treatment planning, prognosis, record maintenance of oral, craniofacial and systemic region.
• Ability for comprehensive rehabilitation concept with pre prosthetic treatment plan including surgical re-evaluation and prosthodontic treatment planning, impressions, jaw
relations, utility of face bows, articulators, selection and positioning of teeth, teeth arrangement for retention, stability, esthetics, phonation, psychological comfort, fit and insertion.
• Instructions for patients in after care and preventive Prosthodontics and management of failed restorations shall be possessed by the students.
• Understanding of all the applied aspects of achieving physical, psychological well-being of the patients for control of diseases and / or treatment related syndromes with the
patient satisfaction and restoring function of Cranio mandibular system for a quality life of a patient.
• Ability to diagnose and plan treatment for patients requiring Prosthodontic therapy
• Ability to read and interpret radiographs, and other investigations for the purpose of diagnosis and treatment planning.
• The theoretical knowledge and clinical practice shall include principles involved for support, retention, stability, esthetics, phonation, mastication, occlusion, behavioral,
psychological, preventive and social aspects of Prosthodontics science of Oral and Maxillofacial Prosthodontics and Implantology
• Tooth and tooth surface restorations, Complete denture Prosthodontics, removable partial denture Prosthodontics, fixed prosthodontics and maxillofacial and Craniofacial
Prosthodontics, implants and implant supported Prosthodontics, T.M.J. and occlusion, craniofacial esthetics, and biomaterials, craniofacial disorders, problems of psychogenic origin.
• Should have knowledge of age changes, geriatric psychology, nutritional considerations and prosthodontic therapy in the aged population.
• Should have ability to diagnose failed restoration and provide prosthodontic therapy and after care.
• Should have essential knowledge on ethics, laws, and Jurisprudence and Forensic Odontology in Prosthodontics.
• Should know general health conditions and emergency as related to prosthodontics treatment like allergy of various materials and first line management of aspiration of prosthesis
• Should identify social, cultural, economic, environmental, educational and emotional determinants of the patient and consider them in planning the treatment.
• Should identify cases, which are outside the area of his specialty / competence, refer them to appropriate specialistsand perform interdisciplinary case management.
• To advice regarding case management involving surgical and interim treatment
• Should be competent in specialization of team management in craniofacial prosthesis design.
• To have adequate acquired knowledge, and understanding of applied basic, and systemic medical science knowledge in general and in particular to head and neck regions.
• Should attend continuing education programmes, seminars and conferences related to Prosthodontics, thus updating himself/herself.
• To teach and guide his/her team, colleagues and other students.
• Should be able to use information technology tools and carry out research both in basic and clinical areas, with the aim of publishing his/ her work and presenting his/her work at various scientific forums.
• Should have an essential knowledge of personal hygiene, infection control, prevention of cross infection and safe disposal of waste, keeping in view the risk of transmission of potential communicable and transmissible infections like Hepatitis and HIV.
• Should have an ability to plan and establish Prosthodontics clinic/hospital teaching department and practice management.
• Should have a sound knowledge (of the applications in pharmacology, effects of drugs on oral tissues and systems of body and in medically compromised patients.
SKILLS:
• The candidate should be able to examine the patients requiring Prosthodontic therapy, investigate the patient systemically, analyze the investigation results, radiographs, diagnose the ailment, plan the treatment, communicate it with the patient and execute it.
• To understand the prevalence and prevention of diseases of the craniomandibular system related to prosthetic dentistry.
• The candidate should be able to restore lost functions of a stomatognathic system like mastication, speech, appearance and psychological comforts by understanding biological, biomedical, and bioengineering principles and systemic conditions of the patients to provide quality health care in the craniofacial regions.
• The candidate should be able to demonstrate good interpersonal, and communication skills and a team approach in interdisciplinary care by interacting with other specialties including medical specialty for planned team management of patients for craniofacial & oral acquired and congenital defects, temporomandibular joint syndromes, esthetics, Implants supported Prosthetics and problems of Psychogenic origins.
• Should be able to demonstrate the clinical competence necessary to carry out appropriate treatment at higher level of knowledge, training and practice skills currently available in their specialty area with a patient centered approach.
• Should be able to interpret various radiographs like IOPA, OPG, CBCT and CT. Should and be able to plan and modify treatment plan based on radiographic findings
• Should be able to critically appraise articles published and understand various components of different types of articles and be able to gather the weight of evidence from the same
• To identify target diseases and create awareness amongst the population regarding Prosthodontic therapy.
• To perform Clinical and Laboratory procedures with a clear understanding of biomaterials, tissue conditions related to prosthesis and have required dexterity & skill for performing clinical and laboratory all procedures in fixed, removable, implant, maxillofacial, TMJ and esthetics Prosthodontics.
• To carry out necessary adjunctive procedures to prepare the patient before prosthesis like tissue preparation and preprosthetic surgery and to prepare the patient before prosthesis / prosthetic procedures
• To understand the demographic distribution and target diseases of the Cranio mandibular region related to Prosthodontics.
ATTITUDES:
• To adopt ethical principles in Prosthodontic practice, Professional honesty, credibility and integrity are to be fostered. Treatment to be delivered irrespective of social status, caste, creed or religion of patient.
• Should be willing to share the knowledge and clinical experience with professional colleagues.
• Should develop an attitude towards quality, excellence, non-compromising in treatment.
• Should be able to self-evaluate, reflect and improve on their own.
• Should pursue research in a goal to contribute significant, relevant and useful information, concept or methodology to the scientific fraternity.
• Should be able to demonstrate evidence-based practice while handling cases
• Should be willing to adopt new methods and techniques in prosthodontics from time to time based on scientific research, which are in patient’s best interest.
• Should respect patient’s rights and privileges, including patient’s right to information and right to seek second opinion.
COMMUNICATIVE ABILITIES:
• To develop communication skills, in particular and to explain treatment options available in the management.
• To provide leadership and get the best out of his / her group in a congenial working atmosphere.
• Should be able to communicate in simple understandable language with the patient and explain the principles of prosthodontics to the patient. He/She should be able to guide and counsel the patient with regard to various treatment modalities available.
• To develop the ability to communicate with professional colleagues through various media like Internet, e-mails, videoconferences etc. to render the best possible treatment. Should demonstrate good explanatory and demonstrating ability as a teacher in order to facilitate learning among students
COURSE CONTENTS:
The course content has been identified and categorized as essential knowledge given below.
ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE:
The topics to be considered are Applied Basic Sciences, Oral and Maxillofacial
Prosthodontics and Implantology
APPLIED BASIC SCIENCES:
Should develop thorough knowledge on the applied aspects of Anatomy, Embryology, Histology particularly head and neck, Physiology, Biochemistry, Pathology, Microbiology,
Virology, Pharmacology, Health and systematic diseases principles in surgery medicine and Anesthesia, Nutrition, Behavioral sciences, age changes, genetics, Dental Material
Science, congenital defects and Syndromes and Anthropology, Biomaterial Sciences, Bio-engineering and Bio-medical and Research Methodology as related to Masters
degree in Prosthodontics and Crown & Bridge including Implantology It is desirable to have adequate knowledge in Bio-statistics, Research Methodology and
use of computers to develop necessary teaching skills in the specialty of Prosthodontics including crown and bridge.
APPLIED ANATOMY OF HEAD AND NECK:
General Human Anatomy –Gross Anatomy, anatomy of Head and Neck in detail:Cranial and facial bones, TMJ and function, muscles of mastication and facial expression,
muscles of neck and back including muscles of deglutition and tongue, arterial supply and venous drainage of the head and neck, anatomy of the Para nasal sinuses in relation to
the Vth cranial nerve. General considerations of the structure and function of the brain, brief considerations of V, VII, XI, XII, cranial nerves and autonomic nervous system of the
head and neck. The salivary glands, Pharynx, Larynx Trachea, Oesophagus, Functional Anatomy of masticatory muscles, Deglutition, speech, respiration, and circulation, teeth
eruption, morphology, occlusion and function. Anatomy of TMJ, its movements and myofacial pain dysfunction syndrome.
Embryology –Development of the face, tongue, jaws, TMJ, Paranasal sinuses,pharynx, larynx, trachea, esophagus, Salivary glands, Development of oral and Para oral tissues
including detailed aspects of tooth formation.
Growth & Development –Facial form and Facial growth and development overview of Dentofacial growth process and physiology from foetal period to maturity and old age,.
General physical growth, functional and anatomical aspects of the head, changes in craniofacial skeletal development, relationship between development of the dentition and facial growth.
Dental Anatomy –Anatomy of primary and secondary dentition, concept of occlusion,mechanism of articulation, and masticatory function. Detailed structural and
functional study of the oral and Para oral tissues, normal occlusion, development of occlusion in deciduous mixed and permanent dentitions, root length, root configuration & tooth-numbering systems.
Histology –histology of enamel, dentin, Cementum, periodontal ligament and alveolarbone, pulpal anatomy, histology and biological consideration. Salivary glands and
Histology of epithelial tissues including glands.
Histology of general and specific connective tissue including bone, , Salivary glands,
Histology of skin, oral mucosa, respiratory mucosa, connective tissue, bone, cartilage, cellular elements of blood vessels, blood, lymphatics, nerves, muscles, tongue and tooth
Cell biology –Brief study of the structure and function of the mammalian cell
Components of the cell and functions of various types of cells and their consequences with tissue injury
APPLIED PHYSIOLOGY AND NUTRITION :
Introduction, Mastication, deglutition, digestion and assimilation, Homeostasis, fluid and electrolyte balance, blood composition, volume, function, blood groups and hemorrhage, Blood transfusion, circulation, Heart, Pulse, Blood pressure, capillary and lymphatic circulation. Shock, respiration, control, anoxia, hypoxia, asphyxia, artificial respiration.
Endocrine glands in particular reference to pituitary, parathyroid and thyroid glands and sex hormones. Role of calcium and Vit D in growth and development of teeth, bone and jaws. Role of Vit. A, C and B complex in oral mucosal and periodontal health. Physiology and function of the masticatory system. Speech mechanism, mastication, swallowing and deglutition mechanism, salivary glands and Saliva
Endocrines – General principles of endocrine activity and disorders relating to pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, parathyroid, adrenals, gonads, including pregnancy and lactation.
Physiology of saliva, urine formation, normal and abnormal constituents, Physiology of pain, Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, neuromuscular co-ordination of the stomatognathic system.
Applied Nutrition – General principles, balanced diet, effect of dietary deficiencies and starvation, Diet, digestion, absorption, transportation and utilization & diet for elderly patients.
APPLIED BIOCHEMISTRY:
General principles governing the various biological activities of the body, such as osmotic pressure, electrolytic dissociation, oxidation-reductionCarbohydrates, proteins, liquids and their metabolism, Enzymes, Vitamins, and minerals, Hormones, Blood, Metabolism of inorganic elements, Detoxification in the body & anti metabolites.
APPLIED PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS:
Dosage and mode of administration of drugs. Action and fate of drugs in the body, Drug addiction, tolerance and hypersensitive reactions, Drugs acting on the central nervous system, general anesthetics hypnotics, analeptics and tranquilizers. Local anesthetics, Chemotherapeutics and antibiotics, Antitubercular and anti syphilitic drugs, Analgesics and antipyretics, Antiseptics, styptics, Sialogogues and antisialogogues, Haematinics,
Cortisones, ACTH, insulin and other antidiabetics vitamins: A, D, B – complex group C, K etc. Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy. Drug regime for antibiotic prophylaxis and infectious endocarditis and drug therapy following dental surgical treatments like placement of implants, pre and peri prosthetic surgery
APPLIED PATHOLOGY:
Inflammation, repair and degeneration, Necrosis and gangrene, Circulatory disturbances, Ischaemia, hyperaemia, chronic venous congestion, oedema, thrombosis, embolism and infarction. Infection and infective granulomas, Allergy and hypersensitive reactions,
Neoplasms; Classification of tumors, Carcinogenesis, characteristics of benign and malignant tumors, spread of tumors. Applied histo pathology and clinical pathology.
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY:
Immunity, knowledge of organisms commonly associated with diseases of the oral cavity (morphology cultural characteristics etc) of strepto, staphylo, , Clostridia group of organisms, Spirochaetes, organisms of tuberculosis, leprosy, diphtheria, actinomycosis and moniliasis etc. Virology, Cross infection control, sterilization and hospital waste management
APPLIED ORAL PATHOLOGY:
Developmental disturbances of oral and Para oral structures, Regressive changes of teeth, Bacterial, viral and mycotic infections of the oral cavity. Dental caries, diseases of pulp and periapical tissues, Physical and chemical injuries of the oral cavity, oral manifestations of metabolic and endocrine disturbances, Diseases of the blood and blood forming organism in relation to the oral cavity, Periodontal diseases, Diseases of the skin, nerves and muscles in relation to the Oral cavity.
LABORATORY DETERMINATIONS:
Blood groups, blood matching, R.B.C. and W.B.C. count, Bleeding and clotting time, PT, PTT and INR Smears and cultures – urine analysis and culture. Interpretation of RBS, Glycosylated Hb, GTT
BIOSTATISTICS:
Characteristics and limitations of statistics, planning of statistical experiments, sampling, collection, classification and presentation of data (Tables, graphs, pictograms etc) & Analysis of data, parametric and non parametric tests
Introduction to Biostatistics - Scope and need for statistical application to biological data. Definition of selected terms – scale of measurements related to statistics, Methods of collecting data, presentation of the statistical diagrams and graphs.
Frequency curves, mean, mode of median, Standard deviation and co-efficient of variation, Correlation – Co-efficient and its significance, Binominal distributions normal distribution and Poisson’s distribution, Tests of significance.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY:
Understanding and evaluating dental research, scientific method and the behavior of scientists, understanding to logic – inductive logic – analogy, models, authority, hypothesis and causation,. Measurement and Errors of measurement, presentation of results, Reliability, Sensitivity and specificity diagnosis tests and measurements,
Research Strategies, Observation, Correlation, Experimentation and Experimental design. Logic of statistical in(ter)ferences, balance judgements, judgement under uncertainty, clinical vs., scientific judgement, problems with clinical judgement, forming scientific judgements, the problem of contradictory evidence, citation analysis as a Means of literature evaluation, influencing judgement :
Protocol writing for experimental, observational studies, survey including hypothesis, PICO statement, aim objectives, sample size justification, use of control/placebo, standardization techniques, bias and its elimination, blinding, evaluation, inclusion and exclusion criteria.
APPLIED RADIOLOGY:
Introduction, radiation, background of radiation, sources, radiation biology, somatic damage, genetic damage, protection from primary and secondary radiation, Principles of X-ray production, Applied principles of radio therapy and after care.
ROENTGENOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUES:
Intra oral, extra oral roentgenography, Methods of localization digital radiology and ultra sounds. Normal anatomical landmarks of teeth and jaws in radiograms, temporomandibular joint radiograms, neck radiograms.
Use of CT and CBCT in prosthodontics
APPLIED MEDICINE:
Systemic diseases and (its) their influence on general health and oral and dental health.
Medical emergencies like syncope, hyperventilation, angina, seizure, asthma and allergy/anaphylaxis in the dental offices – Prevention, preparation, medico legal consideration, unconsciousness, respiratory distress, altered consciousness, seizures, drug related emergencies, chest pain, cardiac arrest, premedication, prophylaxis and management of ambulatory patients, resuscitation, applied psychiatry, child, adult and senior citizens.
APPLIED SURGERY & ANESTHESIA:
General principles of surgery, wound healing, incision wound care, hospital care, control of hemorrhage, electrolyte balance. Common bandages, sutures, splints, shifting of critically ill patients, prophylactic therapy, bone surgeries, grafts, etc, surgical techniques, nursing assistance, and anesthetic assistance.
Principles in speech therapy, surgical and radiological craniofacial oncology, applied surgical ENT and ophthalmology.
APPLIED PLASTIC SURGERY:
Applied understanding and assistance in programs of plastic surgery for prosthodontics therapy.
APPLIED DENTAL MATERIALS:
• Students should have understanding of all materials used for treatment of craniofacial disorders – Clinical, treatment, and laboratory materials, associated materials, technical considerations, shelf life, storage, manipulations, sterilization, and waste management.
• Students shall acquire knowledge of testing biological, mechanical and other physical properties of all materials used for the clinical and laboratory procedures in prosthodontic therapy.
• Students shall acquire full knowledge and practice of Equipments, instruments, materials, and laboratory procedures at a higher level of competence with accepted methods.
All clinical practices shall involve personal and social obligation of cross infection control, sterilization and waste management.
ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL PROSTHODONTICS AND IMPLANTOLOGY:
I. NON-SURGICAL AND SURGICAL METHODS OF PROSTHODONTICS AND IMPLANTOLOGY
a. Prosthodontic treatment for completely edentulous patients – Complete dentures, immediate complete dentures, single complete dentures, tooth supported complete dentures & Implant supported Prosthesis for completely edentulous patients for typical and atypical cases
- b. Prosthodontic treatment for partially edentulous patients: - Clasp-retained acrylic and cast partial dentures, transitional dentures, immediate dentures, intra coronal and extra coronal precision attachments retained partial dentures & maxillofacial prosthesis for typical and atypical cases
- Prosthodontic treatment for edentulous patients: - Complete Dentures and Implant supported Prosthesis.
- Complete Denture Prosthesis – Definitions, terminologies, G.P.T., Boucher’s clinical dental terminology
- Scope of Prosthodontics – The Cranio Mandibular system and its functions, the reasons for loss of teeth, consequences of loss of teeth and treatment modality with various restorations and replacements
a) Edentulous Predicament, Biomechanics of the edentulous state,
Supportmechanism for the natural dentition and complete dentures, Biological considerations, Functional and Para functional considerations, Esthetic, behavioral and adaptive responses, Temporomandibular joints changes.
b) Effects of aging of edentulous patients –aging population, distribution andedentulism in old age, impact of age on edentulous mouth – Mucosa, Bone, saliva, jaw movements in old age, taste and smell, nutrition, aging, skin and teeth, concern for personal appearance in old age
c) Sequelae caused by wearing complete denture –the denture in the oral environment – Mucosal reactions, altered taste perception, burning mouth syndrome, gagging, residual ridge (reduction) resorption, denture stomatitis, flabby ridge, denture irritation hyperplasia, traumatic Ulcers, Oral cancer in denture wearers, nutritional deficiencies, masticatory ability and performance, nutritional status and masticatory functions.
d) Temporomandibular disorders in edentulous patients –Epidemiology,etiology and management, Pharmacotherapy, Physical modalities, and Bio-behavioral modalities
e) Nutrition Care for the denture wearing patient –Impact of dental status onfood intake, Gastrointestinal functions, nutritional needs and status of older adults, Calcium and bone health, vitamin and herbal supplementation, dietary counseling and risk factor for malnutrition in patients with dentures and when teeth are extracted.
f) Preparing patient for complete denture patients –Diagnosis and treatment planning for edentulous and partially edentulous patients – familiarity with patients, principles of
perception, health questionnaires and identification data, problem identification, prognosis and treatment identification data, problem identification, prognosis and treatment planning contributing history – patient’s history, social information, medical status systemic status with special reference to debilitating diseases, diseases of the joints, cardiovascular disorders, diseases of the skin, neurological disorders, oral malignancies, climacteric, use of drugs, mental health – mental attitude, psychological changes, adaptability, geriatric changes – physiologic, pathological, pathological and intra oral changes. Intra oral health – mucus membrane, alveolar ridges, palate and vestibular sulcus and dental health.
Data collection and recording, visual observation, radiography, palpation, measurement of sulci or fossae, extra oral measurement, the vertical dimension of occlusion, diagnostic casts.
Specific observations – existing dentures, soft tissue health, hard tissue health – teeth, bone
Biomechanical considerations – jaw relations, border tissues, saliva, muscular development – muscle tone, neuromuscular co-ordination, tongue, cheek and lips.
Interpreting diagnostic findings and treatment planning
g) Pre prosthetic surgery –Improving the patients denture bearing areas andridge relations.
h) Non surgical methods –rest for the denture supporting tissues, occlusal correction of the old prosthesis, good nutrition, conditioning of the patients musculature,
i) Surgical methods –Correction of conditions, that preclude optimal prosthetic function – hyperplastic ridge – epulis fissuratum and papillomatosis, frenular attachments and pendulous maxillary tuberosities, ridge augmentation, maxillary and mandibular oral implants, corrections of congenital deformities, discrepancies in jaw size, relief of pressure on the mental foramen, enlargement of denture bearing areas, vestibuloplasty, ridge augmentation, replacement of tooth roots with Osseo integrated denture implants.
j) Immediate Denture –Advantages, Disadvantages, Contraindications,Diagnosis, treatment planning and Prognosis, Explanation to the patient, Oral examinations,
Examination of existing prosthesis, Tooth modification, Prognosis, Referrals/adjunctive care, oral prophylaxis and other treatment needs. First visit, preliminary impressions and diagnostic casts, management of loose teeth, custom trays, final impressions and master casts, two tray or sectional custom impression tray, location of posterior limit and jaw relation records, setting of the posterior denture teeth / verifying jaw relations and the patient try in.
Laboratory phase, setting of anterior teeth, Wax contouring, flasking and boil out, processing and finishing, surgical templates, surgery and immediate denture insertion, post operative care and patient instructions, subsequent service for the patient on the immediate denture.
k) Over dentures (tooth supported complete dentures)–indications andtreatment planning, advantages and disadvantages, selection of abutment teeth, loss of abutment teeth, tooth supported complete dentures. Non-coping abutments, abutment with copings, abutments with attachments, submerged vital roots, preparations of the retained teeth.
l) Single Dentures: Single Mandibular denture to oppose natural maxillaryteeth, single complete maxillary denture to oppose natural Mandibular teeth to oppose a partially edentulous Mandibular arch with fixed prosthesis, partially edentulous
Mandibular arch with removable partial dentures. Opposing existing complete dentures, preservation of the residual alveolar ridge, necessity for retaining maxillary teeth and preventing mental trauma.
m) Art of communication in the management of the edentulous predicament – Communication–scope, a model of communication, why communication is important?
What are the elements of effective communication? special significance of doctor / patient communication, doctor behavior, The iatro sedative (doctor & act of making calm) recognizing and acknowledging the problem, exploring and identifying the problem, interpreting and explaining the problem, offering a solution to the problem for mobilizing their resources to operate in a most efficient way, recognizing and acknowledging the problem, interpreting and explaining the problem, offering a solution to the problem.
n) Materials prescribed in the management of edentulous patients - Denture base materials, General requirements of biomaterials for edentulous patients, requirement of an ideal denture base, chemical composition of denture base resins, materials used in the fabrication of prosthetic denture teeth, requirement of prosthetic denture teeth,denture lining materials and tissue conditioners, cast metal alloys as denture bases – base metal alloys.
o) Articulators – Evolution of concepts, Classification, selection, limitations, precision, accuracy andsensitivity, and Functions of the articulator and their uses. Recent advancements including virtual articulator
p) Fabrication of complete dentures –complete denture impressions–muscles of facial expressions and anatomical landmarks, support, retention, stability, aims and objectives of preservation, support, stability, aesthetics, and retention. Impression materials and techniques – need of 2 impressions the preliminary impression and final impressions.
Developing an analogue / substitute for the maxillary denture bearing area – anatomy of supporting structures – mucous membrane, hard palate, residual ridge, shape of the supporting structure and factors that influence the form and size of the supporting bones, incisive foramen, maxillary tuberosity, sharp spiny process, torus palatinus, Anatomy of peripheral or limiting structures, labial vestibule, Buccal vestibule, vibrating lines. Preliminary and final impressions, impression making, custom tray and refining the custom tray, preparing the tray to secure the final impression, making the final impression, boxing impression and making the casts
Developing an analogue / substitute for the Mandibular denture bearing areaanatomy of supporting structure, crest of the residual ridge, buccal shelf, shape of supporting structure, mylohyoid ridge, mental foramen, genial tubercles, torus mandibularis, Anatomy of peripheral or limiting structure – labial vestibule, Buccal vestibule, lingual border, mylohyoid muscle, retromylohyoid fossa, sublingual gland region, alveolingual sulcus, Mandibular impressions – preliminary impressions, custom tray, refining, preparing the tray-, final impressions.
q) Mandibular movements, Maxillo mandibular relations and concepts of occlusion – Gnathology, identification of shape and location of arch form–Mandibular and maxillary occlusion rims, level of occlusal plane and recording of trail denture base, tests to determine vertical dimension of occlusion, interocclusal & centric relation records. Biological and clinical considerations in making jaw relation records and transferring records from the patients to the articulator, Recording of Mandibular movements – influence of opposing tooth contacts, temporomandibular joint, muscular involvements, neuromuscular regulation of Mandibular motion, the envelope of motion, rest position. Maxillo – Mandibular relations – the centric, eccentric, physiologic rest position, vertical dimension, occlusion, recording methods – mechanical, physiological,
Determining the horizontal jaw relation – Functional graphics, tactile or interocclusal check record method, Orientation / sagittal relation records, Arbitrary / Hinge axis and face bow record, significance and requirement, principles and biological considerations and securing on articulators.
r) Selecting and arranging artificial teeth and occlusion for the edentulous patient – anterior tooth selection, posterior tooth selection, and principles in arrangement of teeth, and factors governing the position of teeth – horizontal & vertical relations. The inclinations and arrangement of teeth for aesthetics, phonetics and mechanics – to concept of occlusion.
s) The Try in –verifying vertical dimension, centric relation, establishment ofposterior palatal seal, creating a facial and functional harmony with anterior teeth, harmony of spaces of individual teeth position, harmony with sex, personality and age of the patient, co-relating aesthetics and incisal guidance.
t) Speech considerations with complete dentures & speech production –structural and functional demands, neuropsychological background, speech production and the roll of teeth and other oral structures – bilabial sounds, labiodental(s) sounds, linguodental sounds, linguoalveolar sound, articulatoric characteristics, acoustic characteristics, auditory characteristics, linguopalatal and linguoalveolar sounds, speech analysis and prosthetic considerations.
u) Waxing contouring and processing the dentures their fit and insertion and after care –laboratory procedure–wax contouring, flasking andprocessing, laboratory remount procedures, selective grinding, finishing and polishing.
Critiquing the finished prosthesis – doctors evaluation, patients evaluation, friends evaluation, elimination of basal surface errors, errors in occlusion, interocclusal records for remounting procedures – verifying centric relation, eliminating occlusal errors.
Special instructions to the patient – appearance with new denture, mastication with new dentures, speaking with new dentures, oral hygiene with dentures, preservation of residual ridges and educational material for patients, maintaining the comfort and health of the oral cavity in the rehabilitated edentulous patients. Twenty-four hours oral examination and treatment and (preventive) Prosthodontic – periodontic recall for oral examination 3 to 4 months intervals and yearly
intervals.
v) Implant supported Prosthesis for partially edentulous patients –Science of Osseo integration, clinical protocol (diagnostic,surgical and prosthetic) for treatment
with implant supported over dentures, managing problems and complications. Implant Prosthodontics for edentulous patients: current and future directions.
Implant supported prosthesis for partially edentulous patients – Clinical and laboratory protocol: Implant supported prosthesis, managing problems and complications
o Introduction and Historical Review
o Biological, clinical and surgical aspects of oral implants
o Diagnosis and treatment planning
o Radiological interpretation for selection of fixtures
o Splints for guidance fort surgical placement of fixtures
o Surgical and Intra oral plastic surgery, if any
o Guided bone and Tissue regeneration consideration for implants fixture.
o Implant supported prosthesis for complete edentulism and partial edentulism
o Occlusion for implant supported prosthesis.
o Peri-implant tissue and Management of peri-implantitis
o Maintenance and after care
o Management of failed restoration.
o Work authorization for implant supported prosthesis – definitive instructions, legal aspects, delineation of responsibility.
Prosthodontic treatment for partially edentulous patients – Removable partial
Prosthodontics –
a. Scope, definition and terminology, Classification of partially edentulous arches - requirements of an acceptable method of classification, Kennedy’s classification,
Applegate’s rules for applying the Kennedy classification
b. Components of RPD –
i) major connector–mandibular and maxillary
ii) minor connectors, design, functions & form and location of major and minor connectors, tissue stops, finishing lines, reaction of tissue to metallic coverage
iii) Rest and rest seats – form of the Occlusal rest and rest seat, interproximal
Occlusal rest seats, internal Occlusal rests, possible movements of partial dentures, support for rests, lingual rests on canines and incisor teeth, incisal rest and rest seat.
iv) Direct retainers- Internal attachments & extracoronal direct retainers. Relative uniformity of retention, flexibility of clasp arms, stabilizing reciprocal clasp, criteria for selecting a given clasp design, the basic principles of clasp design, circumferential clasp, bar clasp, combination clasp and other type of retainers.
v) Indirect Retainers – denture rotation about an axis, factors influencing effectiveness of indirect retainers, forms of indirect retainers, auxiliary Occlusal
rest, canine extensions from Occlusal rests, canine rests, continuous bar retainers and linguoplates, modification areas, rugae support, direct – indirect retention.
(vi) Teeth and denture bases – types, materials, advantages and dis-advantages, indications and contraindications and clinical use.
Principles of removable partial Denture design – Bio mechanical considerations, and the factors influencing after mouth preparations – Occlusal relationship of remaining teeth, orientation of Occlusal plane, available space for restoration, arch integrity, tooth morphology, response of oral structure to previous stress, periodontal conditions, abutment support, tooth supported and
tooth and tissue supported, need for indirect retention, clasp design, need for rebasing, secondary impression, need for abutment tooth modification, type of
major connector, type of teeth selection, patients past experience, method of replacing single teeth or missing anterior teeth.
Difference between tooth supported and tissue supported partial dentures.
Essentials of partial denture design, components of partial denture design, tooth support, tissue support, stabilizing components, guiding planes, use of splint bar for denture support, internal clip attachments, overlay abutment as support for a denture base, use of a component partially to gain support.
c. Education of patient
d. Diagnosis and treatment planning
e. Design, treatment sequencing and mouth preparation
f. Surveying –Description of dental surveyor, purposes of surveying, Aims andobjectives in surveying of diagnostic cast and master cast, Final path of insertion, factors that determine path of insertion and removal, Recording relation of cast to surveyor, measuring amount of retentive area Blocking of master cast – paralleled blockout, shaped blockout, arbitrary blockout and relief.
g. Diagnosis and treatment planning –Infection control and cross infectionbarriers – clinical and laboratory and hospital waste management,
Objectives of prosthodontic treatment, Records, systemic evaluation, Oral examination, preparation of diagnostic cast, interpretation of examination data, radiographic interpretation, periodontal considerations, caries activity, prospective surgical preparation, endodontic treatment, analysis of occlusal factors, fixed restorations, orthodontic treatment, need for determining the design of components, impression procedures and occlusion, need for reshaping remaining teeth, reduction of unfavorable tooth contours, differential diagnosis : fixed or removable partial dentures, choice between complete denture and removable partial dentures, choice of materials
h. Preparation of Mouth for removable partial dentures –Oral surgicalpreparation, conditioning of abused and irritated tissues, periodontal preparation – objectives of periodontal therapy, periodontal diagnosis, control therapy, periodontal surgery.
i. Preparation of Abutment teeth –Classification of abutment teeth, sequenceof abutment preparations on sound enamel or existing restorations, conservative restorations using crowns, splinting abutment teeth, utilization, temporary crowns to be used as abutment.
l. Laboratory Procedures –Duplicating a stone cast, Waxing the partialdenture framework, Anatomic replica patterns, Spruing, investing, burnout, casting and finishing of the partial denture framework, making record bases, occlusion rims, making a stone occlusal template from a functional occlusal record, arranging posterior teeth to an opposing cast or template, arrangement of anterior teeth, waxing and investing the partial denture before processing acrylic resin bases, processing the denture, remounting and occlusal correction to an occlusal template, polishing the denture.
m. Initial placement, adjustment and servicing of the removable partial denture –adjustments to bearing surfaces of denture framework, adjustmentof occlusion in harmony with natural and artificial dentition, instructions to the patient, follow – up services
n. Relining and Rebasing the removable partial denture –Relining toothsupported dentures bases, relining distal extension denture bases, methods of reestablishing occlusion on a relined partial denture.
o. Repairs and additions to removable partial dentures –Broken clasp arms,fractured occlusal rests, distortion or breakage of other components – major and minor connectors, loss of a tooth or teeth not involved in the support or retention of the restoration, loss of an abutment tooth necessitating its replacement and making a new direct retainer, Other types of repairs & repair by soldering.
p. Removable partial denture considerations in maxillofacial prosthetics – Maxillofacial prosthetics, intra oral prosthesis, design considerations, maxillary prosthesis, Obturators, speech aids, palatal lifts, palatal augmentations, mandibular prosthesis, treatment planning, framework design, class I resection,
Class II resection, mandibular flange prosthesis, jaw relation records.
q. Management of failed restorations and work authorization details.
II. MAXILLOFACIAL REHABILITATION:
Scope, terminology, definitions, cross infection control and hospital waste management, work authorization.
Behavioral and psychological issues in Head and neck cancer, Psychodynamic interactions between clinician and patient. Cancer Chemotherapy: Oral Manifestations, Complications, and management, Radiation therapy of head and neck tumors: Oral effects, Dental manifestations and dental treatment:
Etiology, treatment and rehabilitation (restoration).
Acquired defects of the mandible, acquired defects of hard palate, soft palate, clinical management of edentulous and partially edentulous maxillectomy patients, Facial defects, Restoration of speech, Velopharyngeal function, cleft lip and palate, cranial implants, maxillofacial trauma, Lip and cheek support prosthesis, Laryngectomy aids, Obstructive sleep apnoea, Tongue prosthesis, Oesophageal prosthesis, radiation carriers, Burn stents, Nasal stents, Vaginal and anal stents, Auditory inserts, Trismus appliances, mouth controlled devices for assisting the handicapped, custom prosthesis, conformers, and orbital prosthesis for ocular and orbital defects. Osseo integrated supported facial and maxillofacial prosthesis. Resin bonding for maxillofacial prosthesis, cranial prosthesis Implant rehabilitation of the mandible compromise by radiotherapy, Prosthodontic treatment, Material and laboratory procedures for maxillofacial prosthesis.
III. OCCLUSION
EVALUATION, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OCCLUSAL PROBLEMS:
Scope, definition, terminology, optimum oral health, anatomic harmony, functional harmony, occlusal stability, causes of deterioration of dental and oral health.
Anatomical, physiological, neuro – muscular, psychological considerations of teeth; muscles of mastication; temporomandibular joint; intra oral and extra oral and facial musculatures and the functions of Cranio mandibular system.
Occlusal therapy, the stomatognathic system, centric relation, vertical dimension, the neutral zone, the occlusal plane, differential diagnosis of temporomandibular
disorders, understanding and diagnosing intra articular problems, relating treatment to diagnosis of internal derangements of TMJ, Occlusal splints. Selecting instruments for
occlusal diagnosis and treatment, mounting casts, Pankey-Mann-Schuyler philosophy of complete occlusal rehabilitation, long
centric, anterior guidance, restoring lower anterior teeth, restoring upper anterior teeth, determining the type of posterior occlusal contours, methods for determining the plane of occlusion, restoring lower posterior teeth, restoring upper posterior teeth, functionally generated path techniques for recording border movements intra orally, occlusal equilibration.
Bruxism, Procedural steps in restoring occlusion, requirements for occlusal stability, solving occlusal problems through programmed treatment planning, splinting, solving – occlusal wear problems, deep overbite problems, anterior overjet problems, anterior open bite problems. Treating – end to end occlusion, splaed anterior teeth, cross bite problems, Crowded, irregular, or interlocking anterior bite. Using Cephalometric for occlusal analysis, solving severe arch malrelationship problems, transcranial radiography, postoperative care of occlusal therapy.
IV. FIXED PROSTHODONTICS
Scope, definitions and terminology, classification and principles, design, mechanical and biological considerations of components – Retainers, connectors, pontics, work authorization.
• Diagnosis and treatment planning –patients history and interview, patientsdesires and expectations and needs, systemic and emotional health, clinical examinations – head and neck, oral – teeth, occlusal and periodontal,
Preparation of diagnostic cast, radiographic interpretation, Aesthetics, endodontics considerations, abutment selection – bone support, root proximities and inclinations, selection of abutments for cantilever, pier abutments, splinting, available tooth structures and crown morphology, TMJ and muscles of mastication and comprehensive planning and prognosis.
• Management of Carious teeth –caries in aged population, caries control,removal caries, protection of pulp, reconstruction measure for
compromised teeth – retentive pins, horizontal slots, retentive grooves, prevention of caries, diet, prevention of root caries and vaccine for caries.
• Periodontal considerations –attachment units, ligaments, prevention of gingivitis, periodontitis. Microbiological aspect of periodontal diseases, marginal lesion, occlusal trauma, periodontal pockets in attached gingiva, interdental papilla, gingival embrasures, gingival/periodontal prosthesis, radiographic interpretations of Periodontia, intraoral, periodontal splinting – Fixed prosthodontics with periodontially compromised dentitions, placement of margin restorations.
• Biomechanical principles of tooth preparation –individual tooth preparations - Complete metal Crowns – P.F.C., All porcelain – Cerestore crowns, dicor crowns, inceram etc. porcelain jacket crowns; partial 3/4, 7/8, telescopic, pin– ledge, laminates, inlays, onlays. Preparations for restoration of teeth– amalgam, glass Ionomer and composite resins. Resin bond retainers, Gingival marginal preparations – Design, material selection, and biological and mechanical considerations – intracoronal retainer and precision attachments – custom made and prefabricated.
• Isolation and fluid control – Rubber dam application(s), tissue dilation–softtissue management for cast restoration, impression materials and techniques, provisional restorations, interocclusal records, laboratory support for fixed Prosthodontics, Occlusion, Occlusal equilibration, articulators, recording and transferring of occlusal relations, cementing of restorations.
• Resins, Gold and gold alloys, glass Ionomer, restorations.
• Restoration of endodontically treated teeth, Stomatognathic Dysfunction and management
• Management of failed restorations Osseo integrated supported fixed Prosthodontics –Osseo integratedsupported and tooth supported fixed Prosthodontics
• CAD – CAM Prosthodontics
V. TMJ – Temporomandibular joint dysfunction – Scope, definitions, and terminology
Temporomandibular joint and its function, Orofacial pain, and pain from the temporomandibular joint region, temporomandibular joint dysfunction, temporomandibular joint sounds, temporomandibular joint disorders, Anatomy related, trauma, disc displacement, Osteoarthrosis/Osteoarthritis, Hyper mobility and dislocation, infectious arthritis, inflammatory diseases, Eagle’s syndrome (Styloid – stylohyoid syndrome), Synovial chondromatosis, Osteochondrosis disease, Ostonecrosis, Nerve entrapment process, Growth changes, Tumors, Radiographic imaging
• Etiology, diagnosis and cranio mandibular pain, differential diagnosis and management of orofacial pain – pain from teeth, pulp, dentin, muscle pain, TMJ pain
– psychologic, physiologic – endogenous control, acupuncture analgesia, Placebo effects on analgesia, Trigeminal neuralgia, Temporal arteritis
• Occlusal splint therapy – construction and fitting of occlusal splints, management of occlusal splints, therapeutic effects of occlusal splints, occlusal splints and general muscles performance, TMJ joint uploading and anterior repositioning appliances, use and care of occlusal splints.
• Occlusal adjustment procedures – Reversible – occlusal stabilization splints and physical therapies, jaw exercises, jaw manipulation and other physiotherapy or irreversible therapy – occlusal repositioning appliances, orthodontic treatment,
Orthognathic surgery, fixed and removable prosthodontic treatment and occlusal adjustment, removable prosthodontic treatment and occlusal adjustment. Indication for occlusal adjustment, special nature of orofacial pain, Psychopathological considerations, occlusal adjustment philosophies, mandibular position, excursive guidance, occlusal contact scheme, goals of occlusal adjustment, significance of a slide in centric, Preclinical procedures, clinical procedures for occlusal adjustment.
VI. ESTHETICS
SCOPE, DEFINITIONS :
Morpho psychology and esthetics, structural esthetic rules –facialcomponents, dental components, gingival components and physical components. Esthetics and its relationship to function – Crown morphology, physiology of occlusion, mastication, occlusal loading and clinical aspect in bio esthetic aspects, Physical and physiologic characteristic and muscular activities of facial muscle, perioral anatomy and muscle
retaining exercises Smile – classification and smile components, smile design, esthetic restoration of smile, Esthetic management of the dentogingival unit, intraoral materials for management of gingival contours, and ridge contours, Periodontal
esthetics, Restorations – Tooth colored restorative materials, the clinical and
laboratory aspects, marginal fit, anatomy, inclinations, form, size, shape, color, embrasures & contact point.
Prosthodontic treatment should be practiced by developing skills, by treating various and more number of patients to establish skill to diagnose and treatment and after care with bio-mechanical, biological, bio-esthetics, bio-phonetics. All treatments should be carried out in more numbers for developing clinical skills.
• Infection control, cross infection barrier – clinical & lab ; hospital & lab waste management
Teaching / Learning Activities:
The post graduate is expected to complete the following at the end of :
I YEAR M.D.S.
• Theoretical exposure of all applied sciences
• Pre-clinical exercises involved in prosthodontic therapy for assessment
• Commencement of library assignment within six months
• To carry out short epidemiological study relevant to prosthodontics.
• Acquaintance with books, journals and referrals.
• To differentiate various types of articles published in and critically appraise based on standard reference guidelines.
• To develop the ability to gather evidence from published articles.
• To acquire knowledge of published books, journals and websites for the purposeof gaining knowledge and reference – in the field of Oral and Maxillofacial Prosthodontics and Implantology
• Acquire knowledge of instruments, equipment, and research tools in Prosthodontics.
• To acquire knowledge of Dental Material Science – Biological and biomechanical
& bio-esthetics, knowledge of using material in laboratory and clinics including testing methods for dental materials.
• Submit a protocol for their dissertation before Institutional Review Board and Institutional Ethics Committee.
• Participation and presentation in seminars, didactic lectures.
II YEAR M.D.S.
• Acquiring confidence in obtaining various phases and techniques in removable and fixed prosthodontics therapy
• Acquiring confidence by clinical practice with sufficient number of patientsrequiring tooth and tooth surface restorations
• Fabrication of adequate number of complete denture prosthesis following, higher clinical approach by utilizing semi-adjustable articulators, face bow and graphic tracing.
• Understanding the use of dental surveyor and its application in diagnosis and treatment plan in R.P.D.
• Adequate number of R.P.D’s covering all partially edentulous situations.
• Adequate number of Crowns, Inlays, laminates, FDP ( fixed dental prosthesis) covering all clinical situations.
• Selection of cases and following principles in treatment of partially or complete edentulous patients by implant supported prosthesis.
• Treating single edentulous arch situations by implant supported prosthesis.
• Diagnosis and treatment planning for implant prosthesis.
• Ist stage and IInd stage implant surgery
• Understanding the maxillofacial Prosthodontics, treating craniofacial and management of orofacial defects
• Prosthetic management of TMJ syndrome
• Occlusal rehabilitation
• Management of failed restorations.
• Prosthodontic management of patient with psychogenic disorder.
• Practice of child and geriatric prosthodontics.
• Participation and presentation in seminars, didactic and non didactic Teaching and Training students.
III YEAR M.D.S
• Clinical and laboratory practice continued from IInd year.
• Occlusion equilibration procedures – fabrication of stabilizing splint for arafunctional disorders, occlusal disorders and TMJ functions.
• Practice of dental, oral and facial esthetics
• The clinical practice of all aspects of Prosthodontic therapy for elderly patients.
• Implants Prosthodontics – Rehabilitation of Partial Edentulism, Complete
edentulism and craniofacial rehabilitation.
• Failures in all aspects of Prosthodontics and their management and after care.
• Team management for esthetics, TMJ syndrome and Maxillofacial & Craniofacial Prosthodontics
• Management of Prosthodontic emergencies, resuscitation.
• Candidate should complete the course by attending a large number and variety of patients to master the prosthodontic therapy. This includes the practice
management, examinations, treatment planning, communication with patients, clinical and laboratory techniques materials and instrumentation required in different aspects of prosthodontic therapy, Tooth and Tooth surface restoration, Restoration of root treated teeth, splints for periodontal rehabilitations and fractured jaws, complete dentures, R.P.D’s, F.D.P’s, Immediate dentures, over dentures, implant supported prosthesis, maxillofacial and body prosthesis, occlusal rehabilitation.
• Prosthetic management of TMJ syndrome
• Management of failed restorations
• Should complete and submit Main Dissertation assignment 6 months prior to examination.
• Candidates should acquire complete theoretical and clinical knowledge through seminars, symposium, workshops and reading.
• Participation and presentation in seminars, didactic lectures
PROSTHODONTIC TREATMENT MODALITIES
1) Diagnosis and treatment planning prosthodontics
2) Tooth and tooth surface restorations
• Fillings
• Veneers – composites and ceramics
• Inlays- composite, ceramic and alloys
• Onlay – composite, ceramic and alloys
• Partial crowns – ¾ th, 4/5th, 7/8th, Mesial ½ crowns
• Pin-ledge
• Radicular crowns
• Full crowns
3) Tooth replacements
Partial Complete
• Tooth supported Fixed partial denture Overdenture
• Tissue supported Interim partial denture Complete denture
Intermediate partial
denture
Immediate denture
Immediate complete
denture
• Tooth and tissue
Supported
Cast partial denture Overdenture
Precision attachment
• Implant supported Cement retained Bar attachment
Screw retained Ball attachment
Clip attachment
• Tooth and implantmSupported
Screw retained Screw retained
Cement retained Cement retained
• Root supported Dowel and core Over denture
Pin retained
• Precision attachments
• Intra coronal attachments
• Extra coronal attachments
• Bar – slide attachments
• Joints and hinge joint attachments
4) Tooth and tissue defects (Maxillo- facial and Cranio-facial prosthesis)
A. Congenital Defects
a. Cleft lip and palate
b. Pierre Robin Syndrome
c. Ectodermal dysplasia
d. Hemifacial microstomia cast partial dentures
e. Anodontia implant supported prosthesis
f. Oligodontia complete dentures
g. Malformed teeth fixed partial dentures
B. Acquired defects
a. Head and neck cancer patients – prosthodontic splints and stents
b. Restoration of facial defects
– Auricular prosthesis
– Nasal prosthesis
– Orbital prosthesis
– Craniofacial implants
c. Midfacial defects
d. Restoration of maxillofacial trauma
e. Hemimandibulectomy cast partial denture
f. Maxillectomy implant supported
Dentures
g. Lip and cheek support prosthesis complete dentures
h. Ocular prosthesis
i. Speech and Velopharyngeal prosthesis
j. Laryngectomy aids
k. Esophageal prosthesis
l. Nasal stents
m. Tongue prosthesis
n. Burn stents
o. Auditory inserts
p. Trismus appliances
5) T.M.J and Occlusal disturbances
a. Occlusal equilibration
b. Splints - Diagnostic
- Repositioners / Deprogrammers
c. Anterior bite planes
d. Posterior bite planes
e. Bite raising appliances
f. Occlusal rehabilitation
6) Esthetic/Smile designing
a. Laminates / Veneers
b. Tooth contouring (peg laterals, malformed teeth)
c. Tooth replacements
d. Team management
7) Psychological therapy
a. Questionnaires
b. Charts, papers, photographs
c. Models
d. Case reports
e. Patient counseling
f. Behavioral modifications
g. Referrals
8) Geriatric Prosthodontics
a. Prosthodontics for the elderly
b. Behavioral and psychological counseling
c. Removable Prosthodontics
d. Fixed Prosthodontics
e. Implant supported Prosthodontics
f. Maxillofacial Prosthodontics
g. Psychological and physiological considerations
9) Preventive measures
a. Diet and nutrition modulation and counseling
b. Referrals
The bench work should be completed before the start of clinical work during the first year of the MDS Course
I. Complete dentures
1. Arrangements on adjustable articulator for
• Class I
• Class II
• Class III
2. Various face bow transfers to adjustable articulators
3. Processing of characterized anatomical dentures
II. Removable partial dentures
1. Design for Kennedy’s Classification
(Survey, block out and design)
a. Class I
b. Class II
c. Class III
d. Class IV
2. Designing of various components of RPD
3. Wax pattern on refractory cast
a. Class I
b. Class II
c. Class III
d. Class IV
4. Casting and finishing of metal frameworks
5. Acrylisation on metal frameworks for
Class I
Class III with modification
III. Fixed Partial Denture
1. Preparations on ivory teeth / natural teeth
• FVC for metal
• FVC for ceramic
• Porcelain jacket crown
• Acrylic jacket crown
• PFM crown
• 3/4th (canine, premolar and central)
61
61
• 7/8th posterior
• Proximal half crown
• Inlay – Class I, II, V
• Onlay – Pin ledged, pinhole
• Laminates
2. Preparation of different die systems
3. Fabrication of wax patterns by drop wax build up technique
• Wax in increments to produce wax coping over dies of tooth preparations on
substructures
• Wax additive technique
• 3-unit wax pattern (maxillary and Mandibular)
• Full mouth
4. Pontic designs in wax pattern
• Ridge lap
• Sanitary
• Modified ridge lap
• Modified sanitary
• Spheroidal or conical
5. Fabrication of metal frameworks
• Full metal bridge for posterior (3 units)
• Coping for anterior (3 unit)
• Full metal with acrylic facing
• Full metal with ceramic facing
• Adhesive bridge for anteriors
• Coping for metal margin ceramic crown
• Pin ledge crown
6. Fabrication of crowns
• All ceramic crowns with characterisation
• Metal ceramic crowns with characterisation
• Full metal crown
• Precious metal crown
• Post and core
7. Laminates
• Composites with characterisation
• Ceramic with characterisation
• Acrylic
8. Preparation for composites
• Laminates
• Crown
• Inlay
• Onlay
• Class I
• Class II
• Class III
• Class IV
• Fractured anterior tooth
IV. Maxillofacial prosthesis
• Eye
62
62
• Ear
• Nose
• Face
• Body defects
o Cranial
o Maxillectomy
o Hemimandibulectomy
o Finger prosthesis
o Guiding flange
o Obturator
V. Implant supported prosthesis
1. Step by step procedures –Surgical and laboratory phase
VI. Other exercises
1. TMJ splints – stabilization appliances, maxillary and Mandibular
repositioning appliances
2. Anterior disocclusion appliances
3. Chrome cobalt and acrylic resin stabilization appliances
4. Modification in accommodation of irregularities in dentures
5. Occlusal splints
6. Periodontal splints
7. Precision attachments – custom made
8. Over denture coping
9. Full mouth rehabilitation (by drop wax technique, ceramic build up)
10. TMJ appliances – stabilization appliances
ESSENTIAL SKILLS:
*Key
O – Washes up and observes
A – Assists a senior
PA – Performs procedure under the direct supervision of a senior specialist
PI – Performs independently
The following list of procedures are expected of the post graduate to complete in the post graduate programme under faculty guidance [PA] or independently [PI] . Each of
the following procedures should be evaluated for the competencies like critical thinking, patient centered approach, use of evidence based approach,
professionalism, systems based practice approach and communication skills of the student. The mentioned numbers denote minimal requirement. However, the head of the department has the discretion to fix the quota and assess them systematically. There may be procedures which the student has observed [O] or assisted [A]. The student can however make his entry into his log book or portfolio wherein he/she can make his comments with remarks of the facilitator in the form of a feedback which would reinforce his learning.
PROCEDURE CATEGORY
O A PA PI
Tooth and tooth surface restoration
a) Composites – fillings, laminates, inlay, onlay 5
b) Ceramics – laminates, inlays, onlays 5
c) Glass Ionomer 5
CROWNS
FVC for metal 10
FVC for ceramic 10
Precious metal crown or Galvanoformed crown 1 - 1 5
Intraradicular crowns (central, lateral, canine,
premolar, - - 5
and molar)
Crown as implant supported prosthesis As many 5 5 5
FIXED PARTIAL DENTURES
Porcelain fused to metal (anterior and posterior) 10
Multiple abutments – maxillary and Mandibular full arch 5
Incorporation of custom made and prefabricated 2 precision attachments
Adhesive bridge for anterior/posterior - 5
CAD – CAM Anterior/Posterior FPD - - 5
Interim provisional restorations (crowns and FPDs) for all crowns and bridges
Immediate fixed partial dentures (interim) with ovate pontic - - 5
Fixed prosthesis as a retention and rehabilitation means 5 for acquired and congenital defects – maxillofacial Prosthetics
Implant supported prosthesis - 1
Implant – tooth supported prosthesis - 1
REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE
Provisional partial denture prosthesis 10
Cast removable partial denture (for Kennedy’s Applegate 3 classification with modifications)
Removable bridge with precision attachments and 1
Telescopic crowns for anterior and posterior edentulous Spaces Immediate RPD 5
Partial denture for medically compromised and 2 Handicapped patients
COMPLETE DENTURES
Anatomic characterized prosthesis (by using semi - - 25 adjustable articulator)
Single dentures - - 5
Overlay dentures - - 5
Interim complete dentures as a treatment prosthesis for - - 5 abused denture supporting tissues
Complete denture prosthesis (for abnormal ridge relation, - - 5 ridge form and ridge size)
Complete dentures for patients with TMJsyndromes - - 2
Complete dentures for medically compromised and - - 2 handicapped patients
GERIATRIC PATIENTS
Handling geriatric patients requiring nutritional counseling, psychological management and management of co-morbitity including xerostomia and systemic problems. Palliative care to elderly.
IMPLANT SUPPORTED COMPLETE
PROSTHESIS
Implant supported complete prosthesis (maxillary and - - 1 Mandibular)
MAXILLOFACIAL PROSTHESIS
e.g. Guiding flange/ obturators/ Speech and palatal lift prosthesis/ Eye/ Ear/ Nose/ Face/Finger/Hand/Foot 5 different types as PI
TMJ SYNDROME MANAGEMENT
Splints – periodontal, teeth, jaws - - 1 1
TMJ supportive and treatment prosthesis - - 1 1
Stabilization appliances for maxilla and mandible with - - - 1 freedom to move from IP to CRCP
In IP without the freedom to move to CRCP - - - 1
Repositioning appliances, anterior disocclusion - - - 1 appliances
Chrome cobalt and acrylic resin stabilization appliances - - - 1 for modification to accommodate for the irregularities in the dentition
Occlusal adjustment and occlusal equilibrium appliances - - 1 4
FULL MOUTH REHABILITATION
Full mouth rehabilitation – restoration of esthetics and - - 1 2 function of stomatognathic system
INTER-DISCIPLINARY TREATMENT
MODALITIES
Inter-disciplinary management – restoration of
Oro - - 1 2 craniofacial defects for esthetics, phonation, mastication and psychological comforts
MANAGEMENT OF FAILED RESTORATION
Tooth and tooth surface restorations - - - 5
Removable prosthesis - - - 5
Crowns and fixed prosthesis - - - 5
Maxillofacial prosthesis - - - 2
Implant supported prosthesis - - - 1
Occlusal rehabilitation and TMJ syndrome - - - 2
Restoration failures of psychogenic origin - - - 2
Restoration failures to age changes - - - 2
Career Options
After completing MDS, candidates will get employment opportunities in Government as well as in the Private sector.
- Prosthodontist.
- Lecturer.
- Dental Surgeon.
- Dental Hygienist.
- Ceramist.
- Forensics & Oral Pathologist
While in the Private sector, the options include:
Clinical practice- start your own clinic, work in a clinic associated with a hospital or work in private clinics.
Courses After MDS Prosthodontics and Crown & Bridge
Master of Dental Surgery is a postgraduate course that can be pursued after finishing BDS. After pursuing MDS, a candidate could pursue the following course programs, where MDS is a feeder qualification.
These include:
- Fellowship Program in Fixed Prosthodontics and Aesthetic Dentistry.
- Advanced Digital Prosthodontics and Implant (ADPI) Dentistry Fellowship.
- Post-Doctoral Fellowship Programme in Maxillo Prosthetics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – MDS Prosthodontics and Crown & Bridge
Question: What is the full form of MDS?
Answer: The full form of MDS is Masters of Dental Surgery.
Question: What is MDS?
Answer: Masters of Dental Surgery (MDS) is a postgraduate course done by doctors after completing BDS.
Question: What is the duration of MDS?
Answer: MDS is an postgraduate program of three years.
Question: What is the eligibility of MDS?
Answer: The candidate must have qualified NEET PG; have a BDS degree from a Dental College recognized by the Dental Council of India. He/She must have completed satisfactorily one-year compulsory rotating internship from colleges recognized by the Dental Council of India for this purpose.
Question: What is the scope after doing MDS?
Answer: MDS offers candidates various employment opportunities and career prospects.
Question: What is the average salary for MDS candidate?
Answer: The MDS candidate’s average salary ranges between Rs.6.5 lakhs to Rs.18 lakhs depending on the experience. The average salary may vary with experience and the nature of the job.
Question: How is the selection is done?
Answer: The selection is done on an annual basis which is based on performance in NEET PG-MDS and counseling conducted by DCI (Dental Council of India).
Question: Is a prosthodontist the same as a cosmetic dentist?
Answer: Cosmetic dentistry is a term used by general dentists who have received some training in cosmetic tooth restoration. However, this field is not recognized as a specialty. This means there are no educational or professional standards that a dentist must meet to advertise cosmetic dentistry services. In contrast, prosthodontists undergo an additional three years of training specifically in tooth restoration after they graduate from dental school. While they may offer many of the same services, a prosthodontist usually has more experience and training in aesthetic tooth treatments. Since many tooth restorations affect function as well as appearance, having a trained specialist perform cosmetic procedures is usually a good idea.
Fact checking Lead
Nitisha graduated with an MD in Medicine from O.O. Bogomolets National Medical University in Kyiv, Ukraine, in 2024. She joined Medical Dialogues in 2022. Her interests lie in healthcare management, medical writing, and fact-checking to combat the widespread medical misinformation in society.


