- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Breakthrough: Wearable, portable invention offers solution to antibiotic resistance
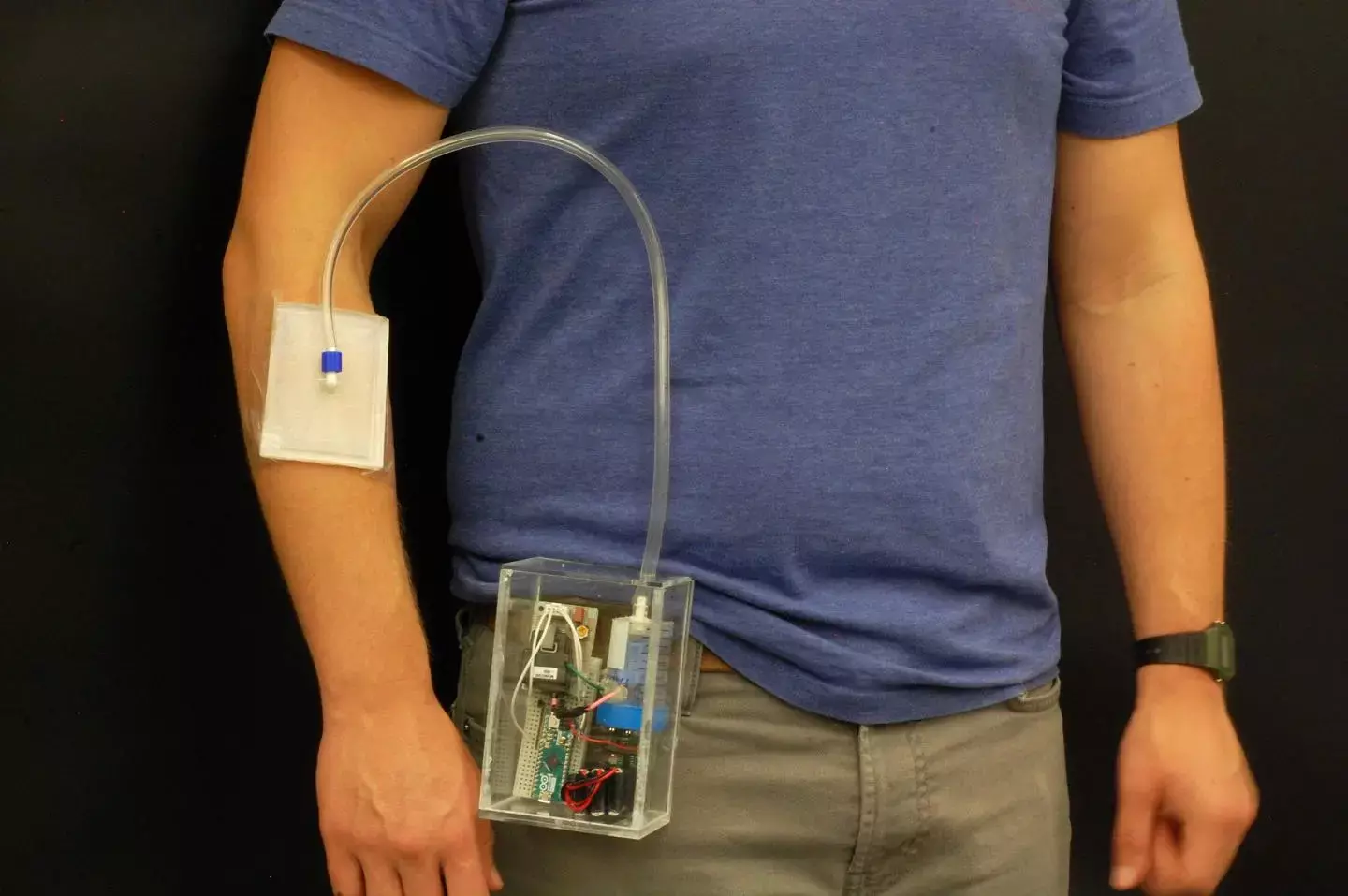
PURDUE UNIVERSITY INNOVATORS CREATED A WEARABLE INVENTION THAT OFFERS OPTIONS FOR TREATING ANTIBIOTIC-RESISTANT INFECTIONS AND WOUNDS. view more
CREDIT: PURDUE UNIVERSITY/RAHIM RAHIMI
Antibiotic resistance is a growing public health concern Globally. A promising alternative to antibiotic therapy is utilizing the antimicrobial properties of topical ozone treatments.
Researchers at Purdue University have developed a portable system designed to apply ozone to a targeted area with increased options for patients to fight resistant infections. The wearable solution allows a patient to receive treatment without leaving home.
They have developed an ozone-releasing wound dressing consist of a disposable gas permeable hydrophobic patch with a reusable and portable ozone-generating unit.
The new research has been published in the journal Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.
The patch incorporated a hydrophobic and highly ozone permeable outer layer and an inner dispersion layer for increased gas distribution uniformity. The antimicrobial effects of the system were tested against common antibiotic resistant strains of bacteria. The results indicated complete elimination of P. aeruginosa and significant reduction in the number of S. epidermidis colonies after 6 h of exposure. These tests also showed a high level of biocompatibility (low cytotoxicity) with human fibroblast cells during the same duration ozone treatment. The described patch is a promising tool in the management of chronic infected wounds and also an answer to bacterial resistance.
The rapid increase of life-threatening antibiotic-resistant infections has resulted in challenging wound complications with limited choices of effective treatments. About 6 million people in the United States are affected by chronic wounds.
"We created a revolutionary type of treatment to kill the bacteria on the surface of the wound or diabetic ulcer and accelerate the healing process," said Rahim Rahimi, an assistant professor of materials engineering at Purdue. "We created a low-cost wearable patch and accompanying components to deliver ozone therapy."
Ozone therapy is a gas phase antimicrobial treatment option that is being used by a growing number of patients in the U.S. In most cases, the ozone treatments require patients to travel to a clinical setting for treatment by trained technicians.
"Our breathable patch is applied to the wound and then connected to a small, battery powered ozone-generating device," Rahimi said. "The ozone gas is transported to the skin surface at the wound site and provides a targeted approach for wound healing. Our innovation is small and simple to use for patients at home."
For further reference log on to:
http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


