- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Hypertension among COVID-19 patients associated with poor prognosis, finds study
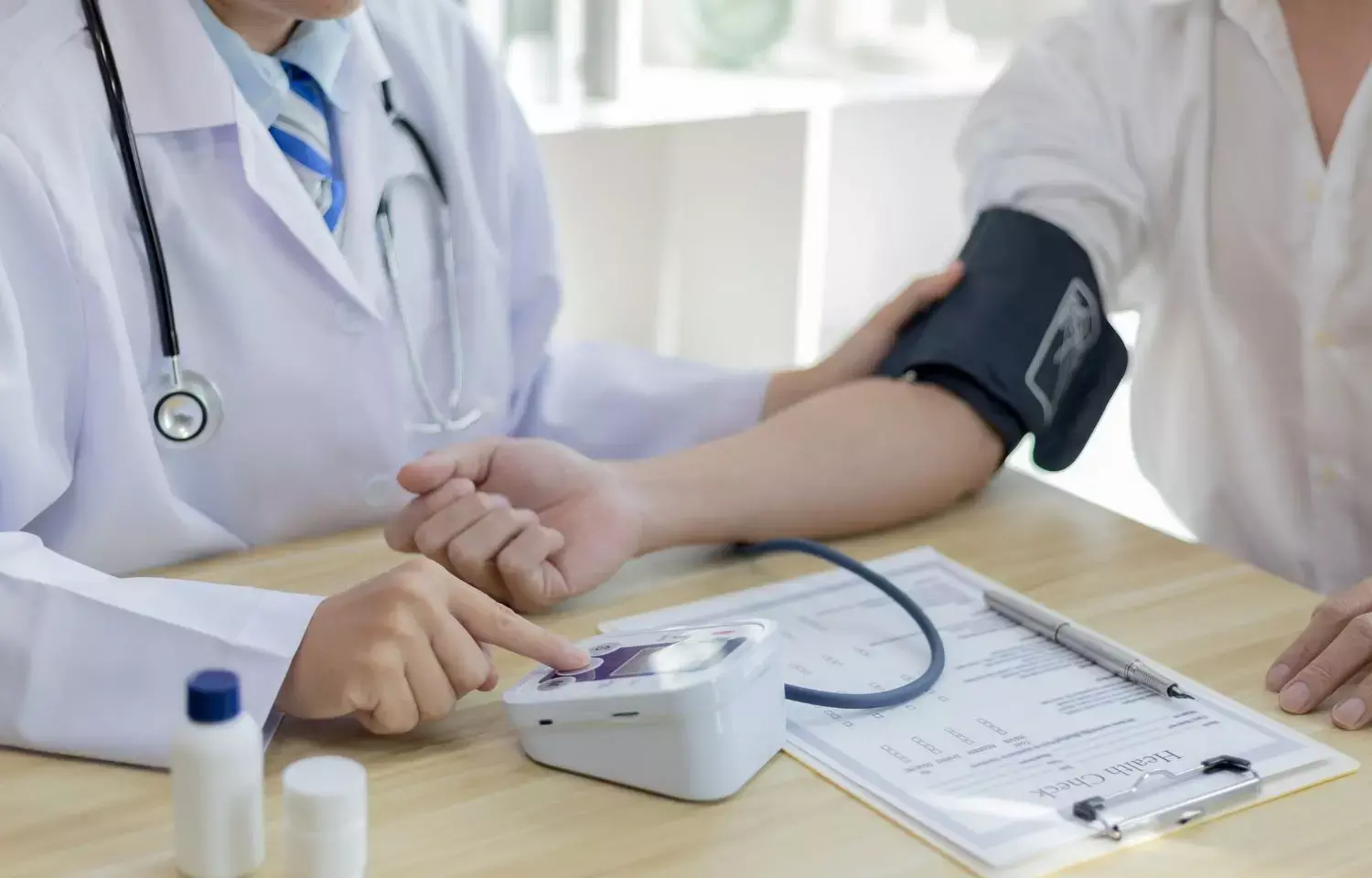
A new investigation revealed that in-hospital mortality and adverse outcomes in COVID-19 are due to hypertension, but angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs)/angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) do not increase the same. The study was published in the 'Journal of Hypertension.'
There are controversial reports on whether hypertension or ACEIs/ARBs causes in-hospital mortality leading to poorer outcomes in COVID 19 infection. Hence researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to summarize the same. Using the MeSH terms all existing studies were retrieved by MEDLINE via PubMed, CENTRAL, and Embase until 30 April 2021. The pooled adjusted odds ratio (AOR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated using a fixed or random effect model. The interaction effect of hypertension and age on in-hospital mortality was performed using the Interactive analysis.
Results:
- In total, 86 articles with 1,87,75,387 COVID-19 patients from 18 countries were included in this study.
- The pooled analysis showed that when compared with those without hypertension, the COVID-19 patients with hypertension had increased risks of in-hospital mortality and other adverse outcomes, with an AOR (95% CI) of 1.36 and 1.32, respectively.
- In countries with more than three independent studies the results were mostly repeated.
- younger and older COVID-19 patients with hypertension showed more evident in-hospital mortality than 60–69-year-old patients.
- ACEI/ARBs did not significantly affect the mortality and adverse outcomes of COVID-19 patients, compared with those receiving other antihypertensive treatment
Thus, it was concluded from the study that an increased risk of in-hospital mortality and adverse outcomes in COVID-19 was significantly associated with hypertension, and it followed a U-shaped curve. It was also found that the increase was not seen in COVID-19 patients under ACEI/ARB treatments.
To read the full article, click here: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003266
Kabia AU, Li P, Jin Z, et al. The effects of hypertension on the prognosis of coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis on the interactions with age and antihypertensive treatment [published online ahead of print, 2022 Aug 9]. J Hypertens. 2022;10.1097/HJH.0000000000003266.
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751