- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
RT-PCR bests rapid tests for diagnosing high risk COVID-19 patients reveals study
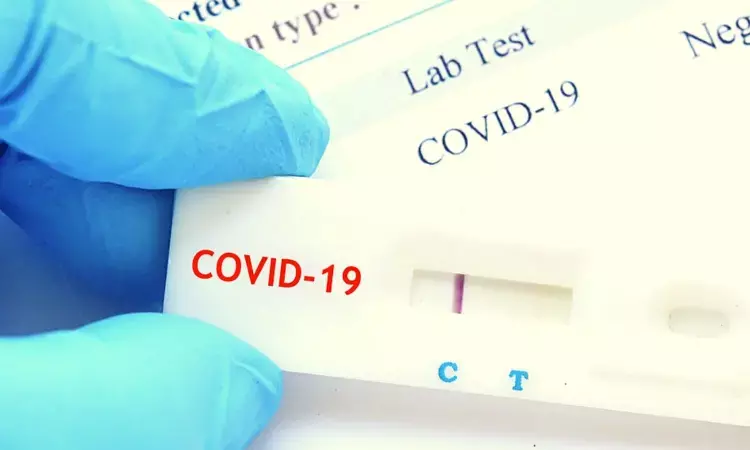
As population immunity to SARS-CoV-2 evolves and new variants emerge, the role and accuracy of antigen tests remain active questions. A recent study published in the CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report highlight the performance of these tests by comparing them with the gold standard RT-PCR and viral culture testing.
The accuracy of diagnostic tools is crucial in the ever-evolving landscape of the COVID-19 pandemic. This study conducted from November 2022 to May 2023 analyzed the performance of antigen tests in detecting SARS-CoV-2 against the more widely used RT-PCR and viral culture testing methods. The participants enrolled in a household transmission study provided valuable insights by completing daily symptom diaries and underwent nasal swab tests for ten consecutive days after enrollment. These samples were then subjected to testing via RT-PCR, culture, and antigen tests.
The findings revealed intriguing patterns in the detection rates of SARS-CoV-2. The peak percentage of positive results for antigen tests, RT-PCR, and culture occurred at different time points following symptom onset with antigen tests lagging behind RT-PCR in sensitivity. The antigen tests expressed a sensitivity of 47% that was markedly lower than the 80% sensitivity observed with RT-PCR when compared against viral culture which serves as the gold standard for confirming active infection.
This disparity in sensitivity has significant implications for clinical practice. Early diagnosis is crucial for initiating timely antiviral treatment for individuals at high risk of severe COVID-19 illness. Therefore, the study suggests a preference for RT-PCR testing in such cases to ensure accurate diagnosis and prompt intervention.
The individuals in the community, especially the participants at high risk, are advised to seek testing from healthcare providers capable of administering RT-PCR tests, given their superior sensitivity compared to antigen tests. This recommendation illuminates the importance of access to accurate diagnostic tools in the context of emerging variants and evolving population immunity. While antigen tests offer rapid results and convenience, their lower sensitivity necessitates careful consideration in clinical decision-making. The insights of the study provide valuable guidance to reinforce the importance of accuracy in managing the challenges of pandemic.
Source:
Smith-Jeffcoat, S. E., Mellis, A. M., Grijalva, C. G., Talbot, H. K., Schmitz, J., Lutrick, K., Ellingson, K. D., Stockwell, M. S., McLaren, S. H., Nguyen, H. Q., Rao, S., Asturias, E. J., Davis-Gardner, M. E., Suthar, M. S., Kirking, H. L., Rolfes, M. A., Biddle, J. E., Zhu, Y., … Ledezma, K. (2024). SARS-CoV-2 Viral Shedding and Rapid Antigen Test Performance — Respiratory Virus Transmission Network, November 2022–May 2023. In MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (Vol. 73, Issue 16, pp. 365–371). Centers for Disease Control MMWR Office. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7316a2
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


