- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Which antihypertensive drugs are associated with gout and hyperuricemia related adverse effects?
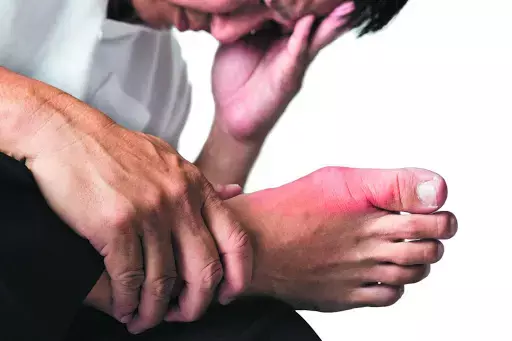
Researchers have found in a new study that antihypertensive drugs like potassium-sparing diuretics, calcium channel blockers and losartan are associated with increase in the risk of adverse events related to hyperuricemia and gout. Further antihypertensive drugs with central action, alpha and beta blockers, renin inhibitors, and vasodilators may also be associated with an increased risk of hyperuricemia, gout, or related adverse events.
The findings were published in Frontiers in Pharmacology.
The use of antihypertensive drugs has long been a topic of concern in regards to inducing hyperuricemia and gout, yet clinical studies in this area have been limited and have produced inconsistent results. So, Xue-Feng Jiao and colleagues aimed to evaluate the association between different antihypertensive drugs and the occurrence of hyperuricemia, gout, and related adverse events using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS).
The findings of this review were:
46 antihypertensive drugs had positive signals for hyperuricemia, 66 for gout, 27 for gouty arthritis, 8 for gouty tophus, and 6 for urate nephropathy. These drugs included diuretics, antihypertensive drugs with central action, alpha blockers, beta blockers, alpha and beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, renin inhibitors, vasodilators, and compound preparations. Additionally, 42 antihypertensive drugs had positive signals for more than one adverse event.
Some potassium-sparing diuretics, calcium channel blockers, and losartan may be associated with an increased risk of hyperuricemia, gout, or related adverse events, which is not consistent with previous studies.
The results also suggest that some antihypertensive drugs with central action, alpha and beta blockers, renin inhibitors, and vasodilators may also be associated with an increased risk of hyperuricemia, gout, or related adverse events, which has not been reported in previous studies.
Overall, this study provides valuable information for healthcare professionals in considering the potential risks of hyperuricemia, gout, and related adverse events when selecting antihypertensive drugs for their patients. It highlights the need for further research in this area to better understand the relationship between antihypertensive drugs and these outcomes.
Source:
Jiao, X.-F., Song, K., Jiao, X., Li, H., Zeng, L., Zou, K., Zhang, W., Wang, H., & Zhang, L. (2023). Hyperuricaemia, gout and related adverse events associated with antihypertensive drugs: A real-world analysis using the FDA adverse event reporting system. In Frontiers in Pharmacology (Vol. 13). Frontiers Media SA. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1045561
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


