- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Antithrombotic therapy not associated with increased traumatic ICH on CT in adults
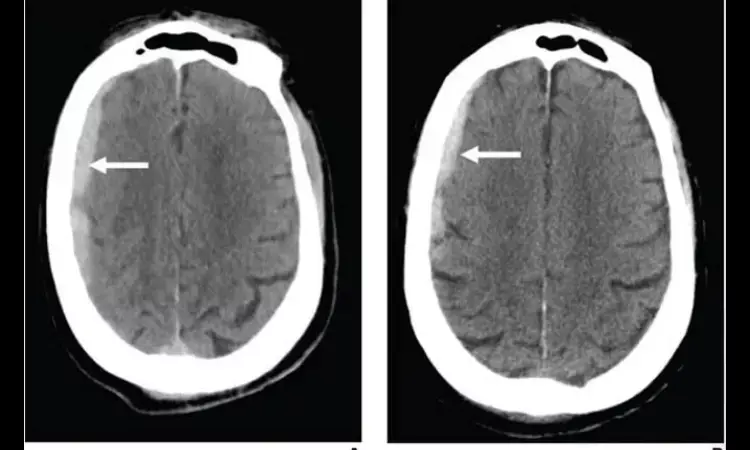
Leesburg, VA - According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), antithrombotic therapy was not linked to increased intracranial hemorrhage on CT in adult patients, although the therapy did show association with hematoma expansion at follow-up.
"The findings suggest, in patients with good neurological status after ground-level fall, application of a similar strategy for selecting patients for initial head CT, regardless of antithrombotic therapy use," wrote first author Zeynep Vardar at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center in Worcester. "If initial head CT shows traumatic intracranial hemorrhage, early follow-up head CT should be systematically performed in those on antithrombotic therapy though possibly deferred in other patients."
Vardar and colleagues' retrospective case-control study included 1,630 patients (693 female, 937 male; mean age, 80 years) who underwent head CT after presenting to the emergency department (ED) with ground-level fall (Glasgow Coma Scale ≥ 14 and no focal neurological deficit) between January 1 and December 31, 2020. Initial head CT examinations were reviewed for traumatic intracranial hemorrhage characteristics and follow-up head CT examinations (performed within 24 hours) were reviewed for hematoma expansion, with clinical outcomes extracted from medical records.
The frequency of intracranial hemorrhage after ground-level fall with good neurological status was not significantly different between patients on antithrombotic therapy and those not on antithrombotic therapy (4.4% vs 3.1% respectively, p = .24). However, hematoma expansion occurred more frequently in patients on antithrombotic therapy (26.2% vs 4.8%, p = .04).
Also noting no significant difference between patients on anticoagulant therapy alone, antiplatelet therapy alone, or both, "the frequency of midline shift and regional mass effect was not significantly different between patients on antithrombotic therapy and control patients," the authors of this AJR article added.
https://www.ajronline.org/doi/10.2214/AJR.21.27274
American Journal of Roentgenology,traumatic intracranial hemorrhage,Zeynep Vardar,University of Massachusetts Medical Center,AJR,
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


