- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Chemotherapy drug originally developed to treat lymphoma outperforms Remdesivir against COVID
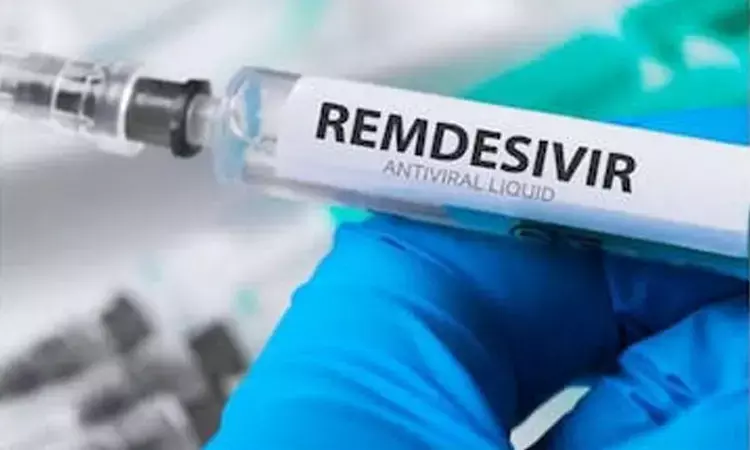
Beijing: A chemotherapy medication originally developed to treat lymphoma has outperformed the popular remdesivir drug against SARS-CoV-2 in lab settings, and could potentially be repurposed to treat Covid-19, say researchers.
A novel computational drug screening strategy combined with lab experiments suggest that pralatrexate drug is a promising candidate for Covid-19 patients.
The novel screening approach identified four promising drugs, which were then tested against SARS-CoV-2 in lab experiments.
Two of the drugs, pralatrexate and azithromycin, successfully inhibited replication of the virus.
Further lab experiments showed that pralatrexate more strongly inhibited viral replication than did remdesivir, a drug that is currently used to treat some Covid-19 patients, said Haiping Zhang of the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology in Shenzhen, China.
Zhanh and team screened 1,906 existing drugs for their potential ability to inhibit replication of SARS-CoV-2 by targeting a viral protein called RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP).
The findings, published in open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology, suggest that pralatrexate could potentially be repurposed to treat Covid-19.
"However, this chemotherapy drug can prompt significant side effects and is used for people with terminal lymphoma, so immediate use for Covid-19 patients is not guaranteed. Still, the findings support the use of the new screening strategy to identify drugs that could be repurposed," the researchers noted.
With the Covid-19 pandemic causing illness and death worldwide, better treatments are urgently needed.
One shortcut could be to repurpose existing drugs that were originally developed to treat other conditions.
"We have demonstrated the value of our novel hybrid approach that combines deep-learning technologies with more traditional simulations of molecular dynamics," Zhang said.
He and his colleagues are now developing additional computational methods for generating novel molecular structures that could be developed into new drugs to treat Covid-19.
Read also: Hub for vaccine developers, Hyderabad to hold special significance in 2021
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.


