- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Montelukast effective steroid-sparing treatment for pediatric Vernal keratoconjunctivitis
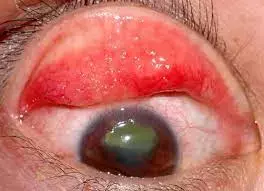
Vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) is a seasonally recurring, bilateral, and severe form of allergic inflammation affecting the ocular surface. This relatively uncommon type of allergic eye disease can cause severe damage to the ocular surface, leading to corneal scarring and vision loss if not treated properly.
Montelukast may be an effective adjunctive, steroid-sparing treatment for managing pediatric vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) according to a recent study published in the Eye.
The study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral montelukast in treating vernal keratoconjunctivitis in pediatric patients.
This is a 26-week, prospective, randomized, open-label study. Fifty-eight patients were randomly assigned to two groups—the treatment (montelukast) and control groups. At the beginning of the study, both the groups received topical loteprednol etabonate (0.1%) in tapering doses for a month, and topical olopatadine (0.1%) for the first 3 months. Symptoms and signs observed before and after treatment and assigned scores were studied. The primary efficacy endpoint was a change in the mean score on the visual analogue scale (VAS) for each subjective symptom. The secondary efficacy endpoint was a change in the total score of objective signs.
Results:
- The montelukast group showed clinically relevant improvements in the signs and symptoms of vernal keratoconjunctivitis, compared to the control group.
- There was considerable improvement in clinical signs. Individual symptoms such as redness, itching, foreign body sensation, and tearing showed significant improvement at 6 months follow-up.
- The gradual improvement in symptoms until the last visit was statistically more significant within the montelukast group.
- The mean VAS score showed statistically significant improvement in itching (p < 0.001) and redness (p < 0.008) in the montelukast group even at 3 months. No adverse events were reported in either group.
Thus, Montelukast was found to be safe and effective as a long-term therapy to prevent relapse in moderate to severe vernal keratoconjunctivitis.
Reference:
Efficacy of montelukast in preventing seasonal recurrence of vernal keratoconjunctivitis in children by Apurva Hardas, et al. published in the Eye
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41433-021-01484-3
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


