- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Cooled radiofrequency ablation promising alternative to treat chronic shoulder pain and stiffnessp
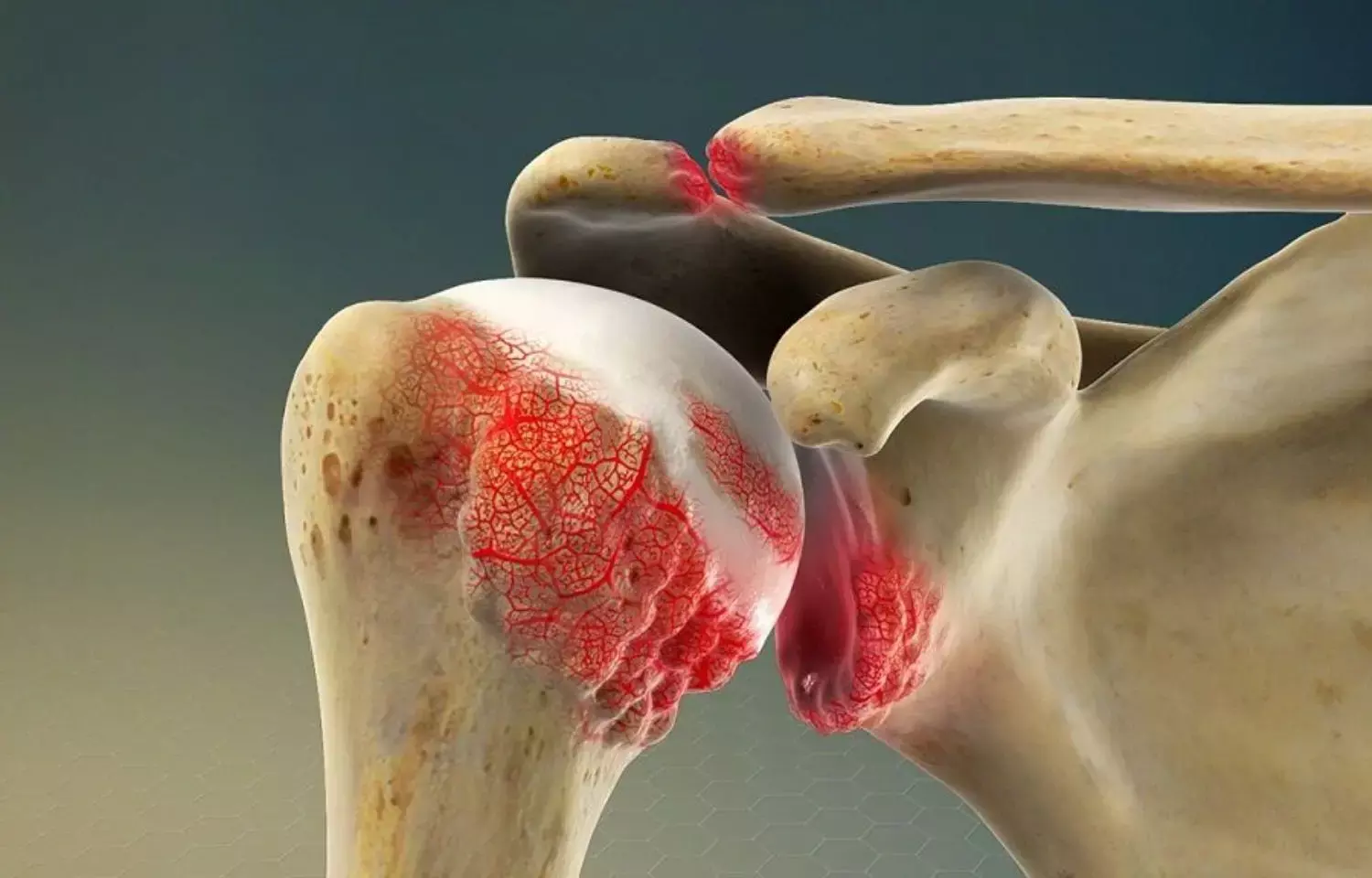
Andrew Tran et al conducted a pilot study to introduce cooled radiofrequency nerve ablation (C-RFA) as an alternative to managing symptomatically moderate to severe glenohumeral osteoarthritis (OA) in patients who have failed other conservative treatments and who are not surgical candidates or refuse surgery. The authors found that Image-guided axillary, lateral pectoral, and suprascapular nerve C-RFA has minimal complications and is a promising alternative to treat chronic shoulder pain and stiffness from glenohumeral arthritis.
The prospective pilot study conducted at Atlanta, GA, USA includes a total of 12 patients experiencing chronic shoulder pain from moderate to severe glenohumeral OA.
Patients underwent anesthetic blocks of the axillary, lateral pectoral, and suprascapular nerves to determine candidacy for C-RFA treatment. Adequate response after anesthetic block was over 50% immediate pain relief. Once patients were deemed candidates, they underwent C-RFA of the three nerves 2–3 weeks later by the interventional musculoskeletal radiology physicians.
Treatment response was evaluated using the clinically validated American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) score and visual analogue scale (VAS) to assess pain, stiffness, and functional activities of daily living. Follow-up outcome scores were collected up to 6 months after C-RFA procedure.
The results of the study were:
• Twelve patients underwent C-RFA procedure for shoulder OA.
• Five patients showed KL grade 3 and 7 showed KL grade 4.
• VAS scores significantly improved from 8.8±0.6 to 2.2±0.4 6 months after the C-RFA treatment (p <0.0001).
• Patient's ASES score results significantly improved in total ASES from 17.2±6.6 to 65.7±5.9 (p<0.005).
• No major complications arose.
• Upon follow-up after the treatments, there was no motor dysfunction or nerve palsy seen on physical exam.
• No patients received re-treatment or underwent shoulder arthroplasty.
The authors opined that: C-RFA is a promising minimally invasive alternative that could be considered for conservative management, especially for patients who are not surgical candidates or refuse surgery. With this pilot study, C-RFA's effects have shown to last up to 6 months, but more studies, especially with large multi-centre patient groups, are required to assess the efficacy beyond that time frame and to compare it to other conservative treatments.
Further reading:
Pilot study for treatment of symptomatic shoulder arthritis utilizing cooled radiofrequency ablation: a novel technique
Andrew Tran, David A. Reiter, Jan Fritz et al
Skeletal Radiology (2022) 51:1563–1570
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-022-03993-y
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


