- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Digital interventions meaningfully improve pain,disability and quality of life after TKR for osteoarthritis: JAMA
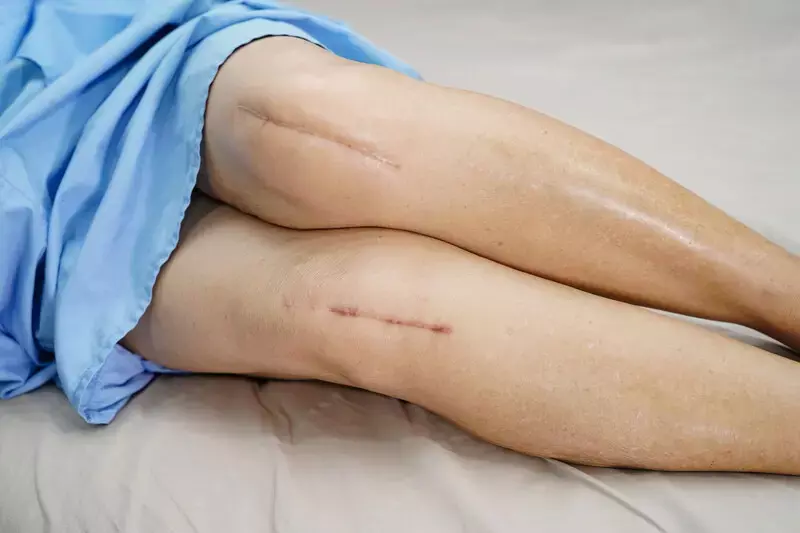
Researchers have found in a new study that patients randomized to a combined digital intervention experienced less pain, less disability, and increased physical activity at 12 months follow-up, compared to care usual following total knee replacement (TKR) for osteoarthritis.
Digital technology represents an opportunity to improve outcomes following total knee replacement (TKR). Digitally delivered interventions have been shown to be similar to face-to-face interventions and to increase participation levels in people with osteoarthritis.
A study was done to assess the effect of a digital technology package in reducing pain compared with usual care following TKR.
This randomized clinical trial recruited 102 adults after they received TKR in 3 rehabilitation hospitals in Sydney, Australia, between June 2020 and July 2021.
All participants underwent usual care. In addition to usual care, 51 participants received a digital technology package consisting of an exercise app, fitness tracker, and online health coaching. In the usual care group, 51 participants received a fitness tracker but with all notifications turned off and goals for step count, sleep, and active hours removed. Participants were followed up for 12 months (June 2021 to July 2022).
The primary outcome was mean knee pain during the past week assessed using a numerical rating scale (range, 0-10, with 10 indicating worst possible pain) at 3 months. In unadjusted analyses, considered primary and based on multiple imputations, independent t tests were used to compare means between groups. Secondary outcomes, including measures of function, activity participation, and quality of life, were analyzed using a generalized estimating equation model that accounted for repeated measurements.
Results
Of 102 participants (mean [SD] age, 67.9 [7.2] years; 68 [67%] female; and 92 [90%] White) randomly assigned to intervention or usual care groups, 47 (92%) in each group completed the 3-month follow up. At 3 months, participants in the intervention group demonstrated small but not clinically meaningful improvements in pain compared with the usual care group in the unadjusted intention-to-treat analysis (mean difference, −0.84; 95% CI, −1.59 to −0.10; P = .03). Secondary outcomes indicated a statistically significant reduction in pain intensity, (mean difference, −0.94; 95% CI, −1.82 to −0.06), pain disability (mean difference, −5.42; 95% CI, −10.00 to −0.83), and sedentary behavior (mean difference, −9.76; 95% CI, −19.17 to −0.34) favoring the intervention from baseline to 3, 6, and 12 months.
In this randomized clinical trial, a combined digital technology program provided small but not clinically meaningful improvements in pain at 3 months and other longer-term favorable outcomes following TKR compared with usual care. Future studies should tailor digital interventions based on participants’ abilities and preferences to ensure that the intervention is appropriate and fosters long-term self-management.
Reference:
Duong V, Robbins SR, Dennis S, Venkatesha V, Ferreira ML, Hunter DJ. Combined Digital Interventions for Pain Reduction in Patients Undergoing Knee Replacement: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(9):e2333172. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.33172
Keywords:
Researchers, patients, randomize, combined, digital, intervention, experienced, less pain, less, disability, increased, physical, activity, 12 months, follow-up, compared, care, usual, following, total knee, replacement, (TKR), osteoarthritis.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


