- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Hyperuricaemia associated with higher prevalence of hand osteoarthritis
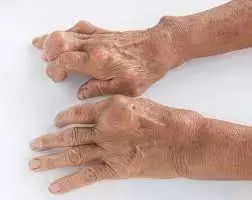
Hyperuricaemia is associated with higher prevalence of hand osteoarthritis suggests a new study published in the Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal diseases.
The pathogenesis of hand osteoarthritis (OA) remains unknown. Hyperuricaemia, which is related to inflammation, may play a role in hand osteoarthritis, but evidence is lacking. In a large population-based study, we examined the association between hyperuricaemia and hand osteoarthritis.
Participants were from the Xiangya osteoarthritis Study, a community-based observational study. Hyperuricaemia was defined as serum urate >416 µmol/L in men and >357 µmol/L in women. Radiographic hand osteoarthritis (RHOA) was defined as presence of the modified Kellgren-Lawrence grade ≥2 in any hand joint. Symptomatic hand osteoarthritis (SHOA) was defined as presence of both self-reported symptoms and RHOA in the same hand. The associations of hyperuricaemia with RHOA or SHOA were examined using generalised estimating equations.
Results
Among 3628 participants, the prevalence of RHOA was higher in participants with hyperuricaemia than those with normouricaemia (26.9% vs 20.9%), with an adjusted OR (aOR) of 1.34 (95% CI 1.11 to 1.61). The associations were consistent in men (aOR 1.33, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.74) and women (aOR 1.35, 95% CI 1.05 to 1.74). Hyperuricaemia was mainly associated with bilateral RHOA (aOR 1.54, 95% CI 1.18 to 2.01) but not unilateral RHOA (aOR 1.13, 95% CI 0.89 to 1.45). Prevalence of SHOA was higher, although statistically insignificant, in participants with hyperuricaemia (aOR 1.39, 95% CI 0.94 to 2.07).
In this population-based study, hyperuricaemia was associated with a higher prevalence of hand osteoarthritis. Future prospective studies are required to investigate the temporal relationship.
Reference:
Zhu Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Doherty M, Yang Z, Cui Y, Zeng C, Lei G, Yang T, Wei J. Association between hyperuricaemia and hand osteoarthritis: data from the Xiangya Osteoarthritis Study. RMD Open. 2023 Dec 1;9(4):e003683. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003683. PMID: 38053456; PMCID: PMC10693871.
Keywords:
Hyperuricaemia, associated, with, higher, prevalence, hand osteoarthritis, Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal diseases, Zhu Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Doherty M, Yang Z, Cui Y, Zeng C, Lei G, Yang T, Wei J
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


