- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Sildenafil Improves CHD-induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Kids
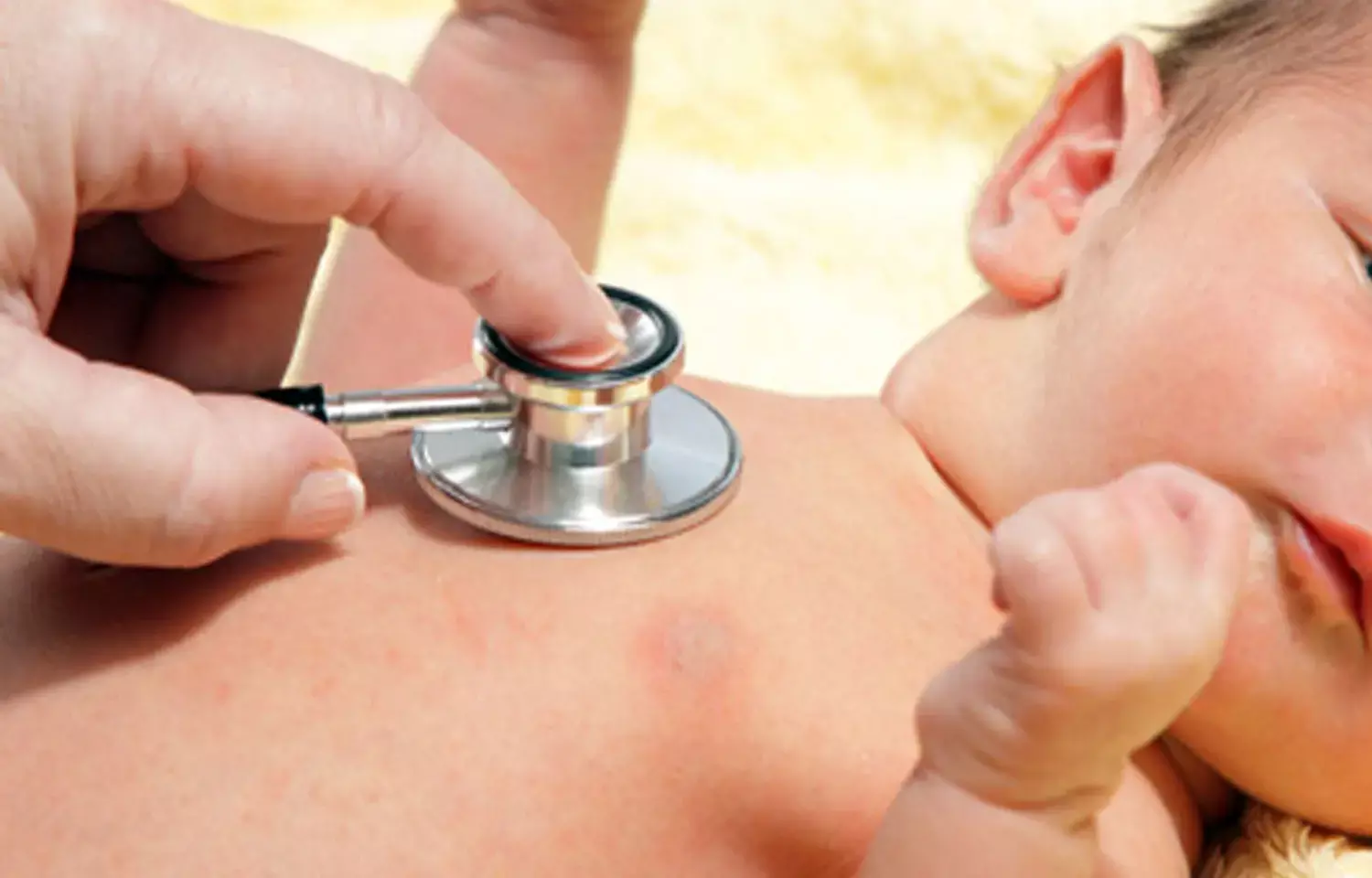
In a recent meta-analysis, Ahmed Awad and team have have found that sildenafil, commonly known by its brand name Viagra, shows significant potential in treating congenital heart disease-induced pulmonary hypertension in children. The findings were published in BMC Pediatrics.
Originally prescribed for angina pectoris, a condition involving chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart, and later for erectile dysfunction, sildenafil's vasodilatory effects on vascular smooth muscle relaxation caught the attention of medical experts in the field of pediatric cardiology.
The meta-analysis, conducted by a team of experts, focused on randomized controlled trials assessing the efficacy of sildenafil compared to a placebo or other vasodilator drugs. They searched major electronic databases, including PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, WOS, Embase, and Scopus, from inception to April 20th, 2022, to compile relevant data.
The study included a comprehensive analysis of 14 studies involving 849 children with an average age of 7.9 months. The findings provided substantial evidence for the efficacy and safety of sildenafil in treating congenital heart disease-induced pulmonary hypertension in children.
Key findings of the meta-analysis include:
Sildenafil demonstrated a statistically significant decrease in mean and systolic pulmonary artery pressure compared to the placebo. This effect can be crucial in reducing the strain on the heart and improving oxygenation.
The drug also showed a decrease in mean aortic pressure and pulmonary artery/aortic pressure ratio compared to the placebo, further indicating its beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system.
Children treated with sildenafil exhibited lower mechanical ventilation time, intensive care unit stay, and hospital stay compared to those on a placebo. This suggests that sildenafil may help expedite recovery and reduce the burden on healthcare resources.
Importantly, there was no significant difference in mortality rates between children treated with sildenafil and those given a placebo or tadalafil, another vasodilator drug.
The results of this meta-analysis are immensely promising for the medical community and families of children with congenital heart disease-induced pulmonary hypertension. Despite these promising results, researchers acknowledge the need for further investigations and clinical trials to validate the findings and establish more robust evidence.
Source:
Awad, A. K., Gad, E. R., Abdelgalil, M. S., Elsaeidy, A. S., Ahmed, O., & Elbadawy, M. A. (2023). Sildenafil for congenital heart diseases induced pulmonary hypertension, a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. In BMC Pediatrics (Vol. 23, Issue 1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-023-04180-1
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


