- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Bamlanivimab may help prevent COVID-19 infection, finds JAMA study
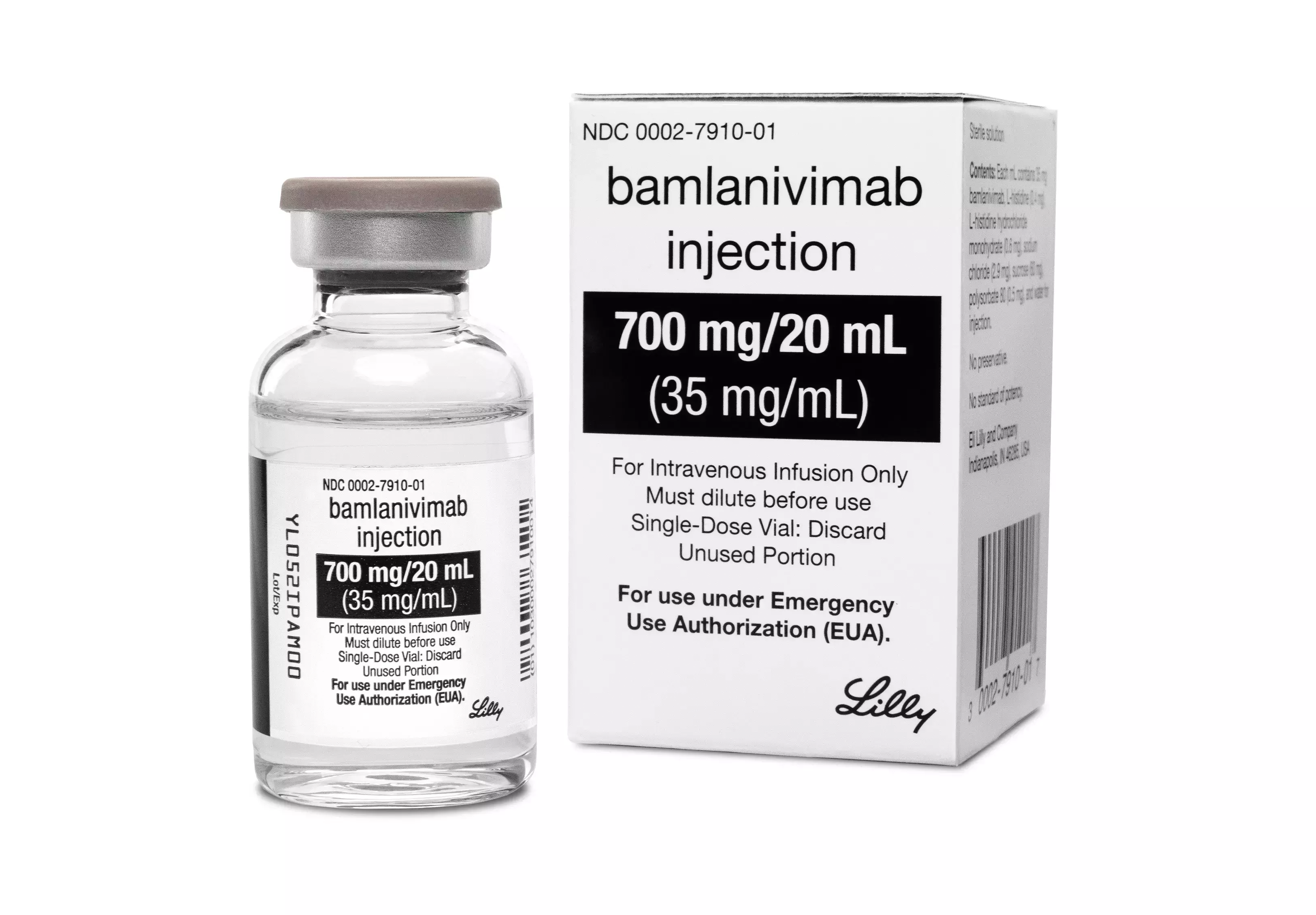
While the emergence of efficacious vaccines is a critical step in addressing the COVID-19 pandemic, other preventive interventions, such as passive immunization, may protect vulnerable populations until widespread immunization is achieved. Bamlanivimab, received an emergency use authorization for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in individuals at high risk of severe COVID-19. The results of placebo-controlled trial published in JAMA, have shown that bamlanivimab was effective in reducing the incidence of COVID-19 infection in residents and participants at high risk of severe COVID-19.
In this phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multipart, single-dose study, participants include residents and staff at 74 skilled nursing and assisted living facilities with at least one confirmed case of direct SARS-CoV-2 detected ≤7 days prior to randomization and aged above 18 years old. Participants were not COVID-19 recovered, serologically negative for SARS-CoV2 antibodies and not previous recipient of monoclonal antibodies.
Participants were screened for enrollment, and, if eligible, randomly assigned and dosed with 4200 mg of intravenous bamlanivimab or placebo (saline). Nasal swabs were obtained on study days 1, 8, 15, 22, 29, 36, 43, 50, and 57 and during post evaluation follow-up for detection of SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR. Serology samples were obtained at baseline, study day 29, and study day 57 during the 8-week evaluation period.
Key findings of the study are:
1. 484 participants who received bamlanivimab had significantly reduced incidence of COVID 19 infection compared with to 482 participants who received placebo (8.5% vs 15.2%, OR 0.43, 95%CI 0.28-0.68, p<0.001).
2. Among the resident population, incidence of COVID-19 disease was significantly lower in bamlanivimab group compared with placebo group (8.8% vs 22.5%, OR 0.20, CI 0.08-0.49, p<0.001)
3. Among the staff group, incidence of COVID-19 was not significantly different in bamlanivimab group compared against placebo group.
4. In the high-risk prevention population, a post hoc analysis showed that the incidence of mild or worse COVID-19 was also lower in the bamlanivimab group compared with the placebo group.
5. Upon analysis it was found that in the overall prevention population, administration of bamlanivimab significantly reduced the incidence of moderate or severe COVID-19 compared with placebo.
6. Bamlanivimab was also associated with lower incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection by week 4 in the resident and high-risk prevention populations.
7. In the study among prevention population, 4 covid related deaths occurred in the placebo group vs zero deaths in the bamlanivimab group.
8. Hypersensitivity reactions with 24 hours of dose administration were seen in 3 participants in bamlanivimab group and none in placebo group.
9. Participants in the prevention population who received bamlanivimab and acquired SARS-CoV-2 had lower baseline viral loads and shorter time to viral clearance compared with participants who received placebo
Authors conclude-"The results presented herein primarily represent validation of the use of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies as protective passive immunotherapy against COVID-19, with potential clinical relevance for antibody therapies in continued distribution".
Source: Cohen MS, Nirula A, Mulligan MJ, et.al; BLAZE-2 Investigators. Effect of Bamlanivimab vs Placebo on Incidence of COVID-19 among Residents and Staff of Skilled Nursing and Assisted Living Facilities: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021 Jun 3. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.8828.
MBBS, M. D. Respiratory Medicine
Dr Sravan Kumar V, completed his M. B. B. S from SRMC, Nandyal and M. D. in Respiratory Medicine from the JSS Medical College, Mysore. After completing MD. he worked as Senior resident in Kasturba Hospital, Manipal. He is actively involved in various research activities of the department. Currently he is working as senior resident in Mallareddy medical college for women, Hyderabad. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


