- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Rapid MRI in suspected stroke patients cuts hosptial length of stay, costs: Study
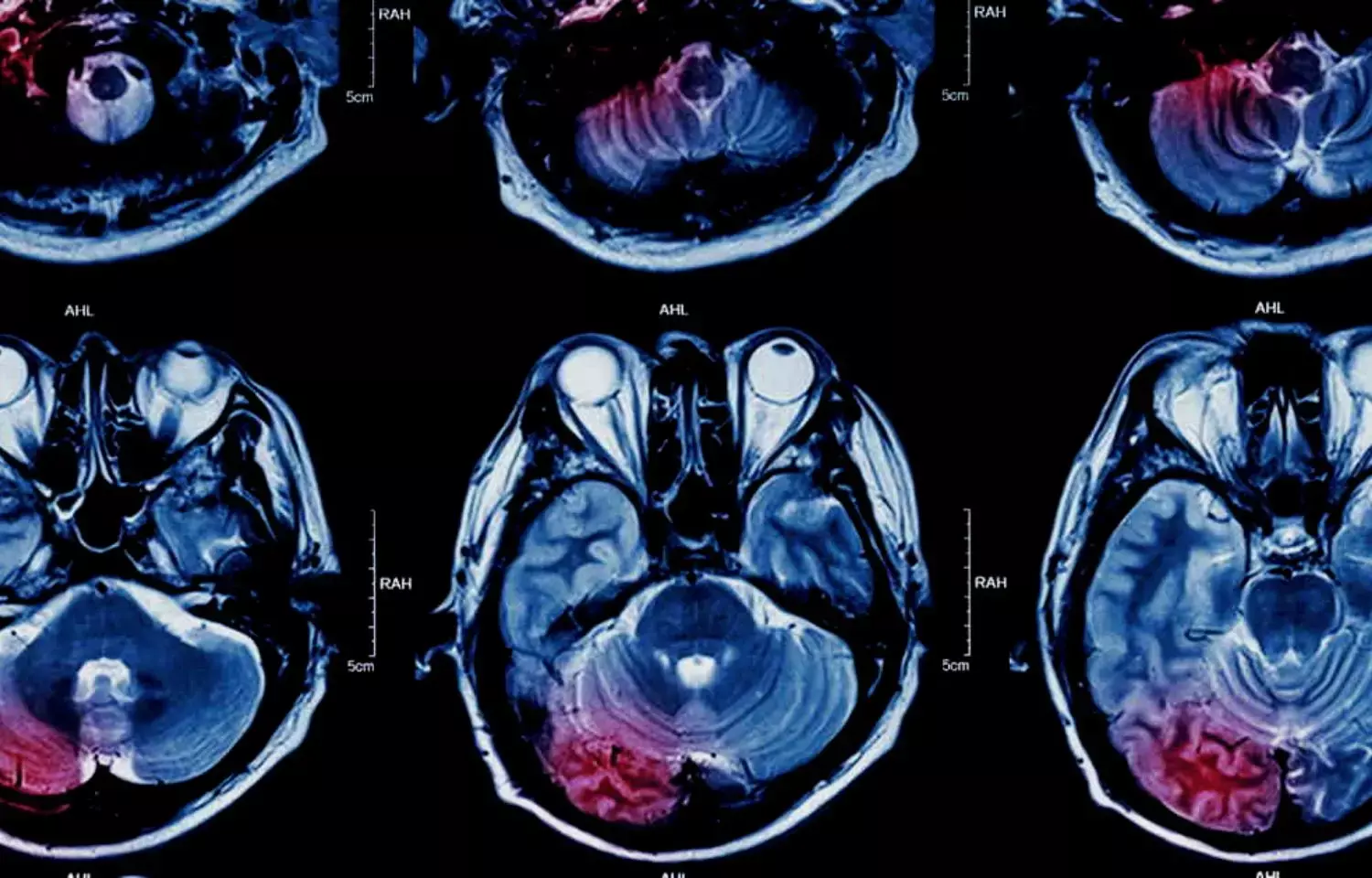
USA: The use of a rapid MRI protocol in the emergency department (ED) in people suspected of acute ischemic stroke was tied to a 17% reduction in hospital length of stay and a 18.7% reduction in total direct cost, shows a recent study in The Neuroradiology Journal. The researchers however states these results to be preliminary and hypothesis-generating.
Abbreviated "rapid MRI" protocols have become more usual for the evaluation of acute ischemic stroke (AIS). No previous study has evaluated the effect of rapid MRIs on cost or hospital length of stay in AIS patients. To fill this knowledge gap, Adam de Havenon, Department of Neurology, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA, and colleagues conducted a study that included 408 patients who presented in the ED for suspected stroke.
They retrospectively identified AIS patients who presented within 6 h of acute neurologic symptom onset to an ED and activated a "brain attack" code. Sequential patients from January 2012 to September 2015 were included, before rapid MRI was available, who had CT perfusion (CTP). These patients were compared with patients from October 2015 to May 2018 who had a rapid MRI.
Inverse-probability-weighting (IPW) was used to balance the cohorts. Direct cost to healthcare system and total hospital length of stay (LOS) were the primary outcomes.
The findings of the study were as follows:
· 408 brain attack activations (mean ± SD age 62.1 ± 17.6 years, 47.8% male) were included: 257 in the CTP cohort and 151 in the MRI cohort.
· Discharge diagnosis was ischemic stroke in 193/408 (47.3%).
· After patient matching, significant reductions were found for the MRI cohort in total cost (−18.7%) and hospital LOS (−17.0%), with no difference in ED LOS as compared to the CTP cohort.
The authors conclude, "although these results are preliminary and hypothesis-generating, we found that the rapid MRI protocol use in ED brain attacks was associated with a 18.7% reduction in total direct cost and 17% reduction in hospital length of stay."
Reference:
de Havenon A, Orlando C, Delic A, et al. Direct cost analysis of rapid MRI in the emergency department evaluation of patients suspected of having acute ischemic stroke. The Neuroradiology Journal. June 2022. doi:10.1177/19714009221108681
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


