- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Early surgical resection- a benefit for Giant Liver Hemangiomas: Case report
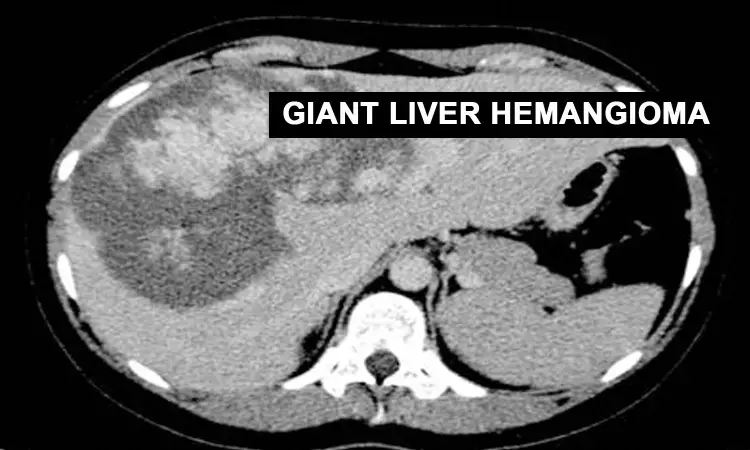
Alvin Chang et al from the Virginia Commonwealth University reported a case of rapidly enlarging Giant Liver Haemangioma which was managed by surgical resection. The case was presented in the journal, 'Case reports in Surgery' 2020.
Early surgical resection (or enucleation) should be considered for giant hemangiomas by recognizing early signs before they cause irreparable anatomic distortion of liver parenchyma.
Hemangiomas in the liver are the most common, benign mesenchymal hepatic lesions occurring in various sizes. Giant hemangiomas which occur from > 5-10cm size may cause abdominal pain, congestive heart failure, or even Kasabach-Merritt Syndrome which is a life threatening condition. Present guidelines advocate conservative management of asymptomatic giant liver hemangiomas via serial imaging to monitor growth where as symptomatic cases are treated by resection.
Also Read: Jubilant Life Sciences gets DCGI nod to JUBI-R for treating COVID-19 patients
A 37-year-old female with a known history of giant hepatic hemangioma was referred with a year old history of aggravating abdominal pain associated with progressive nausea, weight loss and constipation. The patient was treated conservatively for lumbar disk herniation and newly diagnosed irritable bowel syndrome. Examination of the patient revealed generalized distention with a palpable liver edge below the right subcostal margin. She was pale, malnourished and with lumbar lordosis during examination.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen revealed a huge mass located in the right posterior hepatic lobe consistent with giant hemangioma and review of the previous records showed its steady growth. Due to enormous tumor size, the mass was explored by anterior approach and resected. Liver parenchyma was transected using an ultrasonic surgical aspirator. Pringle maneuver and low central venous pressure anesthesia were used to limit the blood loss during surgery. The 3.7kg specimen was removed and later sent for histopathologic examination to confirm cavernous haemangioma. Post operative findings were uneventful and the patient was discharged. Her six month follow up showed resolution of her abdominal pain and improved bowel function except for mild lower back pain due to lumbar disk herniation.
This case throws a light on how progressively enlarging hepatic hemangiomas may benefit from early surgical resection prior to presentation of typical symptoms.
For further reading, click the following link: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5923787
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


