- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Colorectal liver metastases: Tranexamic acid reduces blood transfusions after hepatectomy
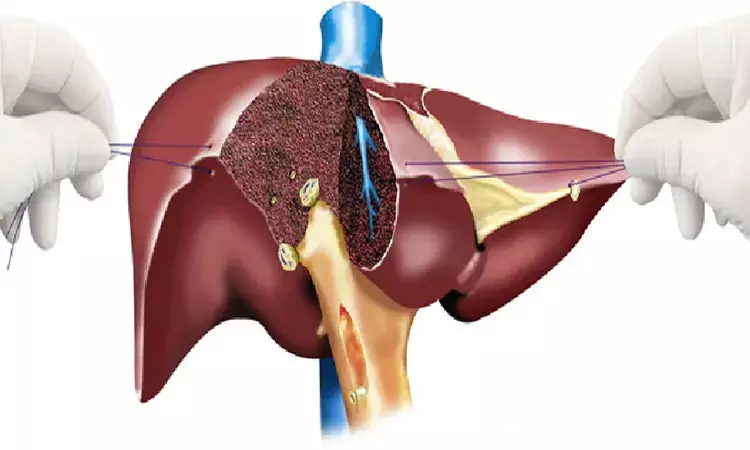
Canada: Intraoperative administration of tranexamic acid (TXA) decreases red blood cell transfusions (RBCT) in hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases (CRLM), according to a recent study in the journal HPB. The study found that TXA led to a 41% reduction in the risk of 30-day receipt of RBCT.
Colorectal cancer is a major health problem and is the third most common cancer in the world. About 65% of all the CRC patients develop distant metastasis, the most common site being the liver (40%) -- colorectal liver metastases. Liver resection remains the most important modality in the treatment of colorectal liver metastases. But, RBCT remain a concern for patients undergoing hepatectomy.
Alisha A. Jaffer, Sunnybrook Research Institute Toronto, ON, Canada, and colleagues examined the effect of TXA, anti-fibrinolytic, on receipt of RBCT in CRLM metastases.
The researchers included hepatectomies for CRLM over 2009–2014. The primary outcome was 30-day receipt of RBCT. A total of 433 patients were included, of which,146 (34%) received TXA.
Read Also: Tranexamic Acid effective treatment for hemorrhagic stroke if administered early
Key findings of the study include:
- TXA patients were more likely to have inflow occlusion (41.8% vs. 23.1%) and major hepatectomies (56.1% vs. 45.6%).
- TXA was independently associated with lower risk of RBCT (Relative risk (RR) 0.59), but not with 30-day major morbidity (adjusted RR 1.02) and 90-day mortality (univariable RR 0.99).
"Intraoperative TXA was associated with a 41% reduction in risk of 30 -day receipt of RBCT after hepatectomy for CRLM. This finding is important to potentially improve healthcare resource allocation and patient outcomes. Pending further evidence, intraoperative TXA may be an effective method of reducing RBCT in hepatectomy for CRLM," concluded the authors.
Read Also: High BP drugs may reduce risk of colorectal cancer: AHA Journal
The study, "The impact of tranexamic acid on the administration of red blood cell transfusions for resection of colorectal liver metastases," is published in the journal HPB.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpb.2020.06.004
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


