- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Laparoscopic surgery better than open surgery in treating perforated peptic ulcers: study
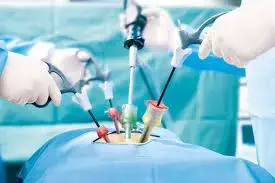
Laparoscopic surgery resulted in results in better functional recovery than open surgery in perforated peptic ulcers according to a recent study published in the BMC Surgery
Perforated peptic ulcer (PPU) is a common emergency condition requiring surgery using laparoscopy or open repair of the perforated site.
The aim of this study was to assess the role of laparoscopic surgery (LS) based on the safety and efficacy for Perforated peptic ulcers.
Medical records of the consecutive patients who underwent laparoscopic surgery or open surgery (OS) for Perforated peptic ulcers at five hospitals between January 2009 and December 2019 were retrospectively reviewed. After propensity score matching, short-term perioperative outcomes were compared between laparoscopic surgery and open surgery in selected patients.
Results:
- Among the 598 patients included in the analysis, open surgery was more frequently performed in patients with worse factors, including older age, a higher American Society of Anesthesiologists score, more alcohol use, longer symptom duration, a higher Boey score, a higher serum C-reactive protein level, a lower serum albumin level, and a larger-diameter perforated site.
- After propensity score matching, 183 patients were included in each group; variables were well-balanced between groups.
- Postoperative complications were not different between groups
- However, postoperative length of hospital stays and postoperative time to liquid intake were shorter in the laparoscopic surgery group.
Thus, laparoscopic surgery resulted in better functional recovery than open surgery and can be safely performed for the treatment of Perforated peptic ulcers. When performed by experienced surgeons, laparoscopic surgery is an alternative option, even for hemodynamically unstable patients.
Reference:
Laparoscopic repair of perforated peptic ulcer: a multicenter, propensity score matching analysis by Chang Woo Kim et al. published in the BMC Surgery
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-022-01681-1
Keywords:
Laparoscopic, repair, perforated, peptic, ulcer, multicenter, propensity, score, matching, analysis, Chang Woo Kim, Jong Wan Kim, Sang Nam Yoon, Bo Young Oh, Byung Mo Kang, Peptic ulcer, Peptic ulcer perforation, Laparoscopy, Complication, Propensity score, BMC Surgery
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


