- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
One anastomosis gastric bypass effective in children with severe obesity
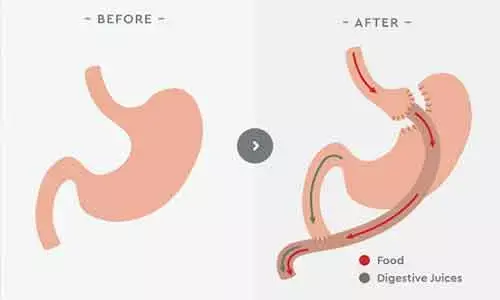
A recent study published in Obesity Surgery found that one anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB) is a safe and effective weight loss procedure for children and adolescents with severe obesity compared to two other weight loss procedures - sleeve gastrectomy (SG) and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) - over a five-year follow-up period.
Childhood obesity remains a pressing global issue with serious medical and social implications. In the quest to combat this problem, medical professionals have been exploring different weight loss procedures. Among them, OAGB has gained approval as an effective and durable method for weight loss and the resolution of obesity-related health problems in adults. However, its suitability and safety for children and adolescents have been a subject of debate.
The study, conducted at an academic hospital, spanned from March 2016 to December 2020 and included 228 patients with severe obesity aged between 9 and 18 years. Among the participants, 107 underwent SG, 37 had RYGB, and 84 received OAGB as primary weight loss interventions.
The findings of the study revealed promising results for OAGB in the pediatric population. Over the 60-month follow-up period, the patients who underwent OAGB experienced a significant decrease in body mass index (BMI) compared to those who received SG and RYGB. The mean ∆BMI values at the 12th, 36th, and 60th months postoperatively were consistently lower in the OAGB group, indicating better weight loss outcomes for this procedure.
The study also emphasized the safety of OAGB in children and adolescents. The procedure was found to be well-tolerated and associated with favorable outcomes during the 24 to 60 months of follow-up.
These findings contribute to the growing body of evidence supporting OAGB as a viable option for combating childhood obesity. As the prevalence of obesity continues to rise among young populations, effective interventions are crucial to addressing the associated health risks and improving the quality of life for affected individuals.
However, it is important to note that any surgical procedure comes with potential risks and should only be considered after careful evaluation and consultation with medical professionals. Additionally, further research and longer-term studies are needed to assess the sustained efficacy and safety of OAGB in pediatric patients.
Reference:
Yarigholi, F., Shahsavan, M., Salman, A., Pazouki, A., Mazaherinezhad, A., & Kermansaravi, M. (2023). Safety and Efficacy of One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass in Children and Adolescents: a 5-Year Cohort Study. In Obesity Surgery. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-023-06749-2
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


