- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Prolonged exposure to 5- ARIs does not impair detection of prostate cancer on MRI: Study
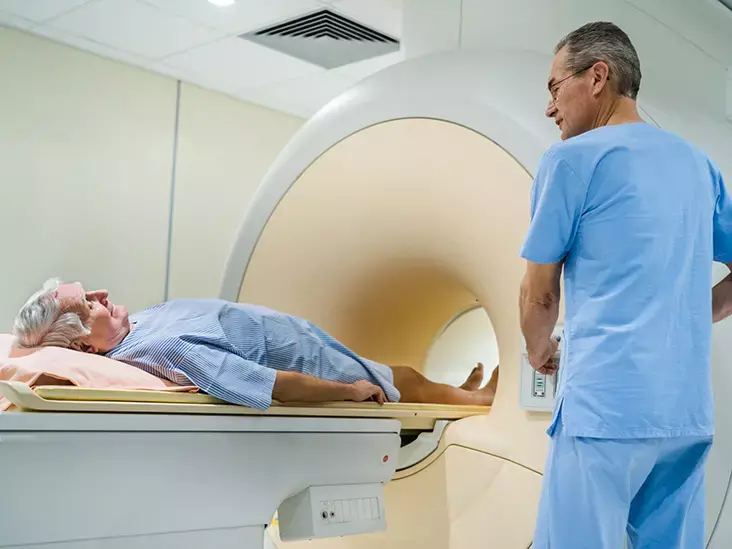
Prolonged exposure to 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors (5- ARIs) does not seem to weaken the detection of significant prostate cancer on MRI, suggests a study published in The Journal of Urology.
A group of researchers from Cleveland, Ohio, U.S.A. conducted a study to evaluate the influence of 5-ARIs on the performance of MRI for detection of Gleason grade group (GG) ≥2 prostate cancer, and on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps.
The researchers conducted this single-center, retrospective study wherein they included men who had MRI for initial detection or active surveillance of prostate cancer. The study group included a total of 59 men who used for 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors (5-ARIs) for ≥12 months, and the control group included a total of 59 men who were matched for both MRI indication and biopsy results. DeLong's test was used to compare the area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) for the detection of GG ≥2 cancer between the groups. Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used for comparison of lesions ADC metrics between the groups.
The results of the study are as follows:
- MRI accuracy in the study group (AUC=0.778) was not significantly different compared to the control group (AUC=0.821).
- In the control group, all ADC metrics were lower in lesions with GG ≥2 cancer on biopsy than in those with GG 1 cancer or negative results.
- In the study group, this difference was significant only when the mean ADC of the lesions was normalized by the ADC of urine.
The authors concluded that long-term exposure to 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors (5-ARIs) does not seem to impair the detection of significant cancer on MRI but may affect the ability of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) metrics to discriminate between lesions that harbor significant cancer and those that harbor insignificant cancer or benign tissue.
Reference:
A study titled. "Influence of 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors on Prostate Cancer Detection With MRI: A Matched Cohort Study" by Purysko A et. al published in The Journal of Urology.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


