- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Prostatic Artery Embolization beneficial for treating LUTS in localized prostate cancer: Study
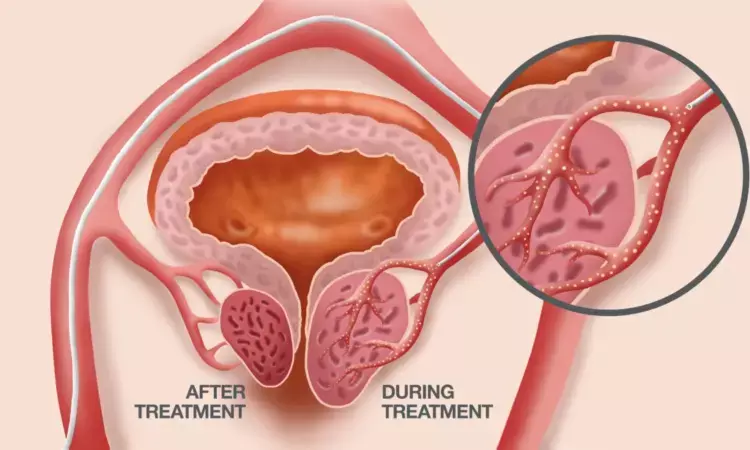
Prostatic Artery Embolization is an effective option for treating lower urinary tract symptoms from Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in men with localized prostate cancer, suggests a study published in the Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology (JVIR).
A study was conducted by a group of researchers from Tampa, Florida, U.S.A, to evaluate the efficacy and safety of prostatic artery embolization (PAE) on lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in the setting of localized prostate cancer.
The researchers conducted a retrospective, single-center, institutional review board-approved study from December 2016 to June 2020.
They selected a total of 21 patients (median age, 72; range, 63–83 years) with moderate LUTS and localized prostate cancer.
Clinical effectiveness was evaluated at 6 and 12 weeks using International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and quality of life (QoL) improvement.
Out of the total 21, Seventeen patients were scheduled to receive definitive radiotherapy (RT) after Prostatic Artery Embolization and 13 patients completed radiotherapy.
Short-term imaging signs of oncologic progression was evaluated at 6 and 12 weeks defined by at least one of the following on magnetic resonance imaging:
Ø Increased Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System score of index lesion(s) to at least 4
Ø New extracapsular extension
Ø Seminal vesicle involvement
Ø Pelvic lymphadenopathy
Nonparametric Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for analysis.
The results of the study are as follows:
Ø International prostate symptom score (IPSS) improved by a median of 12 and 14 at 6 and 12 weeks, respectively.
Ø Quality of life improved by a median of 2 and 3 at 6 and 12 weeks. Prostate volume decreased by a median of 24% and 36% at 6 and 12 weeks.
Ø No patients demonstrated disease progression at 6 or 12 weeks by imaging.
Ø No patients experienced increased prostate-specific antigen after radiotherapy, grade ≥3 adverse events, or greater genitourinary toxicity.
The researchers concluded that Prostatic Artery Embolization is an efficient and safe treatment modality in men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms developed due to benign prostatic hyperplasia in the setting of associated, localized, and non-obstructive Prostate cancer.
Reference:
A study titled, "Effectiveness and Safety of Prostatic Artery Embolization for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms from Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Men with Concurrent Localized Prostate Cancer" by Parikh N et. al published in Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology (JVIR)
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2021.03.534
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


