- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Complicated crown root fracture managed by reattaching the disjointed crown fragment- Case report
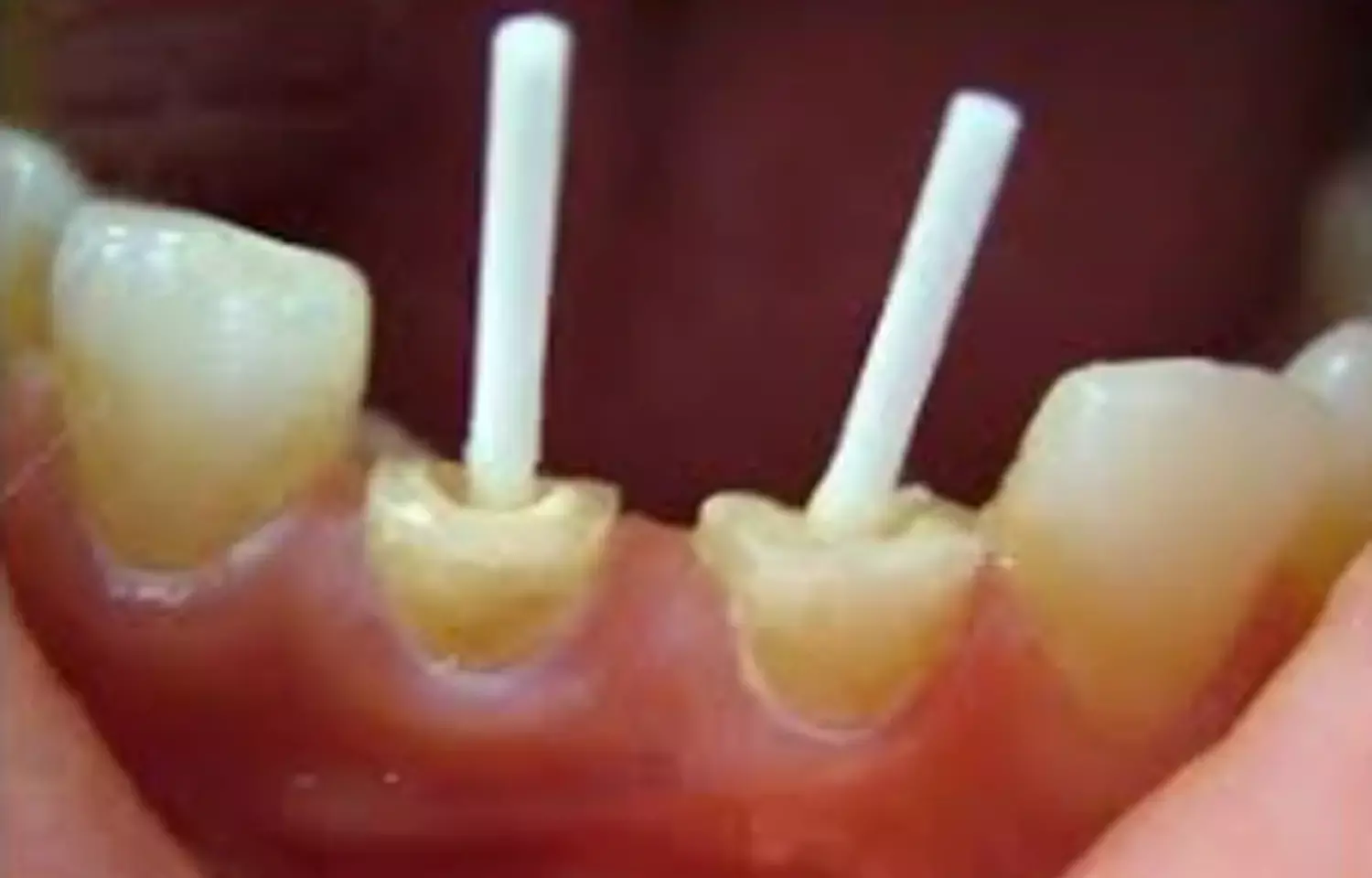
C Saha and associates from the Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Dr. ZA Dental College, AMU, Aligarh, Uttar Pradesh, India have recently observed a series of two case reports where they observed that cases of complicated crown root fracture when managed by utilizing fiber post to reattach the disjointed crown fragment showed reliable retentivity and periodontal health at 1-year follow-up.
The study is published in the Journal of Dental Research and Review.
Advancement in the adhesive system has made fragment reattachment a viable treatment option for treating tooth fractures. It offers a simple and conservative technique to restore esthetics and function. Reattachment of a completely disjointed crown may need additional fiber post retention due to the greater functional load borne by the fragment.
Hence, the authors studied two cases, one of a 20-year-old female patient and the other of a 25-year-old male. In the first case, the patient presented with traumatic dental injury on her upper front teeth. Intraoral examination revealed a horizontal fracture running through the cervical third of the buccal surface of tooth 22. The crown was freely movable and could be completely split along the fracture line. The fracture line ran circumferentially along the cervical third of crown in the buccal surface and extended subgingival along the palatal surface. The natural tooth was retained by re-adhering the tooth fragment with the aid of fiber post retention.
In the second case study, the patient reported with fractured upper front teeth after a road traffic accident. Intraoral examination revealed that both maxillary central incisors (11 and 21) had a fracture line running through the cervical third of the crown. The fracture line of teeth 11 and 21 were supra-gingival on the labial aspect and below the gingival margin on the palatal aspect. Both the crowns were completely mobile and disengaged and were kept in place intraorally by subgingival adherence of the fractured fragment to the periodontal ligament. The same line of treatment plan yielded better results.
Hence, the authors concluded that "Reattachment of disjointed crown fragment utilizing fiber-reinforced post in a crown root fracture may offer the simplicity of clinical technique and chairside time while achieving pleasing esthetics and functional results. Treatment assessment in reattaching disjointed crown with the cemental extension should involve restorative and periodontal considerations to achieve clinical longevity."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


