- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Adapting Occlusal design and adjustment may improve properties of zirconia and resin composite crowns
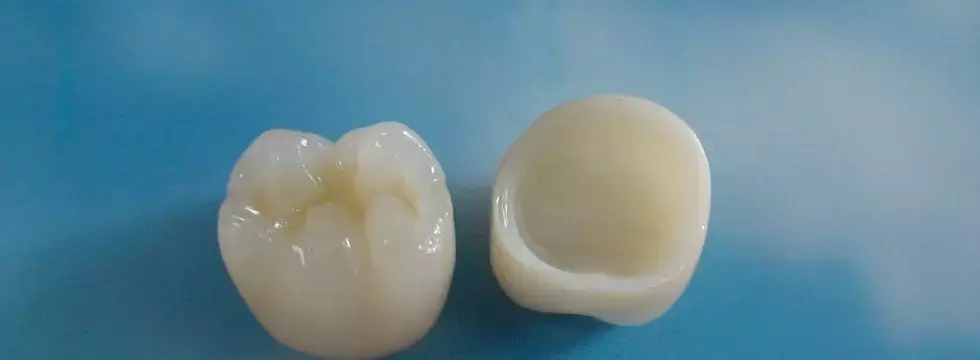
It is necessary to adapt occlusal design and adjustment in order to improve roughness, wear, and stability of zirconia and resin composite crowns according to a recent study published in the Journal Of Dentistry.
Researchers have conducted the study to investigate the impact of the occlusal contact situation and occlusal adjustment on wear, roughness, and fracture force of molar crowns.
CAD/CAM crowns (lower right first molar, n=64; 4 groups à 8, 3Y-TZP zirconia and resin composite) and corresponding antagonists (upper right first molar; 3Y-TZP zirconia) were manufactured. Crowns were constructed according to two principles of occlusion (group "T": Peter K. Thomas' "point-centric" cusp-to-fossa tripodization concept, with 15 contact points; group "RA" Sigurd P. Ramfjord and Major M. Ash, "freedom in centric" concept with four contacts). On one half of the crowns, occlusal adjustment was performed (groups "T adjusted" and "RA adjusted"). All crowns underwent combined thermal cycling (TC) and mechanical loading (ML) (ML: 1.2 × 106 cycles, 50 N, 2 Hz, mouth opening 1 mm; TC: 2 × 3000 cycles, 5/55°C). Wear area and depth of each contact point on the occlusal surfaces of crowns and antagonists were determined using a digital microscope. Surface roughness (Ra, Rz) was measured in and besides (reference) the worn area (3D laser-scanning microscope). Fracture force of the crowns was determined (statistics: Levene-test, one-way-ANOVA; Bonferroni-post-hoc-test; between-subjects effects, Pearson correlation, α=0.05).
The resin composite crowns yielded significantly higher mean values for wear area and depth and lower fracture forces
Resin composite surfaces showed increased roughness after TCML while zirconia exhibited smoothened surfaces.
The occlusal design significantly impacted wear depth and fracture force
Resin composite crowns with fewer contact points (group RA) showed more wear and lower fracture force.
Adjusted resin composite crowns showed increased wear areas and depths
For zirconia crowns, the adjustment impacted wear area, wear depth, and fracture force (p=0.006), with adjusted zirconia crowns exhibiting more wear and lower maximum forces until fracture.
Zirconia wear depth was also impacted by the occlusal design Antagonistic wear was influenced by the restorative material, the occlusal contact pattern, and the adjustment.
The investigated materials show strongly varying performances with zirconia being significantly influenced by the adjustment, while for resin composites, contact design and adjustment had a major impact. The results show the necessity of adapting occlusal design and adjustment in order to improve roughness, wear, and stability of zirconia and resin composite crowns.
Reference:
Karin Schnitzhofer, Angelika Rauch, Micheal Schmidt, Martin Rosentritt,
Impact of the occlusal contact pattern and occlusal adjustment on the wear and stability of crowns, Journal of Dentistry, 2022, 104364, ISSN 0300-5712,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2022.104364
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


