- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Biphasic calcium phosphate tied to higher graft volume stability in lateral window sinus floor elevation
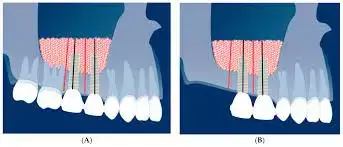
Biphasic calcium phosphate tied to higher graft volume stability in lateral window sinus floor elevation suggests a new study published in the Clinical Oral Implants Research.
A study was done to assess in a prospective randomised trial two psychogenic bone substitutes—biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) versus almost pure hydroxyapatite (HA)—for their volume stability and clinical implications after sinus floor elevation (SFE). Twenty patients requiring lateral-window sinus floor elevation 6 months before implant surgery were randomized to a biphasic calcium phosphate or hydroxyapatite group. As the primary outcome, the grafts were analyzed for volume stability, using four cone-beam computed tomography scans obtained immediately/6/12/24 months after sinus floor elevation. Secondary outcomes were implant survival, success, periotest values, oral-health-related quality of life (OHIP-G14), and pain (VAS).Results: Kolmogorov–Smirnov goodness-of-fit test revealed normal distribution of samples (p = .200). At 6/12/24 months, the augmented volumes decreased to 96/92/90% (HA) or 99/96/96% (biphasic calcium phosphate). Volume changes were significantly a factor of time and reached significantly lower values in the hydroxyapatite group. The significant intergroup difference in volume losses was notable at 24 months (p = .021; t-test for independent samples). Periotest values decreased from −3/−4.1 (HA/BCP) after implant placement to −6.3/−4.5 (HA/BCP) after 6 months. OHIP scores diverged at 2 months and largely resolved by 24 months. VAS scores were comparable, 2.2 at 1 week after sinus floor elevation being their highest mean level. After 2 years, both groups experienced no biological or technical complications, demonstrating a consistent healing trajectory without notable symptoms. Although no significant differences were observed in implant stability and survival, biphasic calcium phosphate demonstrated higher volume stability than hydroxyapatite.
Reference: Sokolowski, A., Theisen, K., Arefnia, B., Payer, M., Lorenzoni, M., & Sokolowski, A. (2023). A randomized clinical trial of phycogenic materials for sinus grafting with hydroxyapatite versus biphasic calcium phosphate: 2 years clinical outcomes. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 00, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.14209
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


