- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Erbium laser ineffective for removing smear layers from mesial roots of mandibular first molars
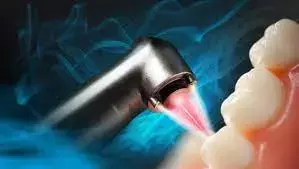
Erbium laser is a cornerstone in oral surgery and implantology in dentistry. It emits at 2940 nm and is characterized by an active medium consisting of a Yttrium–Aluminium–Garnet (YAG) crystal doped with erbium ions.
Erbium laser is ineffective to remove smear layers from the mesial roots of mandibular first molars according to a recent study published in the Journal of Conservative Dentistry.
The aim of the study is to evaluate erbium laser efficiency in removing the smear layer from mesial roots of mandibular first molars at different laser settings.
One hundred (100) mandibular first molars were selected. Ninety-six (96) mesial roots were assigned to two experimental groups according to the laser wavelength applied: I. Er, Cr: YSGG and II. erbium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet laser system. Four samples were used as the control group. Samples of each group were distributed into two subgroups (A and B), following specific irrigation protocol. Each subgroup was divided into four subcategories according to the applied power laser. Each subcategory consisted of six samples. Teeth were observed under scanning electron microscope. The results were statistically analyzed with Kruskal–Wallis and Mann–Whitney test (SPSS statistics software).
The Results of the study are:
No statistically significant difference was observed between experimental groups I and II. However, a statistically significant difference was found among subgroups IA and IB and IIA and IIB. In every root third, groups IIA and IIB had better outcomes but it was not statistically significant. There was no statistically significant difference between the subcategories of Group I (IA1-4 and IB1-4) and Group II (IIA1-4 and IIB1-4).
Thus, the researchers concluded that the erbium laser with tested parameters did not completely remove the smear layer from the root canals. Chelating factors can contribute to the laser mechanism of smear layer removal from the apical part of narrow and curved root canals.
Reference:
Evrykleia Kourti, Ourania, Papadopoulou-Pantelidou, Kosmas Tolidis, Christos Angelopoulos, Dimitris Strakas. Laser applications in smear layer removal from posterior root canals: A comparative study. 2022.Volume25.Issue3. https://www.jcd.org.in/article.asp?issn=0972-0707;year=2022;volume=25;issue=3;spage=283;epage=287;aulast=Kourti;type=0
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


