- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Glass hybrid restorative system may not protect against advanced abrasive wear on long term basis
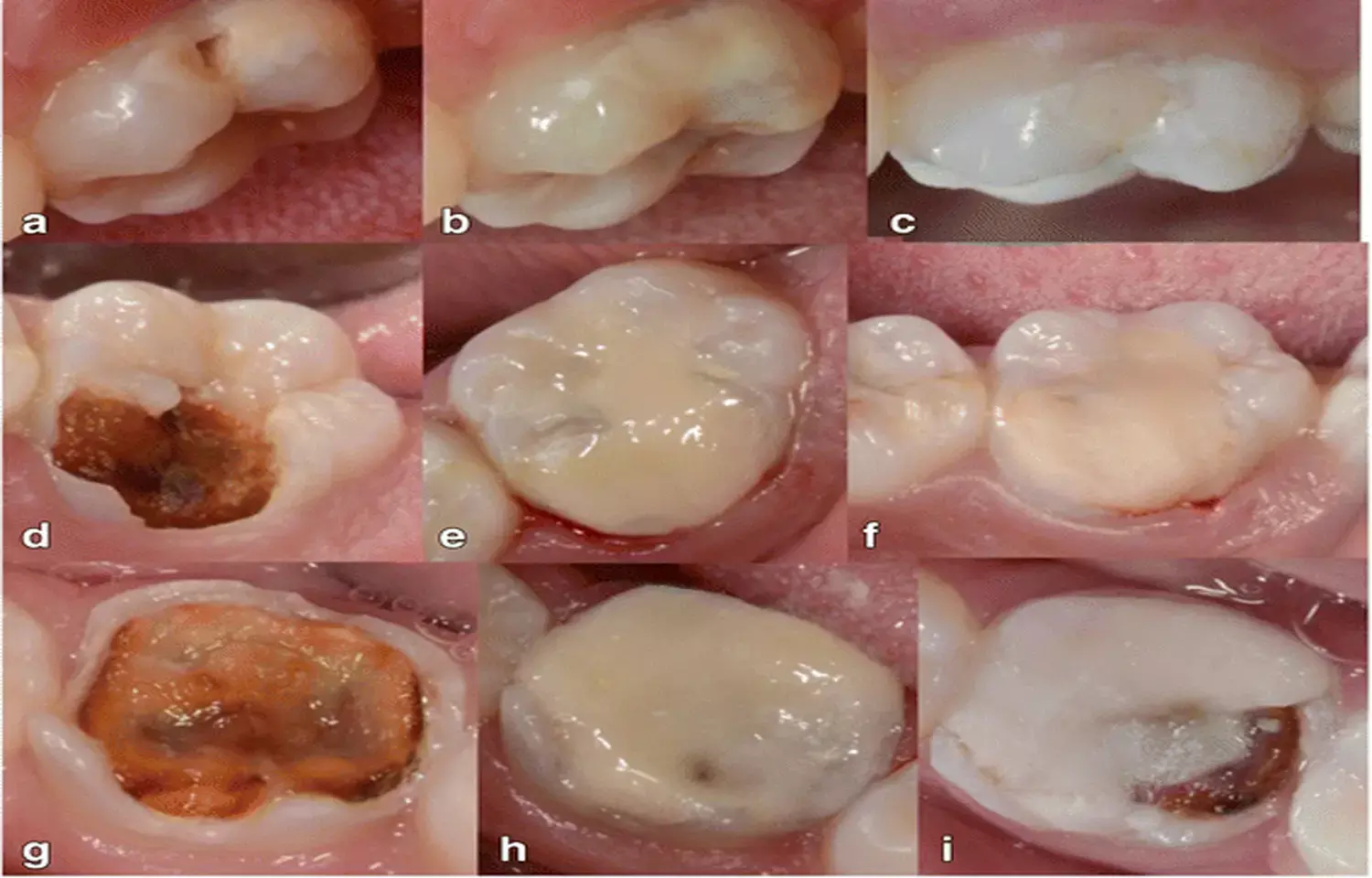
Researchers from the Department of Operative Dentistry, Periodontology, and Endodontology, University School of Dental Medicine and Oral Health, Danube Private University (DPU), Austria have found out in a new study that Resinous coating of high-viscosity glass ionomer cement (hvGIC) or a glass hybrid restorative system (ghRS) does not appear to exert an effective long-term protection against advanced abrasive wear, as published in the Journal of Dentistry.
Andrej M.Kielbassa and colleagues carried out the present study with the sole aim to investigate the volumetric abrasive wear of a high-viscosity glass ionomer cement (hvGIC; Equia Fil) and a glass hybrid restorative system (ghRS; Equia Forte), each being recommended as amalgam alternatives. Both materials were applied with or without their respective resinous coating, and were compared with a conventional GIC (Ketac Fil) and a hybrid composite resin (CR; G-ænial Posterior).
The authors included a total of 78 standardized occlusal Class I cavities which were restored with the various materials (n = 13 per group). Before and after chewing simulation (30,000 cycles at 40 N), each sample underwent optical scanning procedures (Omnicam).
A comparison of the total wear using a fluorescence-aided identification technique (OraCheck) followed, and differences (α = 5%) between groups were compared by means of MANOVA.
The key findings that were highlighted included -
a. Regarding the wear rates of hvGIC and ghRS, no differences could be observed (p > .050), and this was not affected by the resinous coating.
b. All hvGIC and ghRS restorations showed significantly higher abrasive wear than CR (p < .001), while the conventional GIC displayed a significant underperformance compared with any other material (p < .001).
Therefore, it was concluded that "resinous coating of hvGIC or ghRS does not appear to exert an effective long-term protection against advanced abrasive wear. Compared to the conventional GIC showing a considerable substance loss, both hvGIC and ghRS materials revealed an improved abrasion resistance, but clearly failed to meet the excellent values of the CR."
The authors further inferred that occlusal loading should be carefully considered when using hvGIC or ghRS as amalgam (or composite resin) alternatives for the restoration of posterior teeth.
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


