- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Sanitisation of toothbrushes with novel mouthwash reduces number of live microorganisms
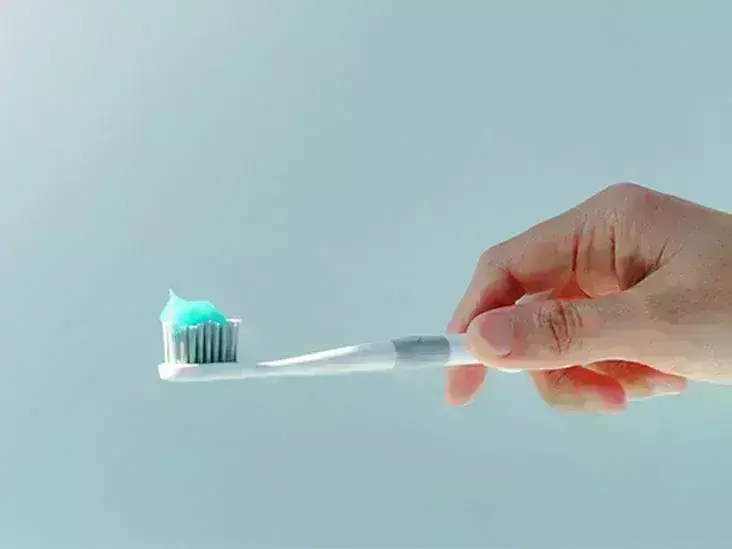
Sanitisation of toothbrushes with this mouthwash reduces the number of live microorganisms adhered to the filament suggests a recent study published in the International Journal of Dental Hygiene
Toothbrushes are colonised by microorganisms, implying a risk of infection. That risk can be reduced by decreasing the microbial contamination of the filaments. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the antiseptic efficacy of a 0.05% chlorhexidine + 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride mouthwash on toothbrushes.
Twelve toothbrushes used 3 times/day for 14 days by orally and systemically healthy people were randomly split into two groups, and their heads were immersed for 2h in PBS (control) or Perio·Aid Active Control (treatment). The microorganisms were recovered, and their number was calculated by culture, quantitative PCR and viability PCR. Statistical differences were first assessed with a Two-Way Mixed ANOVA, and subsequently with the Student's t test.
Results
The results showed no statistical differences in the total number of cells for the treatment and the control groups, but a significantly lower number of live cells in the treatment group than in the control group.
Based on study findings, sanitisation of toothbrushes with this mouthwash reduces the number of live microorganisms adhered to the filaments. Such decrease of the bacterial load could include bacteria from the oral cavity, from the environment and from nearby toothbrushes since the quantification was not limited to any bacterial taxon.
Reference:
Àlvarez, G., Soler-Ollé, A., Isabal, S., León, R. and Blanc, V. (2022), Bacterial decontamination of toothbrushes by immersion in a mouthwash containing 0.05% chlorhexidine and 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride: A randomised controlled trial. Int J Dent Hygiene. Accepted Author Manuscript. https://doi.org/10.1111/idh.12652
Keywords:
Àlvarez, G., Soler-Ollé, A., Isabal, S., León, R. and Blanc, V, Bacterial, decontamination, toothbrushes, immersion, mouthwash, containing, 0.05% chlorhexidine, 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride, randomised, controlled trial, Int J Dent Hygiene
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


