- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Unilateral Palatally displaced canines may not delay tooth formation: Study
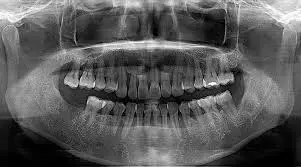
Unilateral Palatally displaced canines (PDC) do not delay delay tooth formation and affect dental developmental age, according to a new study.
The study has been published in the American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.
Palatally displaced canines (PDC) can be associated with significant resorption of adjacent teeth. Furthermore, the treatment of canines, when they become impacted often involves surgical exposure of the tooth and the need for subsequent forced orthodontic eruption Delayed tooth eruption is often seen in patients with palatally displaced canines (PDC), but there is controversy over whether tooth formation is also delayed. This study attempts to elucidate the answer by addressing methodological shortcomings in previous studies.
Dental age estimation (DAE) is the most accurate method of estimating age where a formal birth record is absent. Accurate DAE relies on a reference data set comprising dental panoramic tomographs (DPT) that provide images of all the tooth morphology types. For each tooth development stage (TDS) summary data are the count (n-tds), the mean (-tds), and standard deviation (sd-tds). These data enable Normal distribution and Percentile summary data for each TDS. The DA for a single individual is calculated by taking the average of the TDS on the subject's DPT. This is the surrogate for chronological age.
Archived records were searched, and 100 patients (aged 8-16 years) with unilateral PDC were identified. Records of 50 women and 50 men were matched for age and sex with unaffected controls. The exclusion criteria included hypodontia. Dental age (DA) was calculated using the population-specific Maltese database and subtracted from the chronological age (CA). Nonparametric tests were used to compare CA−DA in patients with PDC and controls to determine the DA of end-of-series teeth.
The Results of the study are:
No statistically significant difference with CA−DA between patients with PDC and controls was found. In addition, there were no particular teeth significantly delayed in development.
Thus, the researchers concluded that unilateral PDC does not affect dental developmental age, and the end-of-series teeth investigated show no delay in development.
Reference:
Dental age estimation of young subjects with unilateral palatally displaced canine teeth by Faisal Hashim et al. published in the American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0889540621004054
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


