- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ligelizumab and omalizumab effective for treating chronic spontaneous urticaria: JAMA
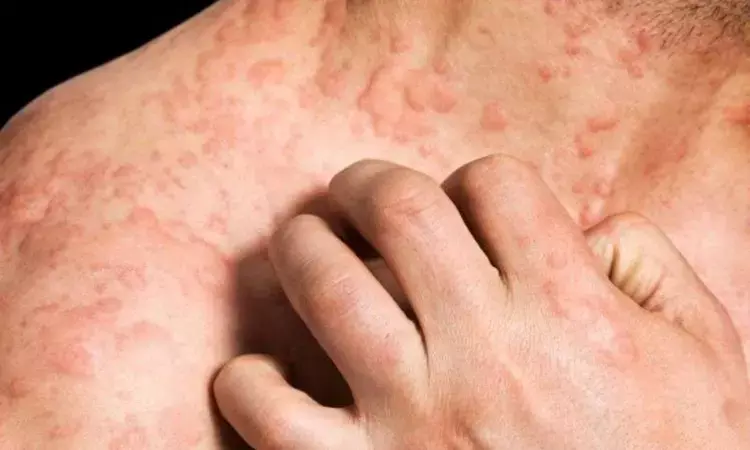
Thailand: Biologic agents ligelizumab, 72 or 240 mg, and omalizumab, 300 or 600 mg can be recommended as effective treatments for chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) that is inadequately controlled with H1 antihistamines. The study is published in JAMA Dermatology.
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is an autoimmune disorder. Therapy is often difficult however the initial approach requires high-dose non-sedating antihistamines. No study has been able to establish a definitive comparison of the benefits and harms of all available treatments for H1 antihistamine–refractory chronic spontaneous urticaria. Surapon Nochaiwong, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand, and colleagues, therefore, aimed to evaluate different treatment effects of pharmacologic treatments among patients with H1 antihistamine–refractory CSU.
For this purpose, the researchers searched the online databases for inception to April 19, 2021. It included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that investigated the benefits and harms of pharmacologic treatments among adolescent or adult patients with CSU who had an inadequate response to H1 antihistamines were screened for inclusion independently by 2 investigators.
A total of 23 randomized clinical trials with 2480 participants that compared 18 different interventions or dosages and placebo were included.
The results of the study were:
• The standardized mean differences for change in urticaria symptoms were −1.05 for ligelizumab, 72 mg; −1.07 for ligelizumab, 240 mg; −0.77 for omalizumab, 300 mg; and −0.59 for omalizumab, 600 mg.
• No significant differences in treatment unacceptability were observed. With respect to benefits and harms, the network estimates illustrated that the most efficacious treatments were achieved with ligelizumab, 72 or 240 mg (large beneficial effect), and omalizumab, 300 or 600 mg (moderate beneficial effect).
Nochaiwong and the team concluded that "The findings in this meta-analysis suggest that the biologic agents ligelizumab, 72 or 240 mg, and omalizumab, 300 or 600 mg, can be recommended as effective treatments for patients with CSU who have had an inadequate response to H1 antihistamines. Head-to-head trials with high methodologic quality and harmonized design and outcome definitions are needed to help inform subsequent international guidelines for the management of CSU."
Reference:
Nochaiwong S, Chuamanochan M, Ruengorn C, Awiphan R, Tovanabutra N, Chiewchanvit S. Evaluation of Pharmacologic Treatments for H1 Antihistamine–Refractory Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. Published online August 25, 2021. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3237
Medical Dialogues consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


