- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Milk, high fat and sugary diet may cause adult acne: JAMA Dermatology
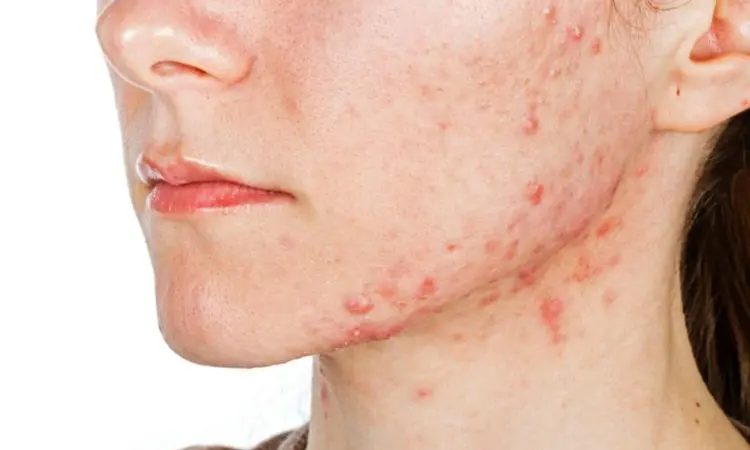
France: If you have acne you should watch out for your diet, a recent study in the journal JAMA Dermatology has suggested. According to the study, consumption of milk, sugary beverages, and fatty and sugary products is associated with current acne in adults.
Acne is a chronic, multifactorial inflammatory disease that occurs due to the plugging of hair follicles with oil and dead skin cells. Though eating of certain foods is known to exacerbate acne, there a lack of clarity on the association between consumption of dairy products and fatty and sugary foods, and the occurrence and progression of acne.
Laetitia Penso, University of Paris, France, and colleagues assessed the association between dietary behavior and current acne in adults.
For the purpose, the researchers performed a cross-sectional study as part of the NutriNet-Santé study -- an ongoing observational, web-based cohort study that was launched in France in May 2009. A total of 24 452 participants completed an online self-questionnaire to categorize their acne status: never acne, past acne, or current acne, from November 14, 2018, to July 8, 2019. The researchers studied associations between dietary behavior (food intake, nutrient intake, and the dietary pattern derived from a principal component analysis) and current or past acne.
Key findings of the study include:
- 11 324 individuals (46%) reported past or current acne.
- After adjustment, there was a significant association between current acne and the consumption of fatty and sugary products (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.54), sugary beverages (aOR, 1.18), and milk (aOR, 1.12).
- An energy-dense dietary pattern (high consumption of fatty and sugary products) was associated with current acne (aOR, 1.13).
"The findings demonstrate that the consumption of milk, sugary beverages, and fatty and sugary products appeared to be associated with current acne in adults. Further large-scale studies are warranted to investigate more closely the associations between diet and adult acne," concluded the authors.
The study, "Association Between Adult Acne and Dietary Behaviors: Findings From the NutriNet-Santé Prospective Cohort Study," is published in the journal JAMA Dermatology.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


