- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Monitoring of immune and inflammatory indicators crucial for alopecia areata diagnosis: Study
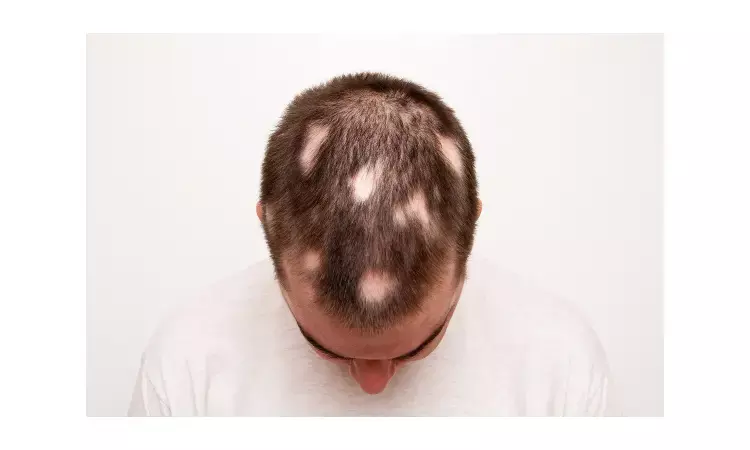
China: A recent study in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology has stated that although the etiopathogenesis of alopecia areata (AA) is not clear but monitoring the levels of T3, T4, thyroid antibodies (TPOAbs), antinuclear antibodies (ANA), and 25 (OH)D is crucial in alopecia areata cases.
Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disorder that often results in unpredictable hair loss. It affects roughly 6.8 million people in the United States. Yamei Gao, Department of Dermatology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China, and colleagues aimed to evaluate several parameters related to autoimmunity and inflammation in AA patients and to evaluate their association with this disease.
The study included a total of 672 eligible AA patients and 580 age- and sex-matched healthy individuals who were treated at a third-class hospital in Hefei from January 2016 to May 2020. Data for serum C-reactive protein (CRP), 25-hydroxy vitamin D (25(OH)D), T3, T4, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroid antibodies (TPOAbs and TGAbs), antinuclear antibodies (ANA), complements (C3, C4), and several immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM, and IgG) were collected for this study.
The results of the study were found to be
• Regarding autoimmune-related functional indicators, there were no statistically significant differences found between TSH, TGAbs, C3, C4, IgA, IgM, and IgG levels between AA patients and healthy controls.
• Only T3, T4, TPOAbs, and ANA values were significantly abnormal in the AA group compared with the healthy individuals.
• In addition, the mean serum 25(OH)D concentration was significantly lower in the patient group than that in the control group, and serum CRP was significantly increased.
Gao and the team concluded that "Although the etiopathogenesis of AA is not clear, the importance of monitoring the levels of T3, T4, TPOAbs, ANA, and 25 (OH)D in AA cases is indispensable."
Reference:
The study titled, "Evaluation of several immune and inflammatory indicators and their association with alopecia areata," is published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
DOI: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jocd.14504
Medical Dialogues consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751